Introduction
With the decline of the physiological function of the elderly, such as the decrease of muscle strength and sense of balance, the risk of falls in the elderly increases significantly [1, 2]. Falls have become one of the leading causes of casualties among the elderly around the world [3]. Therefore, the prevention of falls and the improvement of activity capacity of the elderly have always been the focus of global public health [4]. China has become the country with the largest number of elderly people in the world, and it is estimated that by 2050, the number of people over 60 will reach 40% of the total population. It is reported that among the elderly ≥ 65 years old, 1/3 of people have experienced a fall every year, and 1/2 of the elderly ≥ 85 years old have experienced a fall every year [5–7]. The prevalence of falls over the preceding year for the elderly ranges from 31.6% to 45.14% [5, 8, 9]. The probability of accidental fall and fall injury increases with age, which can lead to death, disability, decline in quality of life, and an increase in personal and social medical expenses [10, 11]. At present, the traditional intervention methods to prevent falls in the elderly include balance training, gait training, and health education to prevent falls. However, some studies [12, 13] have found that the elderly have poor compliance with traditional intervention methods, so the effect of long-term interventions is still controversial and needs further investigations.
Increasing the gait and balance function and fall prevention of the elderly has become a public health challenge that urgently needs to be addressed [14]. At present, the global population aged 65 or above has exceeded the number of people aged 5 and under, and the number and proportion of elderly people in almost every country are on the increase. With the development of science and technology, some emerging technologies have begun to be used in the field of rehabilitation for the elderly, among which virtual reality (VR) technology is the most typical. VR uses computers to generate a simulation environment, which is a multi-source information fusion, interactive three-dimensional dynamic scene and entity behavior system simulation. There are four categories of VR technology: desktop VR, immersive VR, enhanced VR and distributed VR. By providing accurate evaluation, assistance, supervision and training, VR technology ensures the interest and effectiveness of sports training, as well as the enthusiasm and initiative of patients to participate in training [15–17]. VR technology has been used in patients with Alzheimer’s disease, leukemia and Parkinson’s disease [18, 19]. However, whether VR training is safer and more effective than the traditional intervention model in preventing falls in the elderly is still controversial. Therefore, this study aimed to conducted a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on the application of VR in improving the gait and balance function in the elderly, to provide evidence-based support for the nursing care of the elderly.
Material and methods
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [20] was followed in this meta-analysis. Ethics approval was not necessary since the study was a meta-analysis.
Literature search strategy
The two authors independently searched EMBASE, PubMed, Web of Science, Clinical trials, Cochrane library, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang and Weipu databases for potential RCTs. The retrieval time was from the establishment of each database to October 20, 2023. We used subject words combined with keywords and free words based on the Boolean operators for literature retrieval. The search strategy for this meta-analysis was as follows: (“elderly” OR “aged” OR “old” OR “senior”) AND (“virtual reality” OR “VR” OR “computer game” OR “interactive game”) AND (“activity” OR “falls” OR “balance” OR “strength” OR “gait” OR “posture”).
Literature inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria of this meta-analysis were as follows: RCTs evaluating VR intervention on improving the gait and balance function of the elderly. The study population consisted of subjects older than 60 years without cognitive impairment. The VR group received exercise training based on VR technology, while the control group received traditional exercise intervention. Outcome indicators include gait assessment indicators, static balance indicators, dynamic balance indicators, muscle strength and fall fear assessment indicators, such as the Tinetti gait assessment scale, One Leg Stand Test (OLST), Functional Reach Test (FRT), Berg Balance Scale (BBS), Timed Up and Go (TUG), Five Times Sit to Stand Test (FTSST), 30-second Sit to Stand Test (30s SST), Falls Efficacy Scale (FES) and Life Satisfaction Index A (LSIA). The exclusion criteria of this meta-analysis were as follows: research designs other than RCTs such as case report and reviews, non-Chinese and English literature reports.
Literature screening and data extraction
All the literatures in this study were imported into EndNote software for duplicate removal and literature management, and two researchers independently screened the literature according to the established inclusion and exclusion criteria. In case of differences, they would be resolved by consensus or a third party. The extracted literature information included the first author’s name, year of publication, country, sample size, intervention measures, outcome indicators and study conclusions. After the data extraction was completed, the two researchers cross-checked the data for consistency.
