Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the sixth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer-related death in humans worldwide. HCC also accounts for 90% of all malignant liver tumors and usually has an insidious onset in patients with pre-existing cirrhosis (80%). While patients with cirrhosis are often invited to HCC screening programs, many with less advanced liver disease are not even aware of the problem, and thus of the risk of HCC. Hence, the number of deaths due to HCC in many countries around the world, including Poland, still exceeds the number of intravital diagnoses of HCC. Late diagnosis of this cancer is a continuing issue, which often prevents effective treatment or even remission of cancer [1].
For many years, a search has been underway for new specific and sensitive HCC markers. Currently, there are none that detect the cancer at its early stages. The basic marker used in the diagnosis is α-fetoprotein (AFP) level, which is a sensitive indicator of cancer progression and recurrence, but not a very sensitive marker of early forms of HCC. The more sensitive AFP-L3 glycoform is not routinely used in the diagnosis of HCC in most countries. The level of des-γ-carboxy-prothrombin (DCP) in the serum is also being investigated more and more widely [2]. By combining the use of AFP and DCP, and taking into account patients’ age and sex, multifactorial algorithms are created that are useful in surveillance programs for the detection of early forms of HCC [3, 4].
The significance of adipokines in the pathogenesis and diagnosis of liver cancer has been researched for several years now [5, 6]. So far, the adipokines assessed in this respect are betatrophin, irisin, vaspin and a number of others [7, 8]. In recent years, reports have been published suggesting that chemerin – also produced in the liver – could be useful in the diagnosis of not only chronic liver disease, but also of primary liver cancer. Chemerin – or retinoic acid receptor responder 2 (RARRES2) – is a 14 kDa chemotactic protein found in adipose tissue and liver. Its inactive form is produced from tazarotene inducible gene 2 (TIG2). After cleavage of the C-terminus by serine proteases, the protein becomes active. Chemerin plays a significant role in the innate immunity processes, inflammatory processes, endothelial and metabolic disorders and angiogenesis. The relationship between chemerin and fatty liver disease (MAFLD) in various stages [9] has already been studied, as well as the relationship between chemerin and hepatitis C, which is the main cause of cirrhosis and HCC [10, 11]. It has also been shown that chemerin is associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome [12]. Another confirmed fact is that the amount of tissue in advanced liver diseases is associated with a decrease in serum chemerin level [13]. Low expression of chemerin in HCC patients was an independent factor of poor prognosis [14]. A negative correlation was found between chemerin level and the severity of cirrhosis assessed with the Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) score, ALT activity and bilirubin level, but the study was prospective. Studies in mice have shown that chemerin increases insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by adipose tissue cells [15].
Fasting insulin level is one of the parameters that help assess insulin resistance [16]. Some studies suggest that insulin resistance increases with cirrhosis, which is a risk factor for the progression of fibrosis and the development of HCC. Since chemerin is also produced in adipose tissue, the amount of which changes in cirrhosis and neoplasia, we also assessed serum insulin [17–19].
The study was approved by the Bioethics Committee at DIL (Lower Silesian Chamber of Physicians) in Wrocław (4/NT/2012). Patients were informed about the study in detail and signed informed consent to participate. The study was carried out in accordance with the principles of good medical practice, following the Declaration of Helsinki 2012–2020. Project participants agreed to be included in the study.
The aim of the paper was to determine whether the assessment of chemerin level may facilitate early diagnosis of primary liver cancer.
Material and methods
The study cohort comprised patients supervised and treated for chronic liver disease of various etiologies at Department I of Jerzy Gromkowski Regional Specialist Hospital and at the Department of Infectious Diseases and Hepatology of Wrocław Medical University.
The cohort comprised 76 people with cirrhosis: 45 with hepatocellular carcinoma and 21 without cancer. Thirteen patients had a single lesion HCC (12 men, 1 woman) and 32 had metastatic lesions (21 men and 11 women). The control group consisted of 10 healthy people.
