Introduction
Myocardial infarction is an ischaemic cardiovascular disorder in which the blood supply to the cardiac muscle is reduced [1]. It is one of the leading causes of mortality throughout the world. Mortality and disability can be reduced by treatment with reperfusion therapies such as coronary artery bypass grafting, thrombolysis, and percutaneous coronary intervention [2]. However, reperfusion of tissues or blood flow restoration causes the destruction of tissues known as myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI), which decreases the effect of reperfusion therapy in MI [3]. Several pathogeneses are involved in the development of MI, including oxidative stress, platelet activation, autophagy, apoptosis, and inflammation [4]. I/R is reported to induce inflammatory reactions, which lead to myocardial injury [5]. Several inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), are enhanced in inflammatory reactions, which further enhances the infiltration of neutrophils at the site of injury [6]. The NF-κB/TLR4 pathway is involved in MI, causing the activation of endogenous molecules, leading to myocardial tissue damage [7]. Several conventional therapies are available, but no therapy effectively manages the problem. Thus, there is a need for the development of effective therapies for the treatment of MI.
Several miRNAs have been reported to regulate cellular functions such as cell growth and metabolism, and are also involved in cardiovascular disorders [8]. Moreover, miRNAs have roles in the regulation of myocardial fibrosis and hypertrophy and also regulate the cellular metabolic pathway [9]. miR-103 inhibition improves adipose tissue and hepatic metabolism, as well as insulin sensitivity [10–12]. Moreover, miR-103 inhibitor is under clinical trials for the treatment of liver disorders and type 2 diabetes [13, 14]. miR-103 inhibition also has a role in the regulation of cortical function [15]. Thus, the present investigation evaluated the effect of miR-103 inhibition on MI.
Material and methods
Animals
Healthy 7- to 8-week-old male Sprague Dawley rats were cared for as per Care and Use of Laboratory Animals instructions. All animals were given free access to water and food under the standard 12-h light and dark cycle conditions. All experimental protocols were approved by the institutional animal ethical committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Northwest University/Xi’an No. 3 Hospital, China (IAEC/AH-NU-XH/2017/09).
Chemicals
mRNA-103 inhibitor was procured from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). ELISA kits for the estimation of mediators of inflammation were purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA). The RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis kit was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA). The primers used for the qRT-PCR assay were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA).
Experimental
Animals were anesthetized by injecting 40 mg/kg of pentobarbital i.p., and an incision was made to the left thoracic wall, exteriorizing the heart. Ischaemia was produced by keeping a knot around the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD) with 5-0 silk suture. Cardiac tissues were reperfused for 2 h by releasing the knot after 30 min of ischaemia. The animals were separated into three groups: the sham group, the MI group, and the mRNA-103 inhibitor group, which received mRNA-103 inhibitor 10 min before reperfusion.
mRNA-103 administration
mRNA-103 was administered 20 min after the induction of ischaemia. LV mRNA-103 (1 × 107 TU) was injected around the infarcted area into the myocardium.
Assessment of myocardial enzyme levels
Blood was collected from the inferior vena cava, and serum was separated out by centrifuging the blood at 4°C for 10 min at 2,500 RPM. The levels of myocardial enzymes, such as lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and creatine kinase-muscle/brain (CK-MB), were estimated in the serum of MI rats using an automatic biochemical analyser.
Assessment of myocardial infarcted area
A double-staining technique was used for the assessment of size of the infarcted area in the myocardial tissues. Evans Blue dye was injected after blocking the coronary blood flow so that it was rapidly distributed in the body by the right ventricle. The heart was isolated immediately and sliced into 1-mm sized specimens. Later, tissue sections were incubated for 15 min with 1% 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC). A computerized digital imaging system was used to estimate the myocardial infarcted area.
Assessment of cytokine levels
The levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the cerebral tissues were determined using ELISA. Supernatant solution was separated from tissue homogenates, and ELISA kits were used to determine the level of cytokines in the tissue homogenate per the manufacturers’ instructions.
Assessment of MPO level
The level of MPO in the tissue homogenate of myocardial tissue was determined using an MPO kit per the manufacturer’s instructions.
