Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
Ultrasonographic features of the intrinsic foot muscles in patients with and without plantar fasciitis: a novel case-control research study
1
Department of Physiotherapy, Faculty of Sport Sciences, Universidad Europea de Madrid, Villaviciosa de Odón, Madrid, Spain
2
Research, Health and Podiatry Unit, Department of Health Sciences, Faculty of Nursing and Podiatry, Universidade da Coruña, Ferrol, Spain
3
Frailty Research Organized Group (FROG), Department of Nursing, Faculty of Nursing and Podiatry, University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain
4
Department of Physiotherapy, Medicine and Biomedical Sciences,
Universidade da Coruña, Spain
Submission date: 2021-09-23
Final revision date: 2021-10-13
Acceptance date: 2021-10-15
Online publication date: 2021-11-21
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
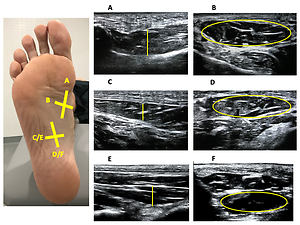
The aim of the present study was to compare by ultrasound imaging (USI) the thickness and cross-sectional area (CSA) of the flexor hallucis brevis (FHB), flexor digitorum brevis (FDB), abductor hallucis brevis (AHB) and quadratus plantae (QP) muscles between individuals with and without plantar fasciitis (PF).
Material and methods:
A case-control study was performed with 64 participants divided into two groups: A, PF group (n = 32) and B, healthy group (n = 32).
Results:
USI measurements for FHB CSA (p = 0.035) decreased, showing statistically significant differences for the PF group, while the QP CSA (p = 0.40) increased, showing statistically significant differences for the PF group with respect to the healthy group. The rest of the intrinsic foot muscles (IFM) did not show statistically significant differences; however in FHB, FDB, QP and AHB thicknesses and FDB CSA showed a slightly decrease for the PF group.
Conclusions:
USI measurements showed that the CSA of the FHB muscle is reduced in patients with PF while the CSA of the QP muscle is increased in patients with PF.
The aim of the present study was to compare by ultrasound imaging (USI) the thickness and cross-sectional area (CSA) of the flexor hallucis brevis (FHB), flexor digitorum brevis (FDB), abductor hallucis brevis (AHB) and quadratus plantae (QP) muscles between individuals with and without plantar fasciitis (PF).
Material and methods:
A case-control study was performed with 64 participants divided into two groups: A, PF group (n = 32) and B, healthy group (n = 32).
Results:
USI measurements for FHB CSA (p = 0.035) decreased, showing statistically significant differences for the PF group, while the QP CSA (p = 0.40) increased, showing statistically significant differences for the PF group with respect to the healthy group. The rest of the intrinsic foot muscles (IFM) did not show statistically significant differences; however in FHB, FDB, QP and AHB thicknesses and FDB CSA showed a slightly decrease for the PF group.
Conclusions:
USI measurements showed that the CSA of the FHB muscle is reduced in patients with PF while the CSA of the QP muscle is increased in patients with PF.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.