Patient data were analyzed for age, sex, body mass index (BMI), etiology of liver cirrhosis and cancer, liver cirrhosis stage in terms of the CTP and MELD scores, the results of peripheral blood counts, selected biochemical tests: activity of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), γ-glutamyl transferase (GGTP), level of total cholesterol, triglycerides, glucose, urea, creatinine, α-fetoprotein (AFP) carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), cancer antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), chemerin and insulin measured in blood samples (standard separated serum for biochemical parameters) collected in the morning from fasting patients. Chemerin and insulin levels were determined by ELISA tests (Human Chemerin ELISA Kit; Aviscera Bioscience, Santa Clara, USA, and Mercodia Ultrasensitive Insulin ELISA; Mercodia AB, Uppsala, Sweden; respectively) according to the instructions provided by the manufacturer. The results were measured in the program SkanIt RE (for Multiscan GO) based on the 4PL standard.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis for the obtained results was performed in Statistica PL software, version 13.3 with the Medical Kit extension. Normality of values of the examined parameters was determined using the Shapiro-Wilk test and normal probability plots. Quantitative variables were expressed as arithmetic mean, standard deviation, median and range. When comparing the results of the study group (patients with cirrhosis and HCC) and control group, or patients with primary liver tumor and disseminated liver tumor, the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test was used for two independent samples. The non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA test for multiple independent samples was used to compare the results of patients with cirrhosis, primary or metastatic tumor. Differences for which the p-value was ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant. The estimated sample size was calculated based on preliminary studies (n = 24; unpublished). It was evaluated how the chemerin level [ng/ml] differs among the study groups. Means and standard deviations of chemerin levels were utilized in the analysis to estimate the sample size. The estimated sample size for ANOVA (fixed effects, one-way) was employed. The α level was set at 0.05, and the test power was set at 0.8, with an effect size of f = 0.04; there were 3 groups (Liver cirrhosis; HCC tumor in the liver; Control group). Based on these parameters, the estimated sample size was determined to be 76 for all study participants (assuming a 15% attrition rate due to incomplete data).
Results
The studied group comprised 26 women and 50 men. The mean age in the entire group was 60.8 years. For patients with isolated cirrhosis it was 58.5 years, for patients with primary HCC it was 63, and for those with disseminated HCC it was 58.5 years; in the control group it was 44.3 years.
In the studied group, liver disease class assessed using the CTP score was as follows: class A – 34, class B – 28 and class C – 4, while the MELD score was ≤ 12 points for 45 people and > 12 points for 21 people. The etiology of liver disease in the whole study group was diverse and is presented in Table I.
Table I
Baseline characteristics of study cohort and control group
| Parameter | Liver cirrhosis (n = 21) | Single HCC tumor in the liver (n = 13) | Disseminated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (n = 32) | Control group (n = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age | 58.5 (46–77) | 63 (42–75) | 58.5 (46–77) | 44.3 (21–67) |
| Sex (F/M) | 22/44 | 4/6 | ||
| BMI | 25.12 | 28.36 ±5.26 | 24.84 ±4.43 | |
| ALT [IU/l] | 53.14 ±42.68 | 66.93 ±44.40 | 68.36 ±59.67 | 25.1 ±10.64 |
| AST [IU/l] | 76 ±42.04 | 79.07 ±47.86 | 94.54 ±84.02 | – |
| GGTP [IU/l] | 114 ±122.09 | 163.87 ±129.67 | 420.26 ±1030.84 | 25.6 ±7.15 |
| FA [IU/l] | 116.52 ±44.56 | 122.27 ±68.81 | 201.44 ±241.93 | – |
| Glucose [mg/dl] | 127.67 ±47.03 | 107.99 ±26.65 | 130.78 ±60.22 | – |
| Total cholesterol [mg/dl] | 130.26 ±19.12 | 162.27 ±54.7 | 159.72 ±38.84* | – |
| Triglycerides [mg/dl] | 82.2 ±29.92 | 79.05 ±25.96 | 107.34 ±41.00 | – |
| WBC [109/l] | 4.38 ±2.67 | 5.34 ±2.94 | 5.77 ±3.73 | – |
| HGB [g/dl] | 11.54 ±1.91 | 13.28 ±1.76 | 12.63 ±2.20 | – |
| PLT [109/l] | 82.95 ±68.19 | 94.43 ±36.99 | 110.11 ±64.15 | – |
| Creatinine [mg/dl] | 0.89 ±0.4 | 0.76 ±0.26 | 0.78 ±0.16 | – |
| AFP [ng/dl] | 18.76 ±45.84 | 27.36 ±32.77 | 3270.75 ±15056.40** | – |
| Etiology of liver disease | HBV 7, HCV 20, HBV/ALD 5, HCV/ALD 7, ALD 12, HBV/HCV 6, NASH/MASH 5, PBC 1, secondary cardiogenic 1, glycogenosis 1, hemochromatosis 1 | 0 | ||
Selected clinical and laboratory demographic parameters were also assessed depending on the progression of liver disease, regardless of the presence or absence of HCC (Table I).
