Introduction
Endothelial dysfunction is an early feature of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease [1, 2]. The protection of endothelial function can prevent the development of cardiovascular disease [3, 4]. Endothelial dysfunction leads to several pathological conditions such as impairment of the anti-inflammatory properties of the endothelium, impaired modulation of vascular growth, and dysregulation of vascular remodeling [5]. Early studies have demonstrated that endothelial dysfunction is caused by decreases in nitric oxide (NO) bioactivity in the vessel wall [6]. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) catalyzes the generation of NO in endothelial cells. It is a paracrine factor that controls vascular tone [7]. Increases in reactive oxygen species (ROS) production can reduce the bioavailability of NO from endothelial cells, leading to endothelial dysfunction and the initiation and development of cardiac disease [8, 9].
The nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase (NADPH oxidase) system is the main cellular source of ROS in endothelial cells [10]. Reactive oxygen species play fundamental roles in various signaling pathways under normal physiological conditions [11]. They are produced by various oxidase enzymes, including NADPH oxidase and uncoupled eNOS [12]. The antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase (SOD) rapidly dismutates the superoxide anion O2– to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Intracellular concentrations of ROS are regulated by several signaling pathways through interaction with the intracellular antioxidant system. Impairment of this antioxidant system leads to sustainable ROS exposure in cells. These intracellular ROS include superoxide and H2O2. H2O2 has high chemical stability at steady state concentration [13]. Many cell types produce H2O2 in response to growth factors and insulin, which promote cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration [14]. It has been suggested that H2O2 promotes the functions of various proteins such as protein phosphatases, protein kinases and transcription factors [15]. Stimulation with H2O2 initiates downstream signaling events, such as mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) and activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. Interestingly, AKT regulates downstream substrates that mediate apoptosis and plays a crucial role in the regulation of cellular metabolism and cellular growth. The activation of AKT leads to enhanced cardiac protection during oxidative stress, endothelial cell injury and cardiac hypertrophy [16]. mTOR, the downstream effector of AKT, has two complexes: raptor-mTOR (TORC1) and rictor-mTOR (TORC2) proteins, which control cell growth and proliferation. Previous studies showed that chronic activation of mTOR led to vascular dysfunction, while its inhibition has been shown to alleviate cardiovascular disorders [14, 17].
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is involved in the regulation of blood pressure, inflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of insulin resistance [18]. RAS inhibitors play important roles in prevention of diabetes and vascular diseases. There are two types of the inhibitors: angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), which exert various effects on morbidity in hypertensive patients [19]. Captopril was the first identified ACE inhibitor with an antioxidative effect in the treatment of hypertension and heart failure. Recently, it was shown that concomitant administration of captopril can significantly attenuate methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties [20]. However, the role of captopril in oxidative stress-induced endothelial cell dysfunction and H2O2-induced Akt activation remains unclear.
In the present study, a model of oxidative stress was used to investigate the effect of captopril on oxidative stress and cell apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial cells, and the likely underlying mechanism.
Material amd methods
Cell culture
Human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs) were purchased from Cascade Biologics (Portland, OR, USA). The cells were maintained in microvascular endothelium growth medium with endothelial cell growth supplement and 15% fetal bovine serum at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 and 95% air. Cells (between passages 3 and 6) were grown to 80-90% confluence, then subjected to serum starvation (0.4% FBS) for 24 h and treated with H2O2 (500 μM) [21], captopril (10–6 M) [22], AKT inhibitor MK-2206 (250 mmol/l, Cayman Chemical) [23] and the AKT activator SC79 (200 nM, Sigma) [24]. Four groups of cells were used. The HCAECs were pre-treated with captopril alone, or combined with AKT inhibitor or activator, and then exposed to H2O2 for 48 h. Non-treated HCAECs served as a control group.
Western blot analysis
Proteins were extracted by placing the HCAECs from each experiment (30 μg per lane) in lysis buffer, and separated by 10% or 6% SDS-PAGE. The separated proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. After incubation in blocking solution (4% nonfat milk, Sigma), the membranes were probed overnight with 1 : 2000 dilution primary antibody (monoclonal antibody to p53 (Abcam, USA), ICAM-1 (Abcam, USA), p-Akt (Cell Signaling Technology, USA), p-eNOS (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, USA), p-mTOR (Cell Signaling Technology, USA) and β-actin (Abcam, USA)). The membranes were washed and then incubated with 1 : 5000 dilution of second antibody for 1 h, and the bands were detected with an enhanced chemiluminescence system. Data were normalized to the β-actin content of the same sample.
