Introduction
The angiopoietin-like family comprises secreted proteins that share structural similarities with angiopoietins. These proteins play crucial roles in various physiological and pathophysiological processes, such as regulating angiogenesis and inflammatory responses and modulating lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism [1–4]. Some of the angiopoietin-like (ANGPTL) proteins, including ANGPTL4, have been detected in the systemic circulation [5], suggesting that these ANGPTL proteins may act in an endocrine manner and may be good disease biomarkers. Among these ANGPTL proteins, angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) has emerged as a potential therapeutic target and biomarker for cardiometabolic diseases. ANGPTL4 was discovered in 2000 as a key regulator of lipid metabolism [6–8]. It is primarily synthesized by the liver and the adipose tissue [9]. Its clearance from the circulation predominantly occurs via renal excretion [7, 9–11]. Therefore, impaired renal function may attenuate the clearance rate of ANGPTL4, resulting in elevated plasma concentrations [12]. Hepatic dysfunction may also affect systemic levels of ANGPTL4 by diminishing its synthesis [13, 14].
Genetic inactivation of ANGPTL4 in mice improves glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism and results in smaller atherosclerotic lesions [15, 16]. In humans, genetic variants of ANGPTL4 are associated with diabetes and coronary artery disease [17], and plasma ANGPTL4 concentrations are higher in subjects with diabetes and obesity [18]. Further studies then showed that ANGPTL4 consists of three functional domains: the signal peptide, the coiled-coil domain (N-terminal chain), and the fibrinogen-like domain (C-terminal chain) [19]. The N-terminal fragment of ANGPTL4 interacts with lipoprotein lipase to regulate lipoprotein metabolism. On the other hand, the C-terminal fragment of ANGPTL4 plays a role in energy expenditure and various non-lipid-related processes, including vascular permeability, angiogenesis, oxidative stress and inflammation [20]. In human plasma, there is very little full-length and N-terminal ANGPTL4 in their free forms. Most of the ANGPTL4 in human plasma is the C-terminal ANGPTL4 fragment. Several reports have demonstrated the link between ANGPTL4 and cancer progression. Studies have shown that ANGPTL4 is involved in mechanisms of cancer development and progression, such as stem cell regulation, angiogenesis, vascular permeability, chronic inflammation, and tumorigenesis [7]. Also, aberrant expression of ANGPTL4 in tumors has been identified as a predictor of unfavorable prognosis and is linked to the progression of several cancers, including oral cancer, lung cancer, breast cancer, gastric cancer, and colorectal cancer [21–26].
Taken together, these findings suggest a role of plasma ANGPTL4 as a biomarker for cancers and cardiovascular diseases. However, this remains unexplored in the literature. Therefore, we used ELISA to measure the concentrations of plasma ANGPTL4 C-terminal fragments and investigated whether plasma ANGPTL4 can predict cancer mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and all-cause mortality in this community-based cohort study.
Material and methods
Study design and participant recruitment
Data for this investigation were sourced from the Taiwan Lifestyle Study, a large-scale prospective cohort initiative launched in 2006 [27–30]. Residents aged 18 years or older from Yunlin County, Taiwan, were invited to participate, with recruitment and assessment conducted at the National Taiwan University Hospital Yun-Lin branch. Clinical characteristics, demographic profiles, physical examination results, and blood test outcomes were collected by physicians and study nurses during both initial and follow-up visits. Participants were contacted annually after the initial visit and biennially thereafter via telephone, email, or mail. Follow-up appointments were arranged based on participant availability. Prior to enrollment, all participants provided informed consent, and the study protocol received approval from the Institutional Review Board of National Taiwan University Hospital (NTUH-REC No.: 202207009RINA).
All participants completed questionnaires, and their clinical and demographic information was recorded. Trained nurses conducted anthropometric measurements, including height, weight, waist circumference, and hip circumference, in the morning following an overnight fast of at least 8 h. Blood pressure was measured using a mercury sphygmomanometer, with the arm supported at heart level after a 10-minute rest. Three readings were taken at 1-minute intervals by skilled nurses, and the average of the last two readings was utilized for analysis.
Each participant underwent questionnaire-based assessments, followed by collection of clinical and demographic data. Trained nurses performed anthropometric measurements, including height, weight, waist circumference, and hip circumference, in the morning following an overnight fast of at least 8 h. Blood pressure was measured using a mercury sphygmomanometer, with the arm supported at heart level after a 10-minute rest. Skilled nurses took three readings at 1-minute intervals, and the mean of the last two readings was used for analysis.
