Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ONCOLOGY / BASIC RESEARCH
Novel formulation, cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and anti-human lung cancer properties of gold nanoparticles containing Verbascum thapsus L. leaf aqueous extract
1
Department of Thoracic Surgery, Taizhou People’s Hospital of Jiangsu Province, Taizhou city, Jiangsu Province, China
2
Respiratory Medicine, Chongqing Armed Police Corps Hospital, Chongqing, China
3
Department of Oncology, The People’s Hospital of Dazu, Chongqing, China
4
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Changsha Central Hospital of Hunan Province, Changsha, Hunan, China
5
Department of Botany and Microbiology, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
6
Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine and King Khalid University Hospital, King Saud University, Medical City, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
7
Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
Submission date: 2021-07-29
Final revision date: 2021-08-06
Acceptance date: 2021-08-07
Online publication date: 2021-08-17
Corresponding author
Yijia Xiao
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Changsha Central Hospital of Hunan Province, Changsha, Hunan, 410000, China, Iran
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Changsha Central Hospital of Hunan Province, Changsha, Hunan, 410000, China, Iran
KEYWORDS
gold nanoparticlesVerbascum thapsus Llung well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinomalung moderately differentiated adenocarcinomalung poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
In the present study, gold nanoparticles were prepared and synthesized in aqueous medium using Verbascum thapsus leaf extract. We assessed the anti-human lung cancer potential of these nanoparticles against well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma, moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung, and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung cell lines.
Material and methods:
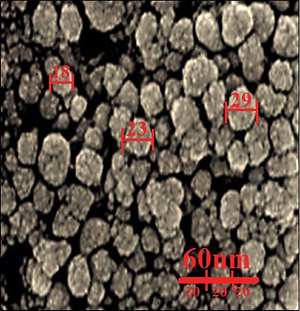
AuNPs were characterized and analyzed by common nanotechnology techniques including Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, field emission-scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. In the FT-IR test, the presence of many antioxidant compounds with related bonds caused excellent conditions for reduction of gold in the gold nanoparticles. In UV-Vis, the clear peak at the wavelength of 548 nm indicated the formation of gold nanoparticles. For determining anti-human lung cancer properties of HAuCl4, V. thapsus, and AuNPs, MTT assay was used on normal (HUVECs), well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma (HLC-1), moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung (LC-2/ad), and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung (PC-14) cell lines.
Results:
AuNPs had excellent anti-human lung cancer effects dose-dependently against HLC-1, LC-2/ad, and PC-14 cell lines. The best result of anti-human lung cancer activities of AuNPs against the above cell lines was observed in the case of the PC-14 cell line.
Conclusions:
The synthesized AuNPs showed significant anti-human lung cancer properties against well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma, moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung, and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung cell lines in a dose-dependent manner.
In the present study, gold nanoparticles were prepared and synthesized in aqueous medium using Verbascum thapsus leaf extract. We assessed the anti-human lung cancer potential of these nanoparticles against well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma, moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung, and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung cell lines.
Material and methods:
AuNPs were characterized and analyzed by common nanotechnology techniques including Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, field emission-scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy. In the FT-IR test, the presence of many antioxidant compounds with related bonds caused excellent conditions for reduction of gold in the gold nanoparticles. In UV-Vis, the clear peak at the wavelength of 548 nm indicated the formation of gold nanoparticles. For determining anti-human lung cancer properties of HAuCl4, V. thapsus, and AuNPs, MTT assay was used on normal (HUVECs), well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma (HLC-1), moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung (LC-2/ad), and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung (PC-14) cell lines.
Results:
AuNPs had excellent anti-human lung cancer effects dose-dependently against HLC-1, LC-2/ad, and PC-14 cell lines. The best result of anti-human lung cancer activities of AuNPs against the above cell lines was observed in the case of the PC-14 cell line.
Conclusions:
The synthesized AuNPs showed significant anti-human lung cancer properties against well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma, moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung, and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the lung cell lines in a dose-dependent manner.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.