Introduction
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication of pediatric cardiosurgical procedures and is associated with elevated mortality.
The incidence of AKI is increasing worldwide, affecting about 6% of all hospitalized patients, and it is an independent predictor of mortality and morbidity [1, 2]. In the critical care setting, the prevalence of AKI requiring dialysis is about 6%, with a mortality rate exceeding 60% [3].
Diagnosis of AKI is based on detecting reduced kidney function by the rise in serum creatinine concentration, a delayed and unreliable measure in the acute setting.
In patients after cardiac surgery, AKI requiring dialysis occurs in up to 5%, in whom the mortality rate approaches 80%, and is indeed the strongest independent risk factor for death [4]. But even a minor degree of postoperative AKI, as manifested by only a 0.2 to 0.3 mg/dl rise in serum creatinine from baseline, is also associated with an increase in mortality [5, 6].
Infants and children with congenital heart diseases may be especially vulnerable to developing AKI because many require multiple operations for step-by-step repair of complex congenital cardiac anomalies.
Early markers of kidney damage are being sought to prevent the development of AKI [7–10].
Netrin-1 (NTN-1) is an anti-inflammatory protein secreted by proximal tubule epithelial cells in reaction to hypoxic or toxic injury. Netrins are molecules with a distinctive domain organization belonging to the laminin-related axon-guidance molecule family [11].
They have many roles in axonal guidance, the development of mammary glands, lung, pancreas, and blood vessels, vascular patterning and maturity in the developing kidney, inhibition of leukocyte migration during sepsis and mitogenesis, and chemoattraction of endothelial cells [12–14]. The kidney has one of the highest levels of NTN-1 expression, and administration of recombinant NTN-1 before ischemia-reperfusion reduces kidney injury and inflammation [15, 16].
In the ischemia AKI mouse model, the NTN-1 appears early in urine (after 1–3 h) [16].
The study aimed to evaluate the role of NTN-1 as a marker of short-term renal outcomes in children after cardiac surgery.
Material and methods
Study group
The present study was a single-center, prospective undertaking. We included 40 children who underwent cardiac surgery in cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) due to congenital heart defects between May and September 2021. The inclusion criteria were age between 1 and 36 months, the presence of congenital heart defect, and eligibility for cardiac surgery in CPB. The exclusion criteria were pre-existing chronic kidney disease (CKD), sudden cardiac arrest in the previous 3 months, urinary tract infection during the last month, and use of nephrotoxic drugs (cisplatin, amphotericin B, cyclosporin, aminoglycosides) in the previous month. The control group consisted of 20 healthy, age- and sex-matched volunteers.
Study protocol
In all recruited patients, we analyzed the following clinical and anthropometric parameters: age [months], sex, body length [cm], weight [kg], type of congenital heart defect, CPB time [min], and aortic clamping time [min].
Blood samples were collected before the initiation of surgery and 48 h after it was completed. Urine samples were collected from the study group before the initiation of cardiac surgery, 6, 24, and 48 h after the surgery was completed, and once from the control group. Standard local laboratory methods were used to evaluate the laboratory tests. They included red blood count (RBC), white blood count (WBC), platelet count (PLT), hemoglobin [g/dl], serum urea [mg/dl], serum and urinary creatinine [mg/dl], cystatin C [mg/l], total protein [g/dl], albumin [g/dl], and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) [pg/ml].
Urine samples were centrifuged under controlled conditions and frozen at –80°C. NTN-1 concentrations [ng/mL] were assessed using the ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method and Assay Genie Human NTN1 kit (catalog number HUEB1973) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) was calculated using the full Schwartz formula [17] based on serum creatinine, cystatin C, and urea. Change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (ΔeGFR) was calculated as the difference between eGFR after 48 h and eGFR before cardiac surgery.
The presence of AKI was assessed using the pediatric RIFLE criteria [18] and eGFR calculated as mentioned above.
After surgery, patients received hydration of 5–10 ml/kg/h and furosemide at a dose of 2–10 mg/kg/day.
Endpoints
The primary endpoint was to evaluate the usefulness of urinary NTN-1 level as a predictor of AKI in pediatric patients after cardiac surgery.