A standard 75-gram oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was administered to determine 2-hour postprandial plasma glucose (2hPG) levels. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG), along with serum concentrations of total cholesterol, triglycerides (TGs), high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, were quantified using an automated analyzer (Toshiba TBA 120FR, Toshiba Medical Systems Co., Ltd. Tokyo, Japan). HbA1c levels were measured using an automated analyzer (HLC-723 G7 HPLC systems, Tosoh Corporation, Tokyo, Japan), with the assay certified by the National Glycohemoglobin Standardization Program and standardized to the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial reference assay.
Measurement of plasma ANGPTL4
The plasma ANGPTL4 concentration was assessed once at enrollment with a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (R&D Systems, Human Angiopoietin-like 4, Catalog Number: DY3485). This ELISA kit recognizes the recombinant human ANGPTL4 C-terminal fragment (amino acids 165-406). The intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation were 5.35% and 7.50%, respectively.
Linkage to the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) in Taiwan
The National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) is collected from the registered data and reimbursement claims of the National Health Insurance (NHI) program in Taiwan, which was initiated in 1995 and has been utilized until now. Approximately 99% of the population in Taiwan is enrolled in the NHI program, and the NHIRD is maintained by the National Health Research Institutes. Information identifiable personally to specific individual patients and healthcare providers is encrypted to protect one’s privacy and confidentiality. Cause of Death Data (CDD) is one of the datasets in NHIRD, containing all the registered death records in Taiwanese populations, which was used to define mortality in this study. We applied to the Health and Welfare Data Science Center (HWDC) in the Ministry of Health and Welfare for the linkage of the Taiwan Lifestyle Study database to the NHIRD and successfully acquired the survival status of all the subjects enrolled in the Taiwan Lifestyle Study until August 30, 2019. The institutional review board of National Taiwan University Hospital reviewed and approved the study protocol.
Statistical analysis
For categorical outcomes, proportions within each category were calculated. The normality of continuous variables was evaluated using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Variables with a normal distribution were summarized as mean values with their corresponding standard deviations (SDs), while those with skewed distributions were transformed logarithmically and presented as median values with their interquartile ranges. Differences in clinical features between the groups of patients who survived and those who did not were analyzed using Student’s t-test and the χ2 test.
The correlation between levels of plasma ANGPTL4 and various clinical indicators was analyzed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient. Survival rates for different groups were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier estimator, and the log-rank test was used to compare these rates. Hazard ratios (HRs) for mortality due to all causes, as well as specifically for cancer and cardiovascular disease, were calculated using Cox proportional hazards models that included variables of clinical importance.
The assumptions of proportional hazards were checked using plots of log-log survival, comparisons of observed and expected outcomes, and goodness-of-fit tests, which included both Schoenfeld and scaled Schoenfeld residuals. The model’s ability to predict mortality or survival over the follow-up period was assessed using concordance statistics, which are comparable to the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, with values ranging from 0.5 (indicating no predictive power) to 1 (indicating perfect prediction).