Patients with isolated cirrhosis (21 people) – Group I
The mean age of study participants in this group was 58.50 years (46–77 years), BMI 25.12 kg/m2 (9 women, 12 men). The chemerin level was 53.33 ng/ml, insulin – 10.16 μg/ml, AFP – 18 ng/ml, creatinine – 0.88 mg/dl, glucose – 127.67 mg/dl. Chemerin and insulin results differentiated the control group from study participants – the latter showed lower chemerin and higher insulin levels than the control group – with the following p-values: chemerin p = 0.008, insulin p = 0.01.
Patients with a single HCC lesion (13 people) – Group II
The mean age of study participants in this group was 63 years (42–75), BMI – 28.36 kg/m2. The chemerin level was 65.18 ng/ml, insulin 0.7 μg/ml, AFP 27.36 mg/dl, glucose 107.99 mg/dl. Chemerin and insulin results differentiated the control group from the study participants – the latter showed lower chemerin and higher insulin levels than the control group.
Patients with disseminated HCC (32 people) – Group III
The mean age of these patients was 58.6 years, BMI 24.87 kg/m2, sex – 21 men, 11 women. The chemerin level was 83.58 ng/dl, insulin 0.57 mg/dl, AFP 428 mg/dl, glucose 130 mg/dl. Neither chemerin nor insulin levels differentiated patients with a single HCC lesion from patients with disseminated HCC; however, chemerin levels in this group were higher than in the group with cirrhosis and primary HCC lesion (Figure 1).
Control group patients (10 people)
The mean age of these patients was 44.3 years. Liver function tests: ALT 25.1 U/l, GGTP 25.6 U/l. The creatinine level was 0.87 mg/dl, chemerin 80.14 mg/dl, insulin 0.27 mg/ml.
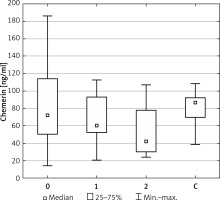
Distribution of patients (groups I, II and III together) according to Child-Pugh Score
The groups differed in numbers: Child-Pugh class A – 34, Child-Pugh class B – 28, and Child-Pugh class C – only 4 patients. The patients in Child-Pugh class A were, on average, 60 years old, BMI 25.8 kg/m2. The chemerin level was 83.9 μg/ml insulin 3.52 μg/ml, AFP 263 mg/dl, glucose 123 mg/dl. The mean age of patients in Child-Pugh class B was 61 years, BMI 26.4 kg/m2. The chemerin level was 61 μg/ml, insulin 4.34 μg/ml, AFP 126.68 mg/dl, glucose 124 mg/dl. The mean age of patients in Child-Pugh class C was 54 years, BMI 31 kg/m2. The chemerin level was 30.1 μg/ml, insulin 1.00 ug/ml, AFP 23 mg/dl, glucose 149 mg/dl.
Chemerin level values differentiated class A patients from class B patients (p = 0.04), whereas chemerin level values in class A as compared to class B and C was significantly different p = 0.007.
Distribution of patients (groups I, II and III together) according to MELD score
Two groups were distinguished: group 1 with MELD score ≤ 12 points and group 2 with MELD score > 12 points. The mean age of patients in group 1 was 60 years, BMI 24.9 kg/m2. The chemerin level was 75 μg/ml, insulin 5.10 ng/dl, glucose 125.60 mg/dl.