Cell viability and apoptosis assays
Cell viability was assessed by MTT assay, and apoptosis was measured by annexin V staining. The cells were pre-incubated for 24 h with captopril (10–6 M) and then divided into three or four groups which were treated with H2O2 (500 μM) or H2O2 (500 μM) + AKT inhibitor MK-2206 (250 mmol/l, Cayman Chemical) or H2O2 (500 μM) + AKT activator SC79 (200 nM, Sigma), or with captopril (10–6 M) alone. For the MTT assay, HCAECs were washed with phosphate-buffered saline and then incubated in a fresh medium containing 1 g/l MTT (MTT Cell Proliferation Assay Kit, BioVision, Inc.) for 4 h at 37°C. After removal of unconverted MTT, absorbance values were measured at 490 nm in an ELISA reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Multiskan). The apoptosis assay was conducted as described previously [25]. Cells were treated with H2O2 (500 μM), captopril (10–6 M), AKT inhibitor MK-2206 (250 mmol/l) and the AKT activator SC79 (200 nM). The cells were harvested and centrifuged at 500×g for 5 min at 4°C and the supernatant was aspirated. The harvested cells were washed with 1 ml of PBS and re-suspended in 100 μl of staining buffer (Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit, Sigma Chemical Co, St Louis, MO, USA) by mixing 2 μl of Annexin-V and PI. The cells were analyzed with a FlowSight imaging flow cytometer (Amnis, part of EMD Millipore). The 488 nm laser was used for excitation. Annexin V positive cells, irrespective of whether they were PI positive or negative, were considered to be apoptotic in nature, either at the early or late stage of apoptosis.
Measurement of nitrite/nitrate
Oxidation products of NO (nitrite and nitrate) were assayed as a measure of total NO [26]. The level of NO in the medium of HCAECs was measured using a commercially available nitrite/nitrate assay kit (Nitrate/Nitrite Colorimetric Assay Kit, Cayman Chemicals) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Absorbance values were measured in 550 nm in an ultraviolet spectrophotometer.
Measurement of ROS generation
Dichlorofluorescein dye (non-fluorescent CM-H2DCFDA) has the ability to diffuse through the cell membrane [27]. The fluorescence intensity is proportional to the ROS content. The levels of ROS in the HCAECs were determined by flow cytometry, using CM-H2DCFDA dye, after incubation with captopril, H2O2, AKT inhibitor and AKT activator. The cells were trypsinized, washed and re-suspended in 2 ml of HBSS after treatment for 48 h. They were then incubated with 5 μM CM-H2DCFDA (prepared in DMSO) for 30 min at 37°C and 5% CO2. The fluorescence of DCFDA was then measured using a BD FACSCanto Flow cytometer (California, USA). At least 10,000 events were acquired in the gated regions at an emission wavelength of 520 nm.
Proliferation, invasion and migration assays
BrdU incorporation
The HCAECs in the different treatments were incubated with 20 mM BrdU (BrdU test kit, Boehringer Mannheim Biochemical) for 2 h and subsequently fixed and treated with 70% formamide for 2 h. BrdU was measured by immunocytochemistry.
Wound healing assay
Fully confluent HCAECs were cultured in 12-well plates. The cells were wounded with a 100 μl tip and treated with 0.5 mM H2O2, captopril (10–6 M), AKT inhibitor or AKT activator for 48 h. The wound healing assay was conducted in a CO2 incubator. Each scratch was randomly photographed at four separate sites using time-lapse video microscopy (Zeiss Axiovert 135M) with a gas lamina flow attachment at 0 h and 48 h. The migration rate of HCAECs was determined by the ratio of the wound area at 48 h to the initial wound area by using Image Pro Plus 6.0 software.
Transwell assay
The HCAECs (1 × 106 cells/ml) were plated on 12-well Transwell inserts. The volume of medium was 2 ml/well and the volume of each transwell insert was 1 ml. The upper chamber (8-μm pores coated with 0.1% gelatin) containing HCAECs from different treatments was transferred to the bottom chamber containing EBM with 0.2% FBS and stimulants. After 5 h of incubation, the non-migrating cells were wiped from the upper side of the membrane. The membrane was fixed and stained using cold methanol. The cell nuclei were stained with 10% Giemsa and counted under the microscope. The invasion ability was determined by counting the stained cells on the bottom surface.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± SEM of independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t test for comparison between two groups. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett multiple comparison. Differences were considered significant at p < 0.05.