Risk of bias assessment
Two researchers independently evaluated the quality of the included RCTs, and each researcher evaluated the risk bias in the literature strictly according to the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomized trials [21]. If there was a disagreement, it would be resolved through consensus and discussion. The evaluation indicators included random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, selective reporting and other bias. Each item could be rated as “high risk”, “low risk” and “unclear” accordingly.
Statistical analysis
In this meta-analysis, RevMan 5.2 software was used to analyze the included data. The χ2 test was used to test heterogeneity. If there was no heterogeneity among studies (p ≥ 0.1, I2 < 50%), a fixed effect model was used for meta-analysis; otherwise subgroup analysis or a random effect model was used for analysis. We calculated the weighted mean difference (WMD) and its 95% confidence interval (confidence interval, CI). The statistical significance level of this meta-analysis was α = 0.05. If the outcome data of each study could not be analyzed by meta-analysis, only descriptive analysis would be carried out. Funnel plot and Egger regression analysis were used to test the bias of meta-analysis results. There was an attempt to assess publication bias even if the results were not significant.
Results
RCT selection
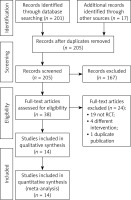
A total of 218 articles were retrieved in the initial search before screening, and 205 related articles after duplicate removal were screened by layers. Finally, 14 RCTs [22–35] were included for data analysis in this study (Figure 1).
Characteristics of included RCTs
As presented in Table I, a total of 662 elderly adults were included, of whom 336 underwent VR intervention and 326 underwent control intervention. There are some differences in VR equipment, frequency and duration of intervention among different RCTs.
Table I
Characteristics of included RCTs
RCT quality assessment
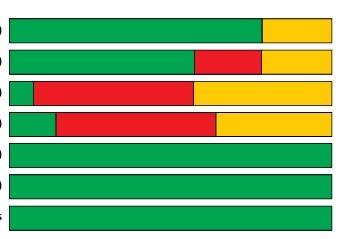
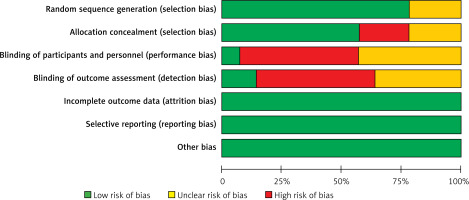
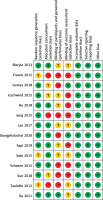
As shown in Figures 2 and 3, of the 14 RCTs included, 11 RCTs specifically described the random method, 8 RCTs reported the allocation concealment, and because the VR intervention model required specific training instructions for the research object, it was difficult to implement the blind design of the research population. Only one article mentioned the blind method of the research object, and two articles used the blind method of evaluator in RCTs. We did not find any quality risks in other aspects.
Meta-analysis
TUG score
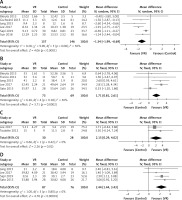
Six RCTs reported the TUG score after the intervention. TUG is a commonly used screening tool to assist clinicians to identify patients at risk of falling. The heterogeneity among the studies was large (p = 0.08, I2 = 50%), so the random effect model was used for analysis. The results showed that the TUG score of the elderly in the VR group was significantly lower than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (MD = –1.34, 95% CI (–1.99, –0.69), p < 0.001, Figure 4 A), suggesting that the dynamic balance function of the VR group was better than that of the control group.
BBS score
Five RCTs reported the BBS score after the intervention. The BBS is a test created by Katherine Berg in 1989 to evaluate balance ability in the elderly; it evaluates both dynamic and static balance through 14 tasks regarding mobility. The heterogeneity among the studies was small (p = 0.18, I2 = 36%), so the fixed effect model was used for analysis. The results showed that the BBS score of the elderly in the VR group was significantly higher than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (MD = 1.71, 95% CI (0.81, 2.61), p < 0.001, Figure 4 B), suggesting that the dynamic balance function of the VR group was better than that of the control group.
OLST score
Two RCTs reported the OLST score after the intervention. OLST is one of the balance tests used to diagnose musculoskeletal ambulation disability symptoms to identify the symptoms of motor organ deterioration and establish preventive strategies. The heterogeneity among the studies was small (p = 0.42, I2 = 0%), so the fixed effect model was used for analysis. The results showed that the OLST score of the elderly in the VR group was significantly higher than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (MD = 2.15, 95% CI (0.29, 4.02), p = 0.02, Figure 4 C), suggesting that the static balance function of the VR group was better than that of the control group.
