Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
NEUROLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
Validation of the ability of ESER score to predict recurrent stroke: a meta-analysis
1
Department of neurology, The third people's Hospital of Dongguan city, China
2
Department of respiratory, The third people's Hospital of Dongguan city, China
3
Department of Cardiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of NanChang University, China
Submission date: 2020-02-15
Final revision date: 2020-08-17
Acceptance date: 2020-09-02
Online publication date: 2021-05-03
Corresponding author
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
A risk stratification model is pretty important to prevent the recurrent stroke for ischemic stroke patients. The present study aimed to meta-analysis the ability of Essen Stroke Risk Score (ESRS) to accurately predict recurrence of ischemic stroke.
Material and methods:
Studies on the diagnostic performance of Essen Stroke Risk Score in predicting recurrent stroke were searched by electronic and manual methods. Quality pooled C-statistics, and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were evaluated.
Results:
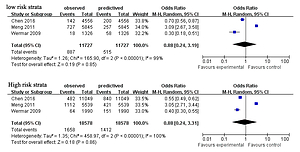
Fifteen studies with a total of 94,052 patients were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled C-statistics of ESER for patients without atrial fibrillation (AF) experiencing recurring strokes at 90-day or one-year were 0.65 (95% CI: 0.58-0.73) and 0.57 (95% CI: 0.53-0.60), and the heterogeneity was weak. The average ratio of one-year recurrent stroke in the low-risk and high-risk groups classified according to ESRS is 5.6%(range 1.4 to 12.1%) and 9.2%( range 3.2 to 20.1%), respectively. And the calibration analysis showed the pooled RR in the low-risk group is 0.88 (95%CI: 0.24-3.19) and 0.88 (0.24-3.31) with wide confidence intervals and high levels of heterogeneity, indicating the calibration ability was low.
Conclusions:
ESRS had low to moderate ability to predict recurrence of stroke in patients with ischemic stroke and low calibration ability, which need to be further improved.
A risk stratification model is pretty important to prevent the recurrent stroke for ischemic stroke patients. The present study aimed to meta-analysis the ability of Essen Stroke Risk Score (ESRS) to accurately predict recurrence of ischemic stroke.
Material and methods:
Studies on the diagnostic performance of Essen Stroke Risk Score in predicting recurrent stroke were searched by electronic and manual methods. Quality pooled C-statistics, and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were evaluated.
Results:
Fifteen studies with a total of 94,052 patients were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled C-statistics of ESER for patients without atrial fibrillation (AF) experiencing recurring strokes at 90-day or one-year were 0.65 (95% CI: 0.58-0.73) and 0.57 (95% CI: 0.53-0.60), and the heterogeneity was weak. The average ratio of one-year recurrent stroke in the low-risk and high-risk groups classified according to ESRS is 5.6%(range 1.4 to 12.1%) and 9.2%( range 3.2 to 20.1%), respectively. And the calibration analysis showed the pooled RR in the low-risk group is 0.88 (95%CI: 0.24-3.19) and 0.88 (0.24-3.31) with wide confidence intervals and high levels of heterogeneity, indicating the calibration ability was low.
Conclusions:
ESRS had low to moderate ability to predict recurrence of stroke in patients with ischemic stroke and low calibration ability, which need to be further improved.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.