Results
Effect of RAS inhibitor on H2O2-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis and p-AKT/mTOR activation in HCAECs
Previous studies showed that endothelial cells exposed to H2O2 exhibited increased intracellular O2– over basal levels via NOS and NAPDH oxidase pathways [28]. Endothelial cell cytotoxicity and apoptosis were increased with H2O2 exposure [29]. The results shown in Figures 1 A and D indicated that H2O2 induced cell apoptosis and up-regulated the protein expression of p53 and ICAM-1. It also significantly increased the NO level in HCAECs (p < 0.05; Figure 1 B). The H2O2-induced NO expression and cell apoptosis were significantly reversed by captopril (p < 0.05; Figure 1 C). Cell viability was significantly enhanced by captopril treatment, when compared with the H2O2 treatment group.
Figure 1
Effect of RAS inhibitor on HCAECs with H2O2 treatment. A – Protective effect of RAS inhibitor on cell apoptosis in HCAECs induced by H2O2. B – Preventive effects of captopril on cell viability against H2O2-induced injury determined by MTT assay. *p < 0.05 compared with the control group. C – Effect of RAS inhibitor on H2O2-induced inducible nitric oxide (NO) synthase expression. D – Effect of RAS inhibitor on H2O2-induced expression of p53, ICAM-1, p-eNOS, p-AKT and p-mTOR. E – Inhibitory effect of RAS inhibitor on production of intracellular ROS
The data are mean values from 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.05, relative to the control group.
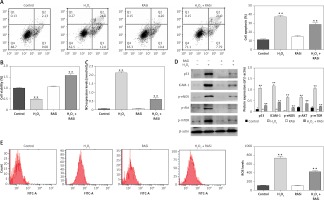
Decreases in eNOS dimer/monomer ratio are indicative of uncoupling of eNOS [30]. Compared with the control group, H2O2 treatment enhanced eNOS protein expression levels. However, co-treatment with captopril inhibited the H2O2-induced in eNOS protein expression in HCAECs (p < 0.05; Figure 1 D).
Intracellular ROS production was assessed by flow cytometry after H2O2 treatment. Cells co-treated with H2O2 and captopril showed significant repressed in fluorescence intensity, when compared with cells treated with H2O2 alone (p < 0.05; Figure 1 E). There were significant repressed in ROS levels between captopril-treated cells and cells in the control group. These results indicate that captopril has the ability to scavenge ROS, thereby protecting the HCAECs from H2O2-induced oxidative stress.
Previous studies showed that the AKT/mTOR pathway is critical for cellular protection against apoptosis [31]. Although the main role of the AKT/mTOR pathway is regulation of cell growth and survival, AKT activation may also impair cellular function [32]. To assess the effect of captopril on H2O2-induced p-AKT and mTOR activation, the HCAECs were exposed to 0.5 mM H2O2 and 10–6 M captopril for 48 h, and cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting. As shown in Figure 1 D, H2O2 exposure significantly enhanced the protein level of p-AKT and mTOR (p < 0.05), while captopril reduced the H2O2-induced AKT and mTOR phosphorylation. These findings show that captopril blocked the phosphorylation of AKT and mTOR induced by H2O2.
RAS inhibitor is critical for mitigation of H2O2-induced oxidative damage via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
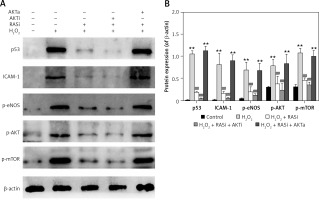
Co-treatment with captopril and the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 significantly protected HCAECs from H2O2-induced apoptosis (Figure 2). Cell viability significantly raised after co-exposure to captopril and MK-2206, when compared with the captopril + SC79 group. Furthermore, protein expression levels of P53, ICAM-1 and eNOS were significantly decreased in HCAECs exposed to H2O2 and captopril + MK-2206 (p < 0.05; Figure 3). In contrast, P53 and ICAM-1 expression levels were significantly upregulated in the group treated with H2O2 + captopril + SC79, relative to the H2O2 group (p < 0.05).
Figure 2
RAS inhibitor attenuated H2O2-induced viability losses and apoptosis in HCAECs via the AKT/mTOR pathway. HCAECs were pre-treated with captopril or combined with AKT inhibitor or activator, then exposed to H2O2 for 48 h. A – Inhibition of apoptosis in HCAECs co-treated with captopril and AKT inhibitor and then exposure to H2O2. B – Preventive effects of captopril and AKT inhibitor on cell viability induced by H2O2, determined by MTT assay
*p < 0.05, when compared with the control group; #p < 0.05, when compared with the H2O2 alone group.