FRT score
Four RCTs reported the FRT score after the intervention. FRT is a useful screening tool to identify the risk for falls. The heterogeneity among the studies was small (p = 0.80, I2 = 0%), so the fixed effect model was used for analysis. The results showed that the FRT score of the elderly in the VR group was significantly higher than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (MD = 2.44, 95% CI (1.44, 3.43), p < 0.001, Figure 4 D), suggesting that the static balance function of the VR group was better than that of the control group.
FTSST score
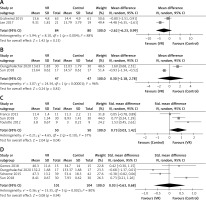
Two RCTs reported the FTSST score after the intervention. The FTSST measures one aspect of transfer skill; it provides a method to quantify functional lower extremity strength and/or identify movement strategies a patient uses to complete transitional movements. The heterogeneity among the studies was small (p = 0.004, I2 = 88%), so the random effect model was used for analysis. The results showed that there were no significant difference in the FTSST score of the elderly between the VR group and the control group (MD = –2.62, 95% CI (–-6.23, 0.99), p = 0.15, Figure 5 A).
30s SST score
Two RCTs reported the 30s SST score after the intervention. The 30s SST is a measurement that assesses functional lower extremity strength in older adults. The heterogeneity among the studies was small (p < 0.001, I2 = 96%), so the random effect model was used for analysis. The results showed that there was no significant difference in the 30s SST score of the elderly between VR group and control group (MD = 0.30, 95% CI (–2.18, 2.78), p = 0.81, Figure 5 B).
Gait improvement
Three RCTs reported the Tinetti score for gait improvement after the intervention. The heterogeneity among the studies was large (p = 0.10, I2 = 57%), so the random effect model was used for analysis. The results showed that the OLST score of the elderly in the VR group was significantly higher than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (SMD = 0.73, 95% CI (0.03, 1.42), p = 0.04, Figure 5 C), suggesting that the gait improvement of the VR group was better than that of the control group.
Fall fear of the elderly
Two RCTs reported the fear of falling after the intervention. The heterogeneity among the studies was large (p < 0.001, I2 = 80%), so the random effect model was used for analysis. The results showed that there was no significant difference in the fear of falling of the elderly between the VR group and the control group (SMD = 0.03, 95% CI (–0.63, 0.68), p = 0.94, Figure 5 D).
Publication bias
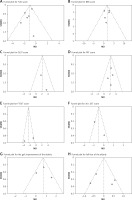
A funnel chart analysis of each index was carried out. As shown in Figure 6, the scattered points were symmetrically distributed on both sides of the midline, showing an inverted funnel shape. The results of Egger regression analysis showed that there was no significant bias in the results of literature analysis (all p > 0.05).
Discussions
With aging, various functions of the human body decline, the motor system being the most prominent: the lower limb joint activity decreases, and muscle strength and proprioceptive function decline seriously, impacting the activity function of the elderly, and increasing the risk of falls [36, 37]. On the one hand, the routine rehabilitation training process is monotonous, the content is boring, and the interest of the elderly is low. On the other hand, the labor intensity of rehabilitation teachers is large, the workload is high, it is easy to produce fatigue, and the training efficiency is low [38, 39]. VR technology refers to the realistic vision, hearing, touch, smell, taste and other integrated virtual environment generated by modern high-tech means with the computer as the core [40–42]. With the help of some special input and output devices, users interact and interact with objects in the virtual world in a natural way, so as to produce the feeling and experience of being in the real environment [43]. The results of this meta-analysis show that VR intervention can better improve the gait and dynamic and static balance function of the elderly, and increase their gait and balance function, but the effects on their lower limb muscle strength and fear of falling are still unclear, and need to be further analyzed in follow-up studies.
