Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
DIABETOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
MiR-28-3p regulates high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction by targeting CXXC5
1
Department of Vascular Surgery, Affiliated Hangzhou First People's Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China., China
2
Department of Vascular Surgery, Hangzhou Third People’s Hospital, Hangzhou, China., China
3
Department of Vascular Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China., China
Submission date: 2023-05-29
Final revision date: 2023-07-30
Acceptance date: 2023-08-14
Online publication date: 2023-08-17
Corresponding author
Chenyang Qiu
Department of Vascular Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China., No.79 Qingchun Road, 310003, Hangzhou, China
Department of Vascular Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China., No.79 Qingchun Road, 310003, Hangzhou, China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Introduction: Data from the CEO database shows microRNA (miR) -28-3p levels are elevated in diabetic patients. Nevertheless, the role of miR-28-3p in peripheral artery disease with diabetes have not been investigated.
Material and methods:
The level of miR-28-3p, CXXC5, CXXC-type zinc finger protein 5, and CXXC5’s downstream molecules as well as endothelial function were investigated. Dual luciferase analyses were used to confirm the binding site of miR-28-3p and CXXC5.
Results:
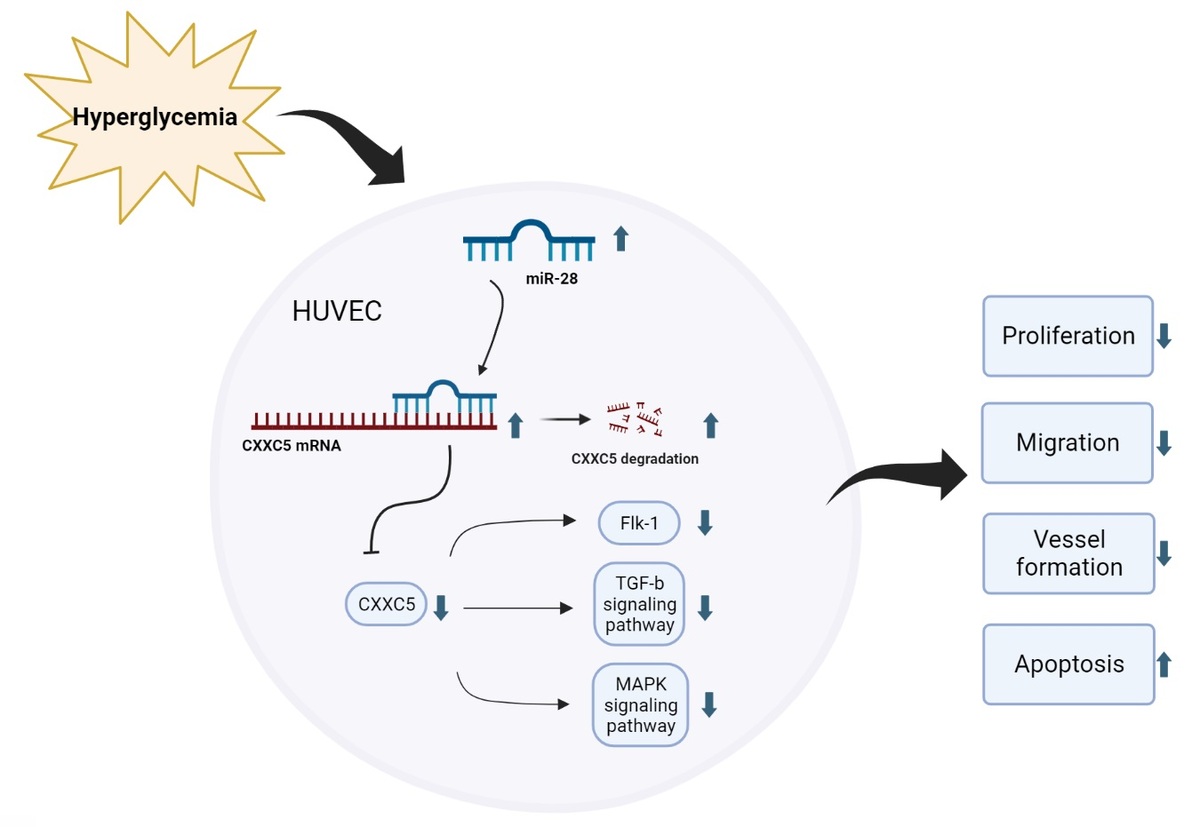
Results: Under high-glucose condition, miR-28-3p expression is increased whereas CXXC5 expression is downregulated. Overexpression of miR-28-3p increased cell apoptosis and inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and vessel formation, whilst inhibiting its expression had the opposite effect. The overexpression and inhibition of miR-28-3p could also influence both the mRNA and protein levels of CXXC5 and its known downstream molecules. Analysis of bioinformatics data revealed a potential binding site for miR-28-3p and CXXC5. Dual luciferase analyses demonstrated that miR-28-3p suppressed CXXC5 expression by targeting the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of CXXC5. Following that, we overexpressed both miR-28-3p and CXXC5. The level of CXXC5 and its known downstream signaling molecules decreased with miR-28-3p overexpression alone. As anticipated, co-overexpression of miR-28-3p and CXXC5 partially reversed the effect of miR-28-3p mimics.
Conclusions:
Conclusion: These findings indicated that miR-28-3p regulated high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction by targeting CXXC5.
Introduction: Data from the CEO database shows microRNA (miR) -28-3p levels are elevated in diabetic patients. Nevertheless, the role of miR-28-3p in peripheral artery disease with diabetes have not been investigated.
Material and methods:
The level of miR-28-3p, CXXC5, CXXC-type zinc finger protein 5, and CXXC5’s downstream molecules as well as endothelial function were investigated. Dual luciferase analyses were used to confirm the binding site of miR-28-3p and CXXC5.
Results:
Results: Under high-glucose condition, miR-28-3p expression is increased whereas CXXC5 expression is downregulated. Overexpression of miR-28-3p increased cell apoptosis and inhibited cell proliferation, migration, and vessel formation, whilst inhibiting its expression had the opposite effect. The overexpression and inhibition of miR-28-3p could also influence both the mRNA and protein levels of CXXC5 and its known downstream molecules. Analysis of bioinformatics data revealed a potential binding site for miR-28-3p and CXXC5. Dual luciferase analyses demonstrated that miR-28-3p suppressed CXXC5 expression by targeting the 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of CXXC5. Following that, we overexpressed both miR-28-3p and CXXC5. The level of CXXC5 and its known downstream signaling molecules decreased with miR-28-3p overexpression alone. As anticipated, co-overexpression of miR-28-3p and CXXC5 partially reversed the effect of miR-28-3p mimics.
Conclusions:
Conclusion: These findings indicated that miR-28-3p regulated high glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction by targeting CXXC5.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.