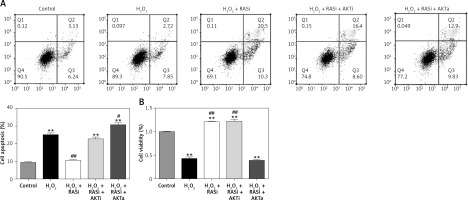
Figure 3
RAS inhibitor attenuated the H2O2-induced increases in expressions of p53, ICAM-1, p-eNOS, p-AKT and p-mTOR via AKT/mTOR pathway. A – HCAECs were pre-treated with captopril or combined with AKT inhibitor or activator, then exposed to H2O2 for 48 h. Cell lysate was analyzed for p53, ICAM-1, p-eNOS, p-Akt and p-mTOR protein levels by immunoblotting. B – Shows a column bar graph analysis
*p < 0.05, when compared with the control group; #p < 0.05, when compared with the H2O2 alone group.
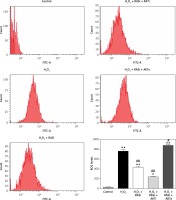
Treatment of HCAECs with captopril + MK-2206 inhibited H2O2-induced ROS generation and NO expression (p < 0.05; Figure 4). In contrast, ROS generation and NO expression were significantly increased in HCAECs treated with captopril + SC79 (Figure 5).
Figure 4
Involvement of the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in RAS inhibitor-mediated protection against H2O2-induced inducible nitric oxide (NO) synthase expression. HCAECs were pre-treated with captopril or combined with AKT inhibitor or activator, then exposed to H2O2 for 48 h. This effect of captopril on H2O2-induced NO expression was reversed by AKT activator but not by AKT inhibitor
*p < 0.05, when compared with the control group;
#p < 0.05, when compared with the H2O2 alone group.
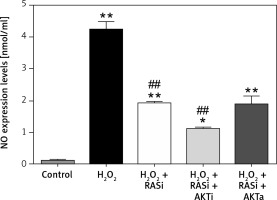
Figure 5
Involvement of the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in inhibitory effect of RAS inhibitor on production of intracellular ROS. The intracellular ROS accumulation was determined by measuring the DCF-derived fluorescence after incubation of cells with DCFH-DA for 30 min. The data are mean values from 3 independent experiments
*p < 0.05, when compared with the control group; #p < 0.05, when compared with the H2O2 alone group.
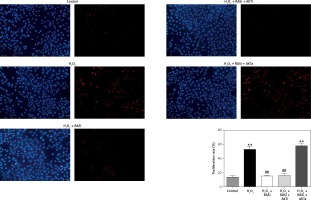
Renin-angiotensin system inhibitor blocked H2O2-induced cell proliferation via the AKT/mTOR pathway
Cell proliferation can be modulated by changes in intracellular ROS levels [33]. Growth signals and stress responses are known to be largely mediated by the AKT pathway [34]. As shown in Figure 6, captopril and captopril + MK-2206 significantly repressed BrdU labeling when compared with treatment with H2O2 alone, but in the captopril + SC79 group, the H2O2-induced cell proliferation was increased (p < 0.05). This finding indicates that captopril inhibited the H2O2-induced cell proliferation via the AKT/mTOR pathway.
Figure 6
Inhibitory effect of RAS inhibitor against H2O2-induced cell proliferation through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. HCAECs were pre-treated with captopril or combined with AKT inhibitor or activator, then exposed to H2O2 for 48 h. Representative images and quantitative analysis illustrate that BrdU expression was significantly increased in the H2O2 alone and captopril + AKT activator group. Captopril + AKT inhibitor reversed the effect of H2O2-induced cell proliferation
*p < 0.05, when compared with the control group; #p < 0.05, when compared with the H2O2 alone group.
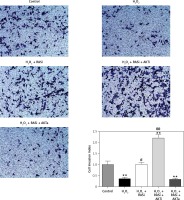
RAS inhibitor reversed H2O2-induced inhibition of cell migration and invasion
Previous studies reported the role of H2O2 as a second messenger in the regulation of mammalian cell proliferation and migration [35, 36]. Results from wound healing and transwell assays showed that co-treatment with captopril and the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 alleviated the H2O2-induced inhibition of HCAEC migration and invasion (p < 0.05; Figures 7 and 8). However, there were no effects on migration and invasion when the cells were co-treated with captopril and the AKT activator SC79.