VR technology provides the technical means of three key elements: repetitive practice, performance feedback and motivation maintenance. It has specific and unique advantages compared with traditional movement training [44]. First of all, the sense of immersion improves the interest and safety of sports training. The sports training of traditional rehabilitation institutions is limited by time, space, manpower and cost, while VR cannot be limited by time and space and can provide a strong sense of immersion. It is often used in some complex, high-risk, high-cost task training [45]. The fitness game based on VR technology can not only show the effect or better effect of traditional sports training, but also increase the interest and safety of the whole rehabilitation process [46]. In the virtual environment, the risk of the elderly caused by mistakes in exercise is greatly reduced. Timely feedback and supervision increase the compliance of participants. Supervision and feedback are very important in the process of rehabilitation exercise, which will directly affect the effect of rehabilitation [47]. Some researchers [48–50] have pointed out that many physiotherapy guidelines for chronic diseases recommend long-term physical rehabilitation, but because repeated physical training is very boring and may affect patients’ compliance with treatment, VR training can be a good alternative. The feedback of VR technology includes both the real-time feedback during training and the performance feedback after training. These two forms of feedback are helpful to improve the awareness of the training results of the elderly [51].
The characteristics of gait, such as stride, stride height, continuity and stability, are significantly related to the activity level of the elderly. At the same time, the decrease of balance ability is the main risk factor of falls, so gait stability and balance ability can be used as one of the indexes to predict falls. The results of the meta-analysis in this study show that VR training is superior to the traditional intervention model in improving gait, balance function, limb sensitivity and body stability of the elderly, which is consistent with the results of previous studies [52, 53]. The balance of the body depends on the integration and coordination of visual, auditory and sensory systems, while the virtual scene produced by VR training provides the elderly with multiple sensory experiences including visual, auditory and somatosensory systems, increasing the input of visual and auditory stimuli while moving, providing a reference to the position of objects in and around the space, and increasing self-awareness, so that the elderly can adjust their body movements and postures in time [54]. By strengthening the skeletal muscle function and nervous system function, this training mode improves the posture control and adjustment ability of the elderly during exercise, thus ensuring the physical stability of the elderly during exercise [55].
The results of this study show that VR training is not superior to traditional fall prevention intervention in enhancing the muscle strength of lower extremities, which is inconsistent with the conclusions of a previous study [56]. On the one hand, this may be related to the small sample size included in this study, in the evaluation of lower limb muscle strength; each index only involves two related items of literature, and there are few data that can be combined, so the results of this study should be treated with caution. In addition, the fear of falling may also become one of the factors affecting the level of activity. Tension and fear will lead to the loss of confidence and the reduction of spontaneous exercise in the elderly, resulting in a decrease in muscle strength and increased physical instability [57]. The results of this study have shown that there is no significant difference between VR training and traditional fall prevention intervention in improving the fear of falls in the elderly. The possible reason is that the fear of falling is influenced by many factors, such as social demographics, physical function, history of falling, and psychological and cognitive conditions [58]. Fall-related adverse events place a clinical and financial burden on the health care system, and the current medical care policy limits reimbursement [59]. Through further research, it is suggested that innovative methods such as VR or big data mining should be used to explore the causes and conditions of falls and the ways to reduce falls [60].
There are some limitations in this study that are worth considering. First, among the 14 RCTs included, the methodological design of some studies is not rigorous enough, and the number of studies included in various evaluation indicators is relatively small, which may be the sources of heterogeneity detected in this meta-analysis. Second, this study only included published Chinese and English literature, which may lead to the risk of incomplete literature review. Thirdly, there is a significant correlation between activity level and age, but due to the small sample size and lack of data in some studies, age subgroup analysis could not be carried out. Finally, this study was not pre-registered in PROSPERO. In the future, higher quality, large-sample studies and long-term follow-up are needed to further verify the long-term effectiveness of VR interventions in proving the gait and balance function of the elderly.
In conclusion, the results of this meta-analysis show that VR interventions are beneficial to improve the gait and dynamic and static balance function of healthy elderly, but they have no significant effect on lower limb muscle strength and fear of falling in the elderly. VR interventions may be effective in the field of elderly care and fall prevention. However, considering the small sample size of some studies, and a certain degree of heterogeneity in the intervention scheme and frequency of each RCT, the results should be treated with caution. Elderly patients may be suggested to use VR to improve gait and balance function, but it may be impossible even in high income countries considering the lack of common availability. Therefore, it is suggested that in future research, we should appropriately increase the sample size, adopt a more standardized and rigorous design, and carry out in-depth research to further verify the role of VR in the elderly.