The secondary endpoint was to evaluate factors influencing the urine NTN-1/creatinine ratio in the study group.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using Dell Statistica 13.3 PL software. We assessed the normality of data using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Where applicable, the results are expressed as median (IQR) or mean ± standard deviation. We applied the following statistical tests: Mann-Whitney U test, Wilcoxon test, Spearman’s rank correlation, and χ2 test. Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analysis was used to calculate the area under the curves (AUC), and Youden’s index was used to identify the proper cut-off values. Multivariate analysis was performed using the general step-wise regression. The variables were introduced into the model, excluding those that correlated with each other with r > 0.60 to avoid collinearity. The criterion for inclusion in the final model was p < 0.050. The results of multivariate analyses were expressed as β, confidence interval (CI), and p-value. All results were considered statistically significant, with p-values < 0.050.
Results
Characteristics and laboratory test results of the study group
Basic characteristics and the comparison of the study and control groups are shown in Table I. Median age in the entire group was 6 (IQR 3–12) months. Sex distribution was equal in both groups, and we observed no sex predomination. In the study group, the most common cardiac defect was ASD/VSD. Median weight was 6.4 (4.8–9.1) kg, and median body length was 67.0 (62.0–77.0) cm. All surgical procedures were conducted in CPB (median duration 107.5, IQR 78.0–146.5 min), with the median aortic clamping time of 58.5 (41.5–74.5) min. None of the patients required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) after the surgery.
Table I
Characteristics of the study group
| Parameter | Study group | Control group | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age [months] | 4.5 (3.0–11.0) | 8.5 (4.8–16.0) | NS (0.098)* |
| Sex [female/male] | 20/20 | 7/13 | NS (0.271)** |
| Type of cardiac defect, n (%) | |||
| ASD/VSD | 14 (35) | – | – |
| AVSD | 6 (15) | – | – |
| F4/DORV + PS | 10 (25) | – | – |
| Other | 10 (25) | – | – |
| Aortic clamping duration [min] | 58.5 (41.5–74.5) | – | – |
| CPB time [min] | 107.5 (78.0–146.5) | – | – |
| Initial NTN1 [ng/ml] | 0.2 (0.0–1.1) | 0.0 (0.0–0.0) | 0.017* |
| Initial NTN1 [n] detectable/ | |||
| not detectable | 22/18 | 4/16 | 0.010** |
Forty-eight h after the surgery, we observed a statistically significant decrease in serum albumin, serum total protein, and platelet count. We also found a statistically significant increase in white blood count and NT-proBNP. However, no statistically significant changes in eGFR were observed, and mean ΔeGFR was –1.1 ±23.9 ml/min/1.73 m2. The laboratory test results are displayed in Table II.
Table II
Laboratory test results
[i] eGFR – estimated glomerular filtration rate, NT-proBNP – N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, Hb – hemoglobin, WBC – white blood cell count, RBC – red blood cell count, PLT – platelet count, ΔeGFR – estimated glomerular filtration rate change after 48 h. Wilcoxon test for paired observations.
Urinary NTN-1
Baseline urinary NTN-1 was statistically significantly higher in the study group than in the control group (Table I). It was also detectable in a significantly higher patient ratio than in healthy children (55% vs. 20%, p = 0.010). Interestingly, in the study group, the detection ratio of urinary NTN-1 was higher before surgery than 6 and 24 h after (55% – 22 patients, 27.5% – 11 patients, and 32.5% – 13 patients, respectively). Median NTN-1 concentration was also significantly lower at both follow-up points than initially (Figure 1). However, we found no statistically significant correlations between NTN-1 at any point and ΔeGFR, decline in eGFR, and AKI after 48 h (Table III).
Figure 1
Urinary NTN1 concentrations in the study group before and 6 and 24 h after the surgery. Friedman’s ANOVA test
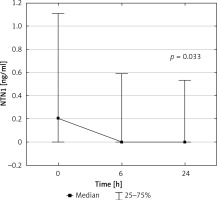
Table III
Correlations of urinary NTN1 measurements with the indicators of kidney function deterioration
Urinary NTN-1/creatinine ratio
There was no difference between the initial and 24 h urinary NTN-1/creatinine ratio regarding the type of cardiac defect (Table IV). In our group, the initial NTN-1/creatinine ratio negatively correlated with ΔGFR (r = –0.36, p = 0.031). NTN-1/creatinine ratio after 24 h did not correlate with aortic clamping time, CPB time, or ΔGFR (Table V).
