Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
CLINICAL RESEARCH
Whole-body water mass and osteoarthritis: a Mendelian randomization study
1
College of Medicine, Hubei Minzu University, Enshi, China
2
Department of Orthopedics, Huanggang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Huanggang, China
3
Second College of Clinical Medicine, Yunnan University of Chinese Medicine, Kunming, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-03-05
Final revision date: 2024-04-15
Acceptance date: 2024-04-28
Online publication date: 2024-05-01
Corresponding author
Wensheng Zhu
Department of Orthopedics, Huanggang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 19 Dongmen Road, Huanggang 438000, China
Department of Orthopedics, Huanggang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 19 Dongmen Road, Huanggang 438000, China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
This study aimed to elucidate the potential impact of whole-body water mass on osteoarthritis at the genetic prediction level through a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.
Material and methods:
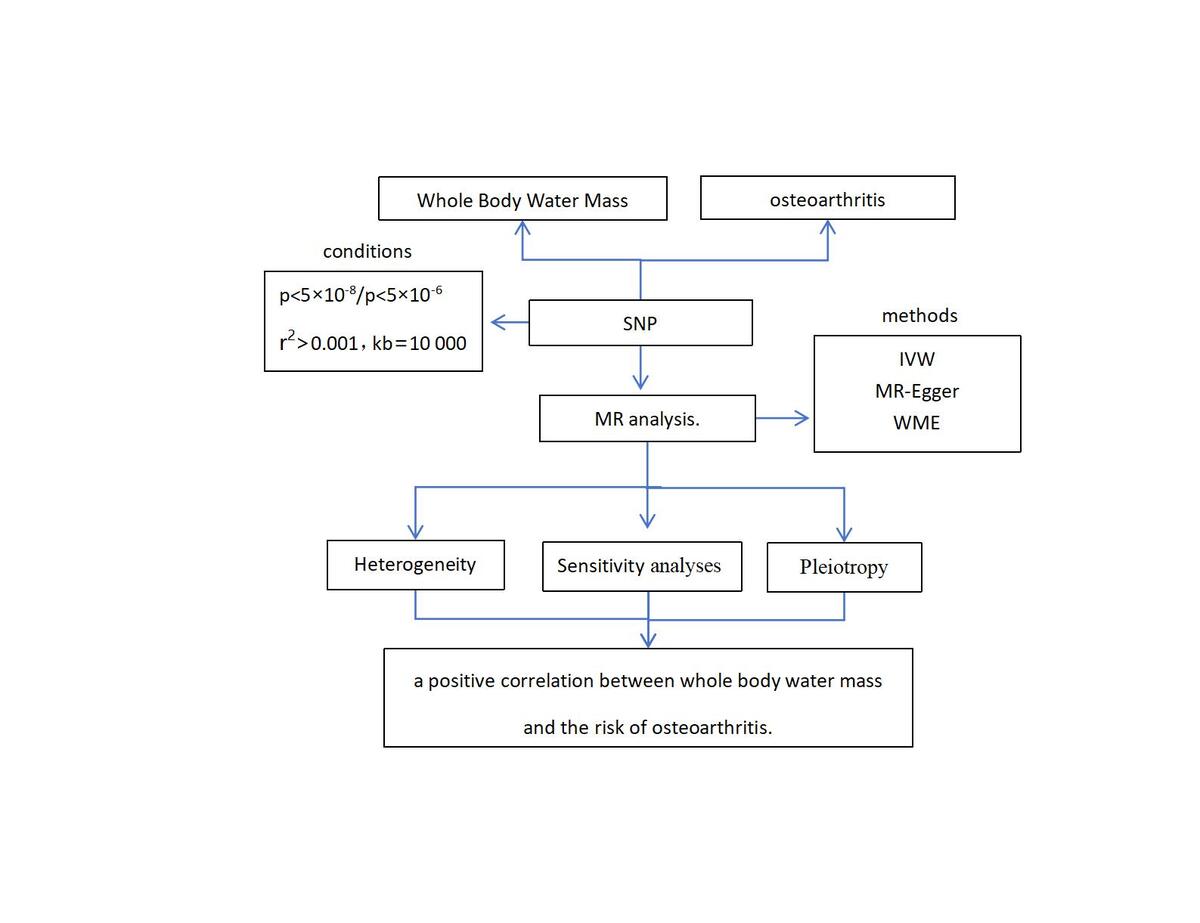
Using summary data from genome-wide association studies, we obtained information on whole-body water mass and various forms of osteoarthritis, including knee and hip osteoarthritis, knee osteoarthritis, and hip osteoarthritis from a large-scale genome-wide association study. MR analysis used inverse variance weighting, weighted median, MR-Egger, simple mode, and weighted estimation. Sensitivity analyses, including the MR-Egger method, MR-PRESSO, Cochran’s Q-test, and leave-one-out assessment, were performed to assess the reliability of the results.