Statistical analyses were conducted using Stata/SE 14.0 software for Windows (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX), and a p-value below 0.05 was deemed to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Clinical characteristics of participants in this study
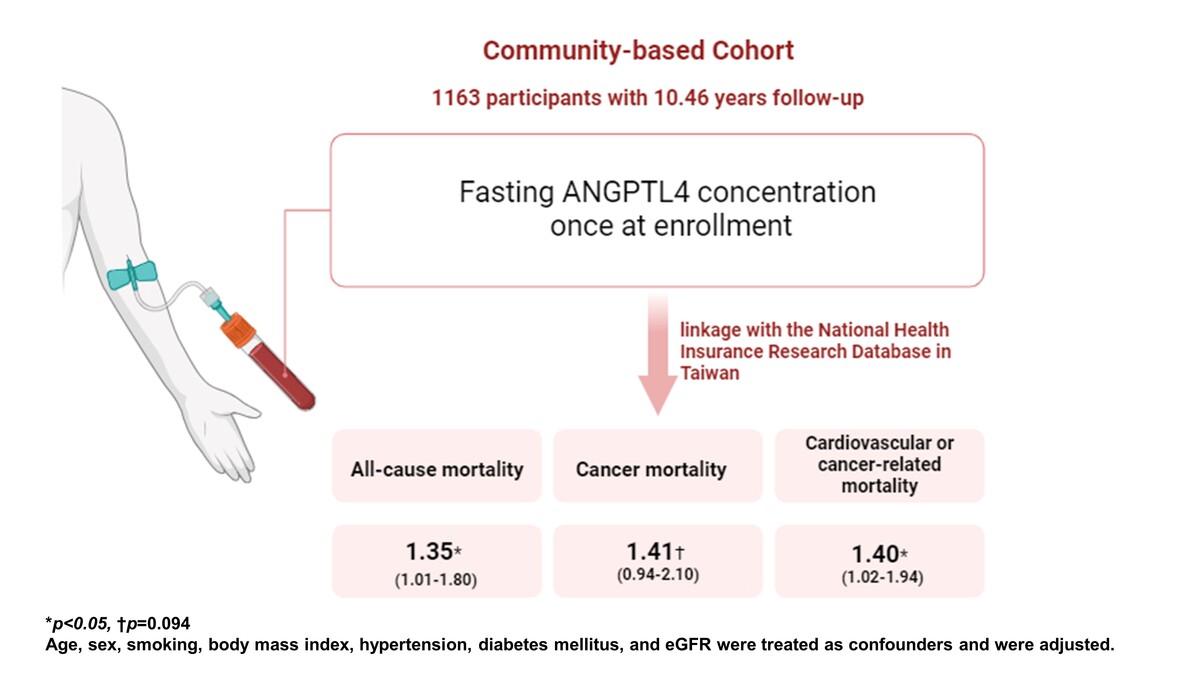
The study included 1163 participants, and the mean age was 60.6 ±11.75 years. During an average follow-up of 10.46 years (interquartile range: 2.24–13.54), 29 participants died, including 13 who died from cancers and 6 who died from cardiovascular diseases. Since the number of subjects who died from cardiovascular diseases was limited, cardiovascular mortality was not used as the sole outcome in further statistical analysis. Instead, cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality was used. Table I summarizes the clinical characteristics of subjects who survived or died during follow-up. Participants who died during follow-up were older and had a shorter follow-up period, lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and higher plasma high-sensitivity C reactive protein (hsCRP) level (all p < 0.001) than participants who were still alive during follow-up. The percentage of male participants was higher among participants who died during follow-up (p = 0.001). The ANGPTL4 concentration was significantly higher in participants who died during follow-up (672.48 ±268.47 ng/ml) than in participants who were still alive during follow-up (499.60 ±202.01 ng/ml) (p < 0.0001). There were no significant differences in the percentage of smoking, body mass index (BMI), hypertension, diabetes, or hyperlipidemia between the two groups.
Table I
Baseline clinical characteristics in subjects who survived or died during follow-up
[i] Means ± SDs or medians (interquartile ranges) are shown. Plasma triglyceride and hsCRP were logarithmically transformed for statistical analyses. BMI – body mass index, SBP – systolic blood pressure, DBP – diastolic blood pressure, HbA1c – glycated hemoglobin, GFR – glomerular filtration rate, HDL-C – high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HsCRP – high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, OGTT – oral glucose tolerance test, LDL-C – low-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Correlation between plasma ANGPTL4 levels and clinical variables
The correlations between plasma ANGPTL4 levels and clinical variables are presented in Table II. Plasma ANGPTL4 was positively associated with age (r = 0.2057; p < 0.0001), BMI (r = 0.0943; p = 0.0013), systolic blood pressure (r = 0.1110; p = 0.0002), diastolic blood pressure (r = 0.1057; p = 0.0003), OGTT 2-hour plasma glucose (r = 0.0672; p = 0.0122), and log hsCRP (r = 0.1235; p ≤ 0.0001) and was negatively associated with estimated GFR (r = –0.2149; p < 0.0001).
Table II
The relationship between plasma ANGPTL4 concentration and clinical characteristics
[i] BMI – body mass index, OGTT – oral glucose tolerance test, HbA1c – glycated hemoglobin, SBP – systolic blood pressure, DBP – diastolic blood pressure, TG, triglyceride, TC – total cholesterol, LDL-C – low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C – high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, hsCRP – high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, GFR – glomerular filtration rate.
The relationship between plasma ANGPTL4 concentration at baseline and all-cause mortality, cancer mortality and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality
Figure 1 presents the Kaplan-Meier curve of all-cause mortality, cancer mortality, and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality by plasma ANGPTL4 tertiles. During follow-up, subjects with plasma ANGPTL4 concentrations in the highest tertile had the highest all-cause mortality, cancer mortality, and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality (all p < 0.05).