Table IV
Urinary NTN1/creatinine ratio regarding the type of cardiac defect
| Type of cardiac defect | Initial NTN1/creatinine ratio [ng/mg] | NTN1/creatinine ratio after 24 h [ng/mg] | P-value** |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entire study group | 0.003 (0.000–0.067) | 0.000 (0.000–0.034) | NS (0.218) |
| ASD/VSD | 0.000 (0.000–0.027) | 0.000 (0.000–0.000) | NS (0.735) |
| AVSD | 0.131 (0.000–0.150) | 0.000 (0.000–0.000) | NS (0.109) |
| F4/DORV + PS | 0.011 (0.000–0.080) | 0.026 (0.000–0.059) | NS (0.345) |
| Other | 0.003 (0.000–0.028) | 0.000 (0.000–0.015) | NS (0.893) |
| P-value* | NS (0.521) | NS (0.386) | – |
Table V
Correlations of urinary NTN1/creatinine ratio with selected clinical parameters
ΔeGFR
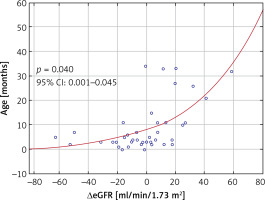
Mean ΔeGFR was –1.1 ±23.9 ml/min/1.73 m2 and did not vary significantly regarding the patient’s sex (p = 0.883) or the type of cardiac defect (p = 0.175). In univariate analysis, we found positive correlations of ΔeGFR with the patient’s age (p = 0.040), weight (r = 0.42, p = 0.007), and body length (r = 0.42, p = 0.007), and negative correlations of ΔeGFR with CPB time (r = –0.38, p = 0.015) and aortic clamping time (r = –0.38, p = 0.016). In the multivariate linear step-wise regression model, age was the only predictor of ΔeGFR (β = 0.53, 95% CI: 0.59–1.90, p < 0.001). The correlation of ΔeGFR and age is shown in Figure 2.
eGFR decline
We noted eGFR deterioration in 50% of patients (n = 20) with a mean value of –18.7 ±17.5 ml/min/1.73 m2. We found negative correlations of age (r = –0.41, p = 0.009) and weight (r = –0.35, p = 0.028) with eGFR decline. No other predictors of eGFR decline were identified in the present study.
Occurrence of AKI
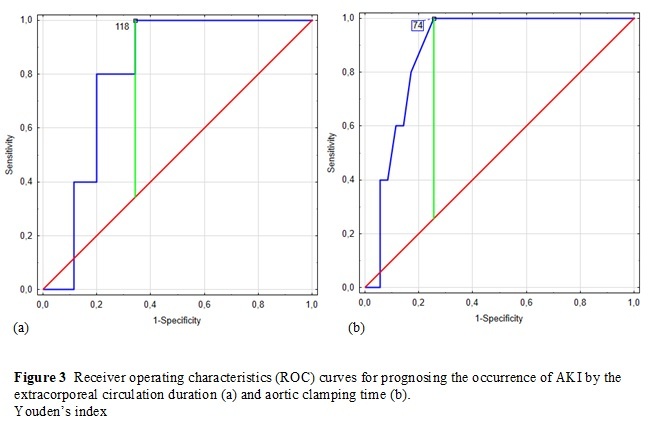
In the present study, AKI occurred in 12.5% of patients (n = 5) within 2 days. Out of them, three children were in the Risk stage, and two were in the Injury stage. None of the patients suffered from more severe AKI, and none required renal replacement therapy (RRT). The occurrence of AKI correlated with CPB time (r = 0.35, p = 0.027) and aortic clamping time (r = 0.44, p = 0.005). ROC analysis also showed statistically significant profiles of both mentioned factors as stimulants of AKI occurrence (Figure 3). For CPB time (AUC = 0.81, 95% CI: 0.67–0.94, p < 0.001), the cut-off value was 118 min (sensitivity 100%, specificity 65.7%), and for aortic clamping time (AUC = 0.88, 95% CI: 0.78–0.99, p < 0.001), the cut-off value was 74 min (sensitivity 100%, specificity 74.3%).