Results:
In the inverse variance weighting model, increased genetic susceptibility to whole-body water mass was significantly associated with knee and hip osteoarthritis, knee osteoarthritis, and hip osteoarthritis (OR = 1.45, 95% CI: 1.27–1.65, p = 3.24 × 10–8; OR = 1.53, 95% CI: 1.30–1.79, p = 2.18 × 10–7; OR = 1.25, 95% CI: 1.04–1.50, p = 0.02). These results indicate a positive causal relationship between whole-body water mass and osteoarthritis. The MR-Egger intercept and Cochran’s Q-test indicated the absence of heterogeneity and horizontal pleiotropy in the analyses of whole-body water mass and knee and hip osteoarthritis, knee osteoarthritis, and hip osteoarthritis.
Conclusions:
The MR analysis suggests a positive correlation between whole-body water mass and risk of osteoarthritis.
This study aimed to elucidate the potential impact of whole-body water mass on osteoarthritis at the genetic prediction level through a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis.
Material and methods:
Using summary data from genome-wide association studies, we obtained information on whole-body water mass and various forms of osteoarthritis, including knee and hip osteoarthritis, knee osteoarthritis, and hip osteoarthritis from a large-scale genome-wide association study. MR analysis used inverse variance weighting, weighted median, MR-Egger, simple mode, and weighted estimation. Sensitivity analyses, including the MR-Egger method, MR-PRESSO, Cochran’s Q-test, and leave-one-out assessment, were performed to assess the reliability of the results.
Results:
In the inverse variance weighting model, increased genetic susceptibility to whole-body water mass was significantly associated with knee and hip osteoarthritis, knee osteoarthritis, and hip osteoarthritis (OR = 1.45, 95% CI: 1.27–1.65, p = 3.24 × 10–8; OR = 1.53, 95% CI: 1.30–1.79, p = 2.18 × 10–7; OR = 1.25, 95% CI: 1.04–1.50, p = 0.02). These results indicate a positive causal relationship between whole-body water mass and osteoarthritis. The MR-Egger intercept and Cochran’s Q-test indicated the absence of heterogeneity and horizontal pleiotropy in the analyses of whole-body water mass and knee and hip osteoarthritis, knee osteoarthritis, and hip osteoarthritis.
Conclusions:
The MR analysis suggests a positive correlation between whole-body water mass and risk of osteoarthritis.
REFERENCES (42)
1.
Abramoff B, Caldera FE. Osteoarthritis: pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am 2020; 104: 293-311.
2.
Czyżewska A, Glinkowski WM, Walesiak K, et al. Effects of preoperative physiotherapy in hip osteoarthritis patients awaiting total hip replacement. Arch Med Sci 2014; 10: 985-91.
4.
Mandl LA. Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2019; 27: 359-64.
5.
Küçükdeveci AA. Rehabilitation interventions in osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2023; 37: 101846.
6.
Waszczykowski M, Fabiś-Strobin A, Bednarski I, et al. Serum and synovial fluid concentrations of interleukin-18 and interleukin-20 in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee and their correlation with other markers of inflammation and turnover of joint cartilage. Arch Med Sci 2022; 18: 448-58.
7.
Huang G, Qian D, Liu Y, et al. The association between frailty and osteoarthritis based on the NHANES and Mendelian randomization study. Arch Med Sci 2023; 19: 1545-50.
8.
Wang C, Zhu Y, Liu Z, et al. Causal associations of obesity related anthropometric indicators and body compositions with knee and hip arthritis: a large-scale genetic correlation study. Front Endocrinol 2022; 13: 1011896.
9.
Hankin ME, Munz K, Steinbeck AW. Total body water content in normal and grossly obese women. Med J Aust 1976; 2: 533-7.
10.
Serra-Prat M, Lorenzo I, Palomera E, et al. Total body water and intracellular water relationships with muscle strength, frailty and functional performance in an elderly population. J Nutr Health Aging 2019; 23: 96-101.
11.
Zhu Q, Chen Q, Tian Y, et al. Genetic predisposition to a higher whole body water mass may increase the risk of atrial fibrillation: a mendelian randomization study. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis 2023; 10: 76.
12.
Zhou T, Xie J, Wang X, et al. Causal association between whole-body water mass and sleep apnea: a mendelian randomization study. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2022; 19: 1913-9.
13.
Bowden J, Holmes MV. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: a review. Res Synth Methods 2019; 10: 486-96.
14.
Mountjoy E, Schmidt EM, Carmona M, et al. An open approach to systematically prioritize causal variants and genes at all published human GWAS trait-associated loci. Nat Genet 2021; 53: 1527-33.
15.
Lin L, Luo P, Yang M, et al. Causal relationship between osteoporosis and osteoarthritis: a two-sample Mendelian randomized study. Front Endocrinol 2022; 13: 1011246.
16.