Patients in group 2, with MELD score > 12 points, were on average 62 years old, BMI 26.80 kg/m2. The chemerin level was 58.66 ng/dl, insulin 0.77 μg/ml, glucose 121.50 mg/dl.
The level of chemerin in the group with more advanced cirrhosis was lower than in the group with less advanced cirrhosis, but the difference was not statistically significant. The situation was similar for insulin levels.
Distribution of HCC patients (groups I and II) according to the BCLC staging system
Patients from the HCC group with primary (n = 13) and metastatic (n = 32) tumors were divided into A, B, C, according to their BCLC results. Chemerin levels were compared between the three groups, and differences were observed between patients in stage A and B, i.e. between patients who have the possibility to undergo radical surgery and patients who do not. The comparison revealed a significant difference of p = 0.02.
Dividing the study cohort into patients with cirrhosis that developed as a result of viral infections and others did not reveal any differences among the participants of our study.
The patients were divided into two subgroups, according to their HOMA-IR result: HOMA-IR ≤ 2 and HOMA-IR > 2.
The first subgroup included 25 patients, and the second subgroup included 33 patients. The correlation between the HOMA-IR index and chemerin level was compared, revealing a negative correlation of r = –0.44 (p < 0.01) (Table II).
Table II
Chemerin and insulin levels and HOMA-IR results in the study cohort
| Parameter | Liver cirrhosis (n = 21) | HCC tumor in the liver (n = 45) | Single HCC tumor in the liver (n = 13) | Disseminated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (n = 32) | Control group (n = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemerin [ng/ml] | 53.33 ±5.93** | 74.38 ±30.8* | 65.18 ±25.71 | 83.58 ±45.90 | 82.14 ±21.53 |
| Insulin [μg/ml] | 10.16 ±30.21** | 0.635 ±0.42 | 0.7 ±0.59 | 0.57 ±0.64 | 0.27 ±0.2 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.77 | 4.23 | 3.9 | 4.56 | – |
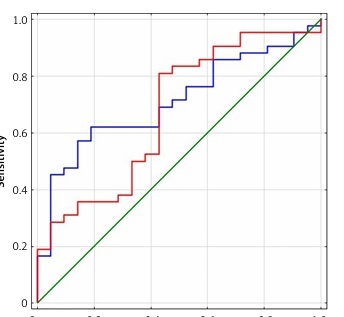
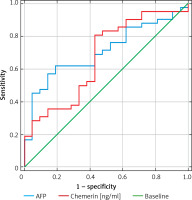
In patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, measuring chemerin level was as successful as measuring AFP level. (Figure 2). In patients with HCC, the results of measuring serum chemerin level were more sensitive and showed more accuracy than AFP level (Figure 2).
Discussion
Our observations showed that chemerin level was lower in patients with cirrhosis as compared to the control group, and that it decreased with the increase of cirrhosis severity, calculated using the CTP score. However, in patients with primary liver cancer, chemerin level was higher and increased in patients with progressing HCC, as compared to patients with cirrhosis not complicated by liver cancer. It reached maximum values, similar to control results, in patients with disseminated cancer. Following the BCLC staging system, class A patients differed significantly from class B patients (p = 0.02). This suggests a potential pathogenetic link between HCC and chemerin.
Chemerin is a significant factor in angiogenetic processes, and, theoretically, its levels in patients with disseminated HCC in cirrhotic liver should be higher with the presence of multiple lesions or dissemination of cancer. Lin et al. reported that chemerin plays a protective role in the development of HCC by inhibiting the expression of IL-6 and GM-CSF, but probably only in the early stages [20]. On the other hand, neoplastic dissemination results in a decrease in the active mass of liver parenchyma, which would explain the lower levels of chemerin in patients with advanced cancer – although these values are still higher than in patients with isolated cirrhosis.
In the study cohort, serum chemerin levels differed between healthy and cirrhotic patients. At the same time, the assessment of blood serum chemerin level allowed patients with cirrhosis to be differentiated from patients with cirrhosis complicated by the development of HCC, regardless of its stage. This observation is groundbreaking and without analogies in the currently available literature.