Immunochemical analysis
The expression of TLR4 in myocardial tissues was examined by immunohistochemistry. Tissues were cut into 3-µm sections. After washing for 30 min with 60% methanol in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and 3% H2O2, the tissue sections were treated with 0.01 mol/l sodium citrate buffer in a microwave oven at 95°C for 13 min. The sections were then treated with BSA (5%) and normal goat serum (5%). Next, the sections were incubated for 12 h with TLR4 antibody at 4°C, followed by incubation with secondary biotinylated goat anti-rabbit EnVision antibody at room temperature for 60 min. 3,3-diaminobenzidine tetra-hydrochloride was used to stain the sections, and images were analysed with Image Pro Plus software.
qRT-PCR
TRIzol reagent was used to isolate total RNA from myocardial tissues per the manufacturer’s instructions. A reverse transcription kit was used to create cDNA by reverse transcription from the RNA per the manufacturer’s instructions. The ABI Prism 7500 system and the SYBR green/fluorescein qPCR Master Mix kit were used to perform qRT-PCR. The qRT-PCR conditions were as follows: 50°C for 2 min; 95°C for 10 min; and 40 cycles of 95°C for 30 s and 60°C for 30 s. The resulting data were analysed using the comparative Ct method (2–ΔΔCt) (Table I).
TUNEL assay
The terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labelling assay (TUNEL) was used to evaluate the apoptosis of myocardial cells as per the previously reported method. The apoptosis index was calculated as the number of stained myocytes divided by the total number of myocytes × 100%.
Statistical analysis
All data are expressed as means ± standard error of the mean (SEM; n = 10), and the statistical analysis consisted of a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Post-hoc comparisons of means were carried out with Dunnett’s post-hoc test using GraphPad Prism software (ver. 6.1; San Diego, CA, USA). P-values < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
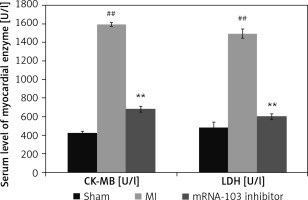
mRNA-103 inhibitor attenuates myocardial enzymes
The levels of the myocardial enzymes CK-MB and LDH were determined in the serum of mRNA-103 inhibitor-treated MI rats, as shown in Figure 1. The activities of CK-MB and LDH were enhanced in the serum of the MI group compared to the sham-operated group. There were significantly lower CK-MB and LDH activities in the serum of the mRNA-103 inhibitor-treated group compared to the MI group.
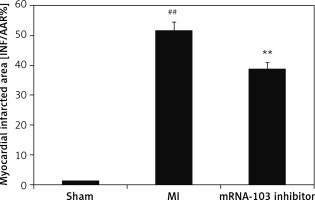
mRNA-103 inhibitor attenuates the myocardial infarcted area
The percentage of the myocardial infarcted area was assessed in the myocardial tissues of mRNA-103 inhibitor-treated MI rats, as shown in Figure 2. The percentage of infarcted area was up to 52% higher in the MI group than the sham-operated group (1%). However, the percentage of infarcted area was up to 39% lower in the myocardial tissues of the mRNA-103 inhibitor treated group than the MI group.
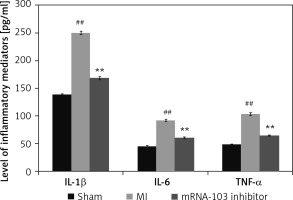
mRNA-103 inhibitor attenuates cytokine levels
Figure 3 shows the inflammatory cytokine levels in mRNA-103 inhibitor-treated MI rats. The cytokine levels were higher in the MI group than in the sham-operated group. However, there were lower levels of inflammatory cytokines in the serum of the mRNA-103 inhibitor-treated group than in the MI group.
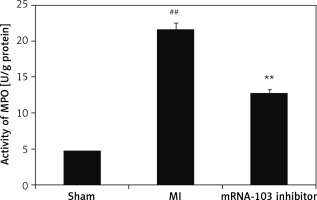
mRNA-103 inhibitor attenuates MPO activity
The MPO activity was determined in the myocardial tissues of the three groups, as shown in Figure 4. There was greater MPO activity, at 22 U/mg protein, in the MI group, compared to the sham-operated group, which showed 4.7 U/mg protein. In the mRNA-103 inhibitor-treated group, the MPO activity was reduced by up to 12.8 U/mg protein compared to the MI group.
mRNA-103 inhibitor attenuates TLR4 expression
The expression of TLR4 in the myocardial tissue sections of MI rats was assessed by immunohistochemical analysis, as shown in Figure 5. TLR4 expression was greater in myocardial tissues of the MI group than in the sham-operated group. However, TLR4 expression was significantly lower in myocardial tissues of the mRNA-103 inhibitor-treated group compared to the MI group.