Zhao H, Zhu J, Ju L, et al. Osteoarthritis and stroke: a bidirectional mendelian randomization study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2022; 30: 1390-7.
17.
Ho J, Mak C, Sharma V, et al. Mendelian randomization studies of lifestyle-related risk factors for osteoarthritis: a PRISMA review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci 2022; 23: 11906.
18.
Hartley A, Sanderson E, Granell R, et al. Using multivariable Mendelian randomization to estimate the causal effect of bone mineral density on osteoarthritis risk, independently of body mass index. Int J Epidemiol 2022; 51: 1254-67.
19.
Larsson SC, Burgess S. Appraising the causal role of smoking in multiple diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of Mendelian randomization studies. EBioMedicine 2022; 82: 104154.
20.
To K, Mak C, Zhang C, et al. The association between alcohol consumption and osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis and meta-regression of observational studies. Rheumatol Int 2021; 41: 1577-91.
21.
Cornelis MC, Munafo MR. Mendelian randomization studies of coffee and caffeine consumption. Nutrients 2018; 10: 1343.
22.
Fan J, Zhu J, Sun L, et al. Causal association of adipokines with osteoarthritis: a Mendelian randomization study. Rheumatology 2021; 60: 2808-15.
23.
Xu S, Fung WK, Liu Z. MRCIP: a robust Mendelian randomization method accounting for correlated and idiosyncratic pleiotropy. Brief Bioinform 2021; 22: bbab019.
24.
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet 2018; 50: 693-8.
25.
Deng Y, Wong M. Association between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis in Japanese populations: a Mendelian randomization study. Arthritis Rheumatol 2023; 75: 1334-43.
26.
Burgess S, Thompson SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol 2017; 32: 377-89.
27.
Sanderson E, Smith GD, Windmeijer F, et al. Corrigendum to: an examination of multivariable Mendelian randomization in the single-sample and two-sample summary data settings. Int J Epidemiol 2020; 49: 1057.
28.
Nolte IM. Metasubtract: an R-package to analytically produce leave-one-out meta-analysis GWAS summary statistics. Bioinformatics 2020; 36: 4521-2.
29.
Bowden J, Del GMF, Minelli C, et al. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: the role of the I2 statistic. Int J Epidemiol 2016; 45: 1961-74.
30.
Taniguchi M, Ikezoe T, Kamitani T, et al. Extracellular-to-intracellular water ratios are associated with functional disability levels in patients with knee osteoarthritis: results from the Nagahama Study. Clin Rheumatol 2021; 40: 2889-96.
31.
Taniguchi M, Fukumoto Y, Yagi M, et al. Enhanced echo intensity and a higher extracellular water-to-intracellular water ratio are helpful clinical signs for detecting muscle degeneration in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 2021; 40: 4207-15.
32.
Taniguchi M, Fukumoto Y, Yagi M, et al. Enhanced echo intensity in vastus medialis is associated with worsening of functional disabilities and symptoms in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a 3 years longitudinal study. Rheumatol Int 2023; 43: 953-60.
33.
Yamada Y, Yoshida T, Yokoyama K, et al. The extracellular to intracellular water ratio in upper legs is negatively associated with skeletal muscle strength and gait speed in older people. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2017; 72: 293-8.
34.
Taniguchi M, Yamada Y, Ichihashi N. Acute effect of multiple sets of fatiguing resistance exercise on muscle thickness, echo intensity, and extracellular-to-intracellular water ratio. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 2020; 45: 213-9.
35.
Ali IA, Abd EA, El-Sayed FE. Integrated neuromuscular inhibition technique versus spray and stretch technique in neck pain patients with upper trapezius trigger points: a randomized clinical trial. J Man Manip Ther 2024; 32: 141-9.
36.
Kumar D, Karampinos DC, MacLeod TD, et al. Quadriceps intramuscular fat fraction rather than muscle size is associated with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2014; 22: 226-34.
37.
El Melhat A, Abbas RL, Zebdawi MR, et al. Effect of adding thoracic manipulation for the management of patients with adhesive capsulitis: a randomized clinical trial. Physiother Theory Pract 2025; 41: 65-78.
38.
McQueen FM. A vital clue to deciphering bone pathology: MRI bone oedema in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2007; 66: 1549-52.
39.
Hu Y, Chen X, Wang S, et al. Subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis and pain. Bone Res 2021; 9: 20.
40.
Wen XL, Cheng SZ. Study on the relationship between severe knee osteoarthritis and bone marrow edema. China J Orthopaed Traumatol 2023; 36: 523-31.
41.
Unal M, Akkus O, Sun J, et al. Raman spectroscopy-based water content is a negative predictor of articular human cartilage mechanical function. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2019; 27: 304-13.
42.
Saarakkala S, Julkunen P, Kiviranta P, et al. Depth-wise progression of osteoarthritis in human articular cartilage: investigation of composition, structure and biomechanics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2010; 18: 73-81.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.