AKI vs. non-AKI
No significant differences were found between the study groups regarding age, sex, type of cardiac defect, and NT-proBNP level.
In the study group, patients with AKI had a higher GFR before surgery and a significantly lower GFR (ΔGFR = –49.61 vs. 2.84, p < 0.001) after surgery. CPB and aortic clamping time were significantly longer in patients with AKI than in patients without AKI.
NTN-1 concentration and NTN-1/creatinine ratio in the AKI group were higher preoperatively and 24 h after surgery than in patients without AKI, but these differences were not statistically significant (Table VI).
Table VI
Clinical parameters regarding the occurrence of acute kidney injury
| Parameter | Study group | AKI | Non-AKI | p: AKI vs. non-AKI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [months] | 4.5 (3.00–11.00) | 3.00 (3.00–5.00) | 5.00 (3.00–11.00) | NS (0.388) |
| Sex [female/male] | 20/20 | 3/2 | 17/18 | NS (0.633)* |
| Initial eGFR [ml/min/1.73 m2] | 83.9 ±25.0 | 104.34 (100.57–109.13) | 76.66 (65.88–99.03) | 0.014 |
| ΔeGFR [ml/min/1.73 m2] | –1.1 ±23.9 | –49.61 (–52.35–-31.44) | 2.84 (–9.45–17.57) | < 0.001 |
| Aortic clamping time [min] | 58.5 (41.5–74.5) | 96.00 (75.00–98.00) | 58.00 (41.00–74.00) | 0.003 |
| CPB time [min] | 107.5 (78.0–146.5) | 147.00 (146.00–160.00) | 97.00 (76.00–130.00) | 0.027 |
| Initial NTN1 [ng/ml] | 0.2 (0.0–1.1) | 0.23 (0.00–1.05) | 0.18 (0.00–1.17) | NS (0.812) |
| NTN1 after 6 h [ng/ml] | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.00 (0.00–0.59) | NS (0.874) |
| NTN1 after 24 h [ng/ml] | 0.00 (0.00–0.00) | 0.59 (0.00–1.21) | 0.00 (0.00–0.48) | NS (0.228) |
| Initial urinary NTN1/creatinine ratio [ng/ml] | 0.003 (0.000–0.067) | 0.10 (0.01–0.21) | 0.00 (0.00–0.05) | NS (0.144) |
| Urinary NTN1/creatinine ratio after 24 h [ng/ml] | 0.000 (0.000–0.034) | 0.01 (0.00–0.06) | 0.00 (0.00–0.03) | NS (0.317) |
| Initial NT-proBNP [pg/ml] | 966.5 (347.0–2723.0) | 951.00 (347.00–1386.00) | 977.00 (382.00–2723.00) | NS (1.000) |
| NT-proBNP after 48 h [pg/ml] | 4750.5 (3309.0–10059.5) | 6255.00 (3181.00–22021.00) | 4661.00 (3437.00–9656.00) | NS (0.524) |
| Type of cardiac defect, % (n) | NS (0.196)* | |||
| ASD/VSD | 35.0% (14) | 20.0% (1) | 37.1% (13) | |
| AVSD | 15.0% (6) | 20.0% (1) | 14.3% (5) | |
| F4/DORV + PS | 25.0% (10) | 60.0% (3) | 20.0% (7) | |
| Other | 25.0% (10) | 0.0% | 28.6% (10) |
AKI – acute kidney injury, eGFR – estimated glomerular filtration rate, CPB – cardiopulmonary bypass, NTN1 – netrin-1, NT-proBNP – N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, ASD – atrial septal defect, VSD – ventricular septal defect, AVSD – atrioventricular septal defect, F4/DORV + PS – tetralogy of Fallot/double-outlet right ventricle with pulmonary stenosis. Mann-Whitney test,
Discussion
Detection of AKI may be delayed in the first 24–48 h, depending on the serum creatinine levels and urine output. Early identification, diagnosis, and renal support strategies are key to improving patient outcomes. Thus, the need for more reliable, earlier indicators and predictors of AKI emerged. The most common studied biomarkers are neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), interleukin-18 (IL-18), cystatin-C, kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), L type fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP), N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase N (NAG), calprotectin, monocyte chemotactic peptide-1 (MCP-1), vanin-1, and YKL-40. Still, none of them have been truly specific for AKI [7–10].