Figure 1
Kaplan-Meier survival curve for (A) allcause mortality, (B) cancer mortality, and (C) cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality in subjects with different tertiles of plasma ANGPTL4 concentrations. Solid line, the lowest tertile of plasma ANGPTL4 concentration; long dashed line, the middle tertile of plasma ANGPTL4 concentration; dashed line, the highest tertile of plasma ANGPTL4 concentration. For all-cause mortality, p-value = 0.0334 in log rank test; for cancer mortality, p-value = 0.0206; for cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality, p-value = 0.0309

As shown in Table III, plasma ANGPTL4 was associated with all-cause mortality, cancer mortality, and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality in unadjusted models (HR for each 1 SD increase in plasma ANGPTL4, 1.53 (95% CI: 1.26–1.87; p < 0.001) for all-cause mortality, 1.55 (95% CI: 1.17–2.03; p < 0.01) for cancer mortality, and 1.53 (95% CI: 1.20–1.95; p < 0.01) for cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality). After adjusting for age, sex, smoking, body mass index, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and eGFR, plasma ANGPTL4 was significantly associated with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality and was associated with cancer mortality with borderline significance (adjusted HR for plasma ANGPTL4, 1.35 (95% CI: 1.01–1.80; p < 0.05) for all-cause mortality, 1.41 (95% CI: 0.94-2.10; p = 0.094) for cancer mortality, and 1.40 (95% CI: 1.02–1.94; p < 0.05) for cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality).
Table III
Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) of every 1 standard deviation (SD) increase in plasma ANGPTL4 concentration to predict all-cause mortality, cancer mortality and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality in unadjusted and adjusted models
| Variable | Unadjusted | Adjusted models |
|---|---|---|
| All-cause mortality | 1.53* (1.26–1.87) | 1.35‡ (1.01–1.80) |
| Cancer mortality | 1.55† (1.17–2.03) | 1.41§ (0.94–2.10) |
| Cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality | 1.53† (1.20–1.95) | 1.40‡ (1.02–1.94) |
The performance of plasma ANGPTL4 levels in predicting all-cause mortality, cancer mortality, and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality
Table IV shows the contribution of each variable to predict all-cause mortality, cancer mortality, and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality by comparing the differences in concordance statistics and AUC with and without the indicated variable. For all-cause mortality, the difference in concordance statistics and AUC for plasma ANGPTL4 were 0.0107 and 0.0106, respectively, which were lower than the contribution of age but higher than the contribution of sex, smoking, BMI, hypertension, DM, and eGFR. The differences in concordance statistics and AUC for plasma ANGPTL4 to predict cancer mortality were 0.0008 and 0.0014, respectively, whereas the differences in concordance statistics and AUC of plasma ANGPTL4 to predict cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality were 0.012 and 0.0142, respectively. Similarly, the contribution of plasma ANGPTL4 to predicting cancer mortality and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality was lower than the contribution of age and was higher than the contribution of other variables.
Table IV
Concordance statistics and area under the ROC curve (AUC) in the full model and without the indicated variable in the full models to predict all-cause mortality, cancer mortality and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality. Differences in concordance statistics and AUC between the full model and the model without the indicated variable are shown in parentheses
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first longitudinal cohort study that explores the relationship between plasma ANGPTL4 levels and all-cause mortality, cancer mortality, and cardiovascular mortality, with an adequate sample size and follow-up period. In this study, we found that plasma ANGPTL4 can independently predict 10-year all-cause mortality and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality in a community-based population. The predictive ability of plasma ANGPTL4 was lower than that of age but higher than the contribution of sex, smoking, BMI, history of hypertension, history of diabetes, and eGFR.
Several studies have identified the presence of ANGPTL4 in various solid tumors, such as lung cancers, breast cancer, colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, hepatocarcinoma, and renal cell carcinoma [21–26]. Previous studies showed that the expression of ANGPTL4 was significantly higher in lung adenocarcinoma [26] and breast cancer tissues [23] and was closely associated with cancer progression and poor prognosis. In addition, the expression of ANGPTL4 is positively correlated with the stage of colorectal cancer [31]. In patients with renal cell carcinoma, elevated serum ANGPTL4 levels have been found to be a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker [32]. In summary, ANGPTL4 may have important roles in cancer growth, progression, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis, which supports the findings of the present study indicating that plasma ANGPTL4 levels predict 10-year cancer mortality.