It should be noted, however, that the level of chemerin depends on many factors, such as age [21], presence of inflammation [6, 9, 22], platelet count [23], coexistence of metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes [22], obesity [6, 9, 22] and fatty liver disease [6], and is not a specific marker for HCC. Therefore, despite the statistically significant differences in chemerin levels obtained in our study between the group of patients with and without HCC (p = 0.026), chemerin can only be treated as an auxiliary marker and interpreted together with the results of imaging tests (which, despite certain limitations, are the basis for the diagnosis of HCC) and other markers of carcinogenesis.
Another interesting observation made in this study is that the entire cohort with cirrhosis and/or HCC had a higher sensitivity of chemerin levels in relation to AFP: 81% vs. 61%, although the specificity was lower: 57.1% vs. 81%. Therefore AFP showed better accuracy. This result suggests again that analyzing a combination of several factors can lead to a rapid diagnosis of HCC [4].
In this study, we looked at patients with cirrhosis of various etiologies accompanied by liver cancer. We compared their results against the results of control patients, without any liver disease. As presented above, we revealed that chemerin levels differed significantly (p = 0.008) between these groups. However, without including the results of cirrhosis scoring or staging models, chemerin level was lower in patients with cirrhosis than in patients with HCC. When we calculated the CTP score for study participants (and, consequently, divided the patients into two CTP groups: CTP A and CTP B with C), it turned out that chemerin level differed significantly (p = 0.007). Also, when the MELD staging system was applied, it was clear that serum chemerin levels were lower in patients with more advanced cirrhosis than in those with less advanced disease. These results suggest that the liver is one of the organs significantly involved in the production of chemerin, which is consistent with our observations. Kraurbauer et al. reached a similar conclusion [24].
Since insulin influences the functioning of adipose tissue, glucose metabolism, and hence possibly also the formation of chemerin, we assessed insulin level in three groups: patients with cirrhosis, patients with cirrhosis and HCC, and healthy people. Insulin levels were higher in people with HCC compared to the control group composed of healthy people, yet the difference was not statistically significant. However, the group with HOMA-IR ≤ 2 showed an inverse correlation with chemerin. Gupta et al. reported that the insulin level in HCC patients was statistically significantly higher than in healthy patients [25]. A similar observation was reported by Chao et al. [26]. The above observations seem to confirm the experimental models showing that insulin stimulates the proliferation of neoplastic cells [23]. Perhaps our study failed to show statistical significance in this matter because the cohort was too small.
We also observed that patients with HCC had a higher serum insulin level compared to patients with cirrhosis but no HCC, yet the difference was not statistically significant. Radwan et al. found in their study that the insulin level was statistically significantly higher in patients with HCC compared to patients with chronic liver disease without HCC [22]. Imai et al. detected a positive correlation between platelet count and a negative correlation of bilirubin level with serum chemerin levels [21]. On the other hand, neither the results of biochemical tests (ALT, AST, GGTP, glucose, cholesterol, creatinine) nor the CBC results distinguished between patients with cirrhosis and patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma, both with a single lesion and with disseminated cancer, with the exception of serum AFP level, which increased with the progression of cancer. We also did not observe any correlation between the analyzed parameters and patients with a single HCC lesion and patients with disseminated HCC.
The etiology of cirrhosis, with or without HCC, varied across our patients. Although the most common etiological factor of cirrhosis and, consequently, HCC was HCV infection, there were also many cases of toxic (ethyl alcohol) or mixed-toxic etiology. We did not observe significant differences between patients with liver disease of viral and other etiologies. In a study by Kukla et al., patients with HCV infection with more advanced fibrosis, depending on the degree, tended to have lower levels of chemerin [27]. However, in the group of patients with both cirrhosis and HCC, similar serum chemerin levels were observed in patients with HCV infection and in patients with liver cancer of other etiologies.
The assessment of serum chemerin levels seems to be helpful in the diagnosis of HCC, but a limitation of this study was the relatively small cohort. Therefore, we intend to continue the study of chemerin levels in HCC patients.
In conclusion, the assessment of serum chemerin levels appears to be useful in the diagnostic and prognostic processes focused on assessing the progression of HCC, complicated by cirrhosis of various etiologies. The assessment of insulin level has proven helpful in differentiating the early stage of hepatocellular carcinoma.