Urinary NTN-1 may be a new marker to demonstrate early kidney damage. The molecular mass of 72 kDa is too high to be filtered by the glomerulus under normal conditions. These considerations suggest that an early increase in urine NTN-1 in humans with AKI directly indicates kidney tubule injury [15, 16, 19–21].
Ramesh et al. were the first to show that the presence of NTN-1 in urine is an early marker of AKI in humans. In their study group, among 60 patients, AKI occurred in 43%, of whom 8 required RRT and 4 patients died [19]. In our study, AKI was diagnosed in only 12% of patients (5); none required dialysis and all survived. Pediatric patients after CPB who developed AKI showed a significant increase in urinary NTN-1 levels 2 h after starting CPB, which was before the creatinine level increased at 48 h [19]. Similar results were reported by Aly et al. in adult patients after cardiac surgery, in which urinary NTN-1 levels increased 6 h after CPB in patients with AKI, which preceded the increase in creatinine by at least 18 h [20]. In our study group, NTN-1 was detectable after surgery in only 11 (27.5%) patients 6 h after CPB and 13 (32.5%) patients 24 h after CPB compared to 22 (55%) patients before surgery. However, there was no correlation between NTN-1 levels before surgery and decreased GFR 48 h after surgery, and it did not correlate with AKI.
The occurrence of AKI in patients after cardiac surgery correlated with CPB time and aortic clamping time [6, 22]. In our patients with AKI, the median CPB time was 147 min, which was shorter than in Ramesh’s pediatric patients with AKI (188.4 min), but CPB time in patients without AKI was comparable to Ramesh’s group (97 min vs. 91.4 min). In adult patients with AKI, CPB time was shorter (60.6 min) than in pediatric groups, and it was non-significantly longer than in patients who did not develop AKI (44.3 min) [20]. CPB time was longer in patients with AKI in Ramesh’s group compared to ours, which may correlate with the number of episodes of AKI and the severity of AKI.
The initial NTN-1/creatinine ratio may predict the occurrence of AKI unrelated to cardiac surgery but related to the presence and type of congenital heart defect. In the study group, netrin was detectable in 55% of patients (22/40) before cardiac surgery; in the control group, we detected netrin in 20% of children (4/20). Furthermore, we found a negative correlation of initial NTN-1/creatinine ratio with ΔeGFR (r = –0.36, p = 0.031). Among the patients with AKI, three had a complex congenital heart defect (tetralogy of Fallot (ToF)/double outlet right ventricle (DORV) with pulmonary stenosis (PS), and probably they had a reduced number of active nephrons before surgery, but the GFR was in the normal range. This may be related to decreased renal functional reserve [2], but this needs further investigation. These patients required more extended cardiac surgery (and consequently longer CPB time and aortic clamping time), which may have been the reason for the development of AKI. However, in our study group, no correlation was confirmed between the initial NTN-1/creatinine ratio and the type of cardiac defect.
None of the patients in our study group required renal replacement therapy, which limits the objective assessment of the usefulness of NTN-1 determination as a predictor of AKI occurrence.
Our study’s limitation is its relatively small sample size and the use of a low-sensitivity NTN-1 detection kit.
All patients in our group were treated immediately after surgery with loop diuretics and adequate hydration to prevent the development of AKI, which could be the reason for low urinary NTN-1 concentration after cardiac surgery.
In conclusion, based on our study, the usefulness of determining urinary NTN-1 levels in pediatric patients after cardiac surgery as an early marker of acute kidney injury was not confirmed. No factors affecting the NTN-1/creatinine ratio were found in the study group. Patients who have longer CPB time and aortic clamping time belong to the high-risk group of AKI after surgery.