Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ATHEROSCLEROSIS / RESEARCH PAPER
Preoperative clinical and renal ultrasonography variables associated with improved systolic and diastolic blood pressure reduction after renal artery stenting
1
Klinika Kardiologii Interwencyjnej UJ CM, Poland
2
Department of Interventional Cardiology, Institute of Cardiology, Jagiellonian University Collegium Medicum, The John Paul II Hospital, Krakow, Poland, Poland, Poland
3
Department of Interventional Cardiology, The John Paul II Hospital, Krakow, Poland, Poland, Poland, Poland
4
Cracow University of Economics. Department of Statistics. Krakow, Poland
5
Department of Interventional Cardiology, Department of Cardiac and Vascular Diseases, Institute of Cardiology, Jagiellonian University Collegium Medicum, The John Paul II Hospital, Krakow, Poland, Poland
Submission date: 2020-06-26
Final revision date: 2020-08-13
Acceptance date: 2020-08-30
Online publication date: 2021-04-30
Corresponding author
Anna Kabłak-Ziembicka
Klinika Kardiologii Interwencyjnej UJ CM, Prądnicka 80, 31-202, Kraków, Poland
Klinika Kardiologii Interwencyjnej UJ CM, Prądnicka 80, 31-202, Kraków, Poland
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Response to stent-assisted angioplasty (PTA) in hypertensive patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis (ARAS) is unpredictable. Therefore, the present study aimed to search for preoperative clinical and renal ultrasonography variables associated with systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) reduction.
Material and methods:
Preoperative clinical assessment and renal ultrasonography were performed in 202 patients who underwent PTA for ARAS (2003–2018). Patients were categorized as responders if decrease of SBP of at least 20mmHg or DBP of 5mmHg was achieved. Logistic regression models, with percentage shares, were evaluated by basic decision characteristics for ultrasonographic and clinical variables.
Results:
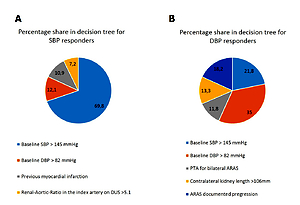
Logistic regression analysis showed that preoperative SBP ≥145mmHg (OR,20.0 [95%CI 8.67–46.2], p<0.001), (2) baseline DBP >82 mmHg (OR,3.46 [95%CI 1.61–7.42], p=0.001), (3) prior myocardial infarction (OR,3.14 [95%CI 1.09–9.0], p=0.033), and (4) Renal-Aortic-Ratio >5.1 (OR,2.67 [95%CI 1.20-6.0], p=0.016) predicted the SBP response, with respective influence shares of 69.8%; 12.1%; 10.9%; and 7.2%. The DBP response was associated with (1) baseline SBP >145mmHg (OR,3.79 [95%CI 1.87–7.70], p<0.001), (2) baseline DBP >82mmHg (OR,6.09 [95%CI 2.88–12.9], p<0.001), (3) ARAS progression (OR,0.32 [95%CI 0.09–1.07], p=0.062), (4) contralateral kidney length>106mm (OR,0.43 [95%CI 0.22–0.86], p=0.017), and (5) bilateral PTA (OR,2.39 [95%CI 1.08–5.27], p=0.03), with respective shares of 21.8%; 35.0%; 18.2%; 13.3% and 11.8%.
Conclusions:
Current study identified clinical and ultrasonographic characteristics of patients who are likely to respond to PTA for ARAS. The RAR and contralateral kidney size may enhance prediction of response likelihood.
Response to stent-assisted angioplasty (PTA) in hypertensive patients with atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis (ARAS) is unpredictable. Therefore, the present study aimed to search for preoperative clinical and renal ultrasonography variables associated with systolic (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) reduction.
Material and methods:
Preoperative clinical assessment and renal ultrasonography were performed in 202 patients who underwent PTA for ARAS (2003–2018). Patients were categorized as responders if decrease of SBP of at least 20mmHg or DBP of 5mmHg was achieved. Logistic regression models, with percentage shares, were evaluated by basic decision characteristics for ultrasonographic and clinical variables.
Results:
Logistic regression analysis showed that preoperative SBP ≥145mmHg (OR,20.0 [95%CI 8.67–46.2], p<0.001), (2) baseline DBP >82 mmHg (OR,3.46 [95%CI 1.61–7.42], p=0.001), (3) prior myocardial infarction (OR,3.14 [95%CI 1.09–9.0], p=0.033), and (4) Renal-Aortic-Ratio >5.1 (OR,2.67 [95%CI 1.20-6.0], p=0.016) predicted the SBP response, with respective influence shares of 69.8%; 12.1%; 10.9%; and 7.2%. The DBP response was associated with (1) baseline SBP >145mmHg (OR,3.79 [95%CI 1.87–7.70], p<0.001), (2) baseline DBP >82mmHg (OR,6.09 [95%CI 2.88–12.9], p<0.001), (3) ARAS progression (OR,0.32 [95%CI 0.09–1.07], p=0.062), (4) contralateral kidney length>106mm (OR,0.43 [95%CI 0.22–0.86], p=0.017), and (5) bilateral PTA (OR,2.39 [95%CI 1.08–5.27], p=0.03), with respective shares of 21.8%; 35.0%; 18.2%; 13.3% and 11.8%.
Conclusions:
Current study identified clinical and ultrasonographic characteristics of patients who are likely to respond to PTA for ARAS. The RAR and contralateral kidney size may enhance prediction of response likelihood.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.