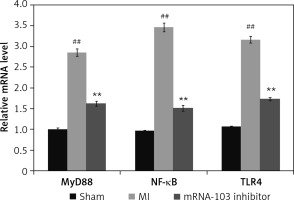
mRNA-103 inhibitor attenuates mRNA expression of NF-κB, TLR4, and MyD88
The expression levels of TLR4, NF-κB, and MyD88 mRNAs were determined in the myocardial tissue of MI rats by qRT-PCR, as shown in Figure 6. The relative expression of TLR4, NF-κB, and MyD88 mRNAs in myocardial tissue was higher in the MI group than in the sham-operated group. However, treatment with mRNA-103 inhibitor ameliorated the relative expression of TLR4, NF-κB, and MyD88 mRNAs in myocardial tissue.
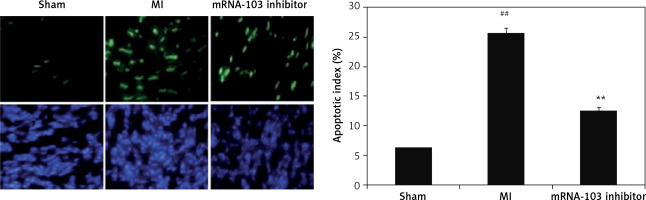
mRNA-103 inhibitor attenuates myocardiocytes apoptosis
The extent of apoptosis of myocardiocytes in myocardial tissues of the three groups was estimated by the TUNEL assay, as shown in Figure 7. There was a significant increase (p < 0.01) in myocardiocyte apoptosis in myocardial tissues of the MI group compared to the sham-operated group. However, the apoptosis index was lower in the mRNA-103 inhibitor-treated group than in the MI group.
Discussion
Myocardial infarction is an ischaemic heart disease that causes injury to myocardial tissues. Its conventional management has several limitations. There is a need for the development of novel therapeutic approaches for its management, and thus the present investigation examined the cardio-protective activity of mRNA-103 inhibitor against MI. The effect of mRNA-103 inhibitor was assessed by determining the levels of myocardial enzymes and cytokines in the serum, MPO activity, and the expression of TLR4, NF-κB, and MyD88 mRNAs in the myocardial tissues of MI rats. Immunocytochemical analysis and a histopathology study were also performed.
Haemodynamic changes and altered levels of myocardial enzymes have been reported to be caused by myocardial infarction [16]. MI damages myocardial tissues, leading to alterations in the activity of LDH and CK-MB enzymes and haemodynamic functions [17]. In the present study, the levels of myocardial enzymes were altered in the MI group, and treatment with mRNA-103 inhibitor reversed the changes in the levels of these enzymes.
It was observed that in MI-induced myocardial injured rats, infiltration of neutrophils occurs, which leads to the development of an inflammatory response and oedema [18, 19]. The levels of TLR-4 and NF-κB proteins have been reported to be increased in injured myocardial tissue [20]. The results of the present investigation also suggest that in MI rats, inflammation occurs due to increases in mediators of inflammation, and treatment with mRNA-103 inhibitor ameliorated the altered level of inflammatory mediators, while also regulating the TLR-4/NF-κB pathway. Inflammatory mediators activate MPO and increase oxidative stress, which leads to the development of injury in different organs, including myocardial tissues. Oxidative stress reduction has been reported to prevent injury of myocardial tissues [21], and the results of our study also show that treatment with mRNA-103 inhibitor reduces the increased level of oxidative stress.
Myocardial infarction occurs due to hypoxia to the myocardial tissues, which activates the apoptosis pathway and increases the apoptosis of myocardiocytes [22–25]. Apoptosis of myocardiocytes contributes to the degeneration of myocardial tissues, which leads to MI. In the present study, there was a decrease in apoptosis in the mRNA-103 inhibitor-treated group compared to the MI group of rats.
In conclusion, this study revealed that inhibition of mRNA-103 protects against myocardial injury in MI rats by regulating the inflammasome pathway. The findings suggest that inhibition of mRNA-103 could be a new therapeutic approach for the management of MI.