Diabetes and atherosclerosis are both well-known risk factors for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular-related mortality [33]. Accumulating evidence has shown that ANGPTL4 is associated with the risk of atherosclerosis and type 2 diabetes. One recent study demonstrated that genetic inactivation of ANGPTL4 is associated with improved glucose homeostasis and a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes in humans [10]. Genetic deficiency of ANGPTL4 in mice also improves glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity [10]. Additionally, ANGPTL4-deficient mice have better lipid metabolism and smaller atherosclerotic lesions than wild-type mice [16]. The amino acid-altering (missense) E40K variant in ANGPTL4 has been associated with decreased levels of triglycerides and increased levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol [16]. In humans, the DiscovEHR human genetics study included 42,930 participants and revealed that carriers of E40K and other inactivating mutations in ANGPTL4 had lower levels of triglycerides and a lower risk of coronary artery disease than did noncarriers [16]. Physiologically, when ANGPTL4 is secreted, it can bind to lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and inhibit its lipolytic activity [3]. This leads to reduced hydrolysis of triglycerides (TGs) from TG-enriched lipoproteins (TRLs) such as very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and chylomicrons in adipose tissue, heart, and muscle [34]. ANGPTL4 also exhibits LPL-independent functions, including regulating energy homeostasis, vascular permeability, angiogenesis, oxidative stress, and inflammation [3]. Among these functions, increased oxidative stress and inflammation are important in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis [35]. ANGPTL4 can interact with integrins and neuropilins to activate pathways involving FAK (focal adhesion kinase), SRC, Rac1, profilin-1, and RhoA [20]. These activations further trigger the PI3K/AKT, JAK/STAT3, ERK, and NF-κB signaling pathways, exacerbating inflammation and tissue damage [20]. ANGPTL4 can also interact with integrins to stimulate NADPH oxidase-dependent production of superoxide [36]. The dysregulation of intracellular ROS levels, resulting in an excessive level or persistent elevation of ROS, has been linked to endothelial dysfunction [37]. Taken together, ANGPTL4 may be involved in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis through its effect on glucose and triglyceride homeostasis, inflammation, and oxidative stress, which supports the finding of the present study that plasma ANGPTL4 was associated with cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality.
ANGPTL4 has several different fragments in human blood, including full-length ANGPTL4, the N-terminal ANGPTL4 fragment, and the C-terminal ANGPTL4 fragment. The majority of the circulating full-length and N-terminal ANGPTL4 is bound to ANGPTL8, rather than being present in free forms, and the binding to ANGPTL8 can effectively impair ANGPTL4’s ability to inhibit lipoprotein lipase [38]. On the other hand, the majority of plasma ANGPTL4 present in humans in free form consists of the C-terminal ANGPTL4 fragment [39]. Unlike the full-length or N-terminal ANGPTL4 fragment, this C-terminal ANGPTL4 fragment does not possess the capability to inhibit lipoprotein lipase. Therefore, the circulating C-terminal ANGPTL4 fragment may not be involved in the regulation of lipoprotein lipase. Instead, it appears to play a role in energy expenditure and various non-lipid-related processes, such as angiogenesis, inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular permeability [20]. In the present study, we measured the concentrations of plasma ANGPTL4 by the ELISA system targeting the ANGPTL4 C-terminal fragment. The findings that plasma ANGPTL4 concentration could predict cardiovascular- and cancer-related mortality in the present study support the concept that the C-terminal fragment is more closely related to non-lipid-related processes stated above.
The present study has some strengths. First, this is the first longitudinal cohort study to explore the relationship between plasma ANGPTL4 levels and all-cause mortality, cancer mortality, and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality. With this design, the temporal relationship between elevated plasma ANGPTL4 and the outcomes is clear. Second, the sample size of the study was large, and the follow-up duration was long. Third, the follow-up rate in this study was 100%, achieved by linking to the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). However, our study had some limitations. First, plasma ANGPTL4 was measured only once at the beginning of the observation period, which may limit the value of plasma ANGPTL4 over time for the prediction of outcomes. Second, generalization of the findings to other populations may be limited because all the subjects in the current study were Han Chinese. Studies in other ethnic groups should be performed to determine whether the findings can be generalized. Third, cancer is heterogeneous, and many factors may modify the risk of cancers, such as lifestyle, occupational exposures, hormonal imbalances, genetic predispositions, etc. [40]. In our analyses, we only included age, sex, smoking, body mass index, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and eGFR as confounders, but did not fully capture the other influencing factors related to lifestyle, occupational exposure, hormonal imbalances, and genetic predispositions. Furthermore, our analyses categorize all cancers as a single outcome, instead of treating them as specific cancer subtypes. Future research with larger sample sizes and more recorded influencing factors is necessary to provide clearer insights into the specific roles of ANGPTL4 in these particular cancers.
In conclusion, the present study demonstrated that plasma ANGPTL4 could predict 10-year all-cause mortality and cardiovascular or cancer-related mortality in a community-based population. In addition, plasma ANGPTL4 can improve mortality prediction over and above established risk factors. These findings suggest that plasma ANGPTL4 could serve as a novel biomarker to predict mortality. However, it is important to note that this conclusion is based on a single study with ANGPTL4 that was measured only once at the beginning of the observation period. Further research in diverse populations is warranted to validate these findings and assess the generalizability of the result.