Figure 7
Effect of RAS inhibitor on H2O2-modulated cell migration through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Confluent monolayer of HCAECs was wounded by scratching in the presence of captopril or combined with AKT inhibitor or activator to stimulate cell migration toward the wound area. Images were captured immediately (0 h), and at 48 h after the wound scratch
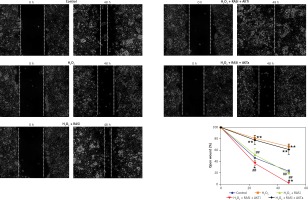
Figure 8
RAS inhibitor reduced H2O2-induced inhibition of HCAEC motility in a transwell migration assay via the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. HCAEC migration rate was examined after H2O2 stimulation with or without AKT inhibitor or activator. Captopril alone or in co-treatment with AKT inhibitor increased the rate of HCAEC migration
*p < 0.05, when compared with the control group; #p < 0.05, when compared with the H2O2 alone group.
Discussion
In the present study, the implications of long-term effects of H2O2-induced oxidative stress on cell viability, apoptosis, eNOS and AKT activation were investigated. The results obtained confirmed that H2O2 induced cell apoptosis, and increased AKT activation and eNOS expression in HCAECs. These findings are consistent with previous results which showed that H2O2 increased eNOS expression in H2O2-treated bovine aortic endothelial cells, and significantly decreased the viability of endothelial cells [37]. The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is a major physiological system which regulates fluid and electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and it is implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance [38]. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors improve the NO system and decrease intracellular oxidative stress [39]. Recent studies showed that inhibition of RAS with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, or a renin inhibitor offers protection from the burden of cardiovascular disease [40, 41]. The AKT/mTOR pathway has an important role in the cardiovascular system in inhibiting autophagy in cardiomyocytes to prevent cardiac atrophy [42]. On the other hand, recent studies also showed that sustained activity of the Akt/mTOR pathway induces extensive hypertrophy and cardiac dysfunction [43]. However, the roles of RAS inhibition in oxidative stress-induced endothelial cell dysfunction and H2O2-induced AKT activation remained uninvestigated.
Captopril, an RAS inhibitor, has been used for more than a decade to treat high blood pressure and reduce mortality and cardiovascular injury among patients with myocardial infarction complicated by ventricular systolic dysfunction and heart failure [44, 45]. Oxidative stress is also considered to play an important role in the pathogenesis of both types of diabetes [46] and cardiovascular disease. In the present study, a H2O2-induced oxidative stress model was used to mimic the characteristic pathologies of cardiovascular disease in vivo, so as to study the protective effects of captopril and its probable mechanisms of action. It has been shown that excess ROS production can cause oxidative damage to DNA, thereby triggering genomic instability and cell death [47].
The effect of captopril on the viability and migration of HCAECs exposed to H2O2 was investigated in this study by wound healing and MTT assays. Apoptosis was also assessed by annexin V-binding and p53 expression. It was found that captopril protected HCAECs from H2O2-induced oxidative cell damage and inhibition of cell migration. It was also found that captopril and the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 significantly protected HCAECs from H2O2-induced apoptosis. Although AKT plays a critical role in regulating the lifespan of primary cultured human cells [48], a previous study showed that constitutive activation of AKT may induce endothelial cell senescence in atheroma tissue, thereby contributing to atherogenesis [49]. In the present study, AKT activation was induced by H2O2, and co-treatment with captopril reversed this effect. However, there were no additional effect of the AKT inhibitor compared with captopril alone. Captopril markedly decreased the phosphorylation of AKT. The AKT signaling pathways are important signaling cascades downstream of ROS. These findings are consistent with previous results which showed that chronic activation of the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway leads to oxidative stress induced apoptosis [50].
The AKT/mTOR signaling pathway is involved in cell migration and invasion [51]. Previous studies showed that the AKT/mTOR pathway could regulate cellular oxidative stress and was involved in mediating vascular dysfunction [52]. Our results are consistent with previously published studies. The results of the present study demonstrated that H2O2 promoted the activation of AKT and inhibited cell migration and invasion, but these effects were suppressed by co-treatment with captopril and the AKT inhibitor MK-2206.
In conclusion, the novel finding in this study is that the protective effect of captopril against H2O2-induced apoptosis occurs through the AKT/mTOR pathway and contributes to enhanced cell survival. This association between H2O2-induced AKT activation and RAS inhibitors, and suppression of oxidative stress-induced apoptosis, has not been reported previously. These findings provide new insight into the protective effects of captopril and novel therapeutic approaches for regulating cell survival and cell death due to disorders such as cellular dysfunction and dysregulation of intracellular oxidative stress.


