Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
NEPHROLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
MiR-125b-5p enclosed in hypoxic HK2 cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating NLRC5
1
Department of Urology, The Affiliated Changzhou No. 2 People's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Changzhou, China
2
Institute of Urology, Surgical Research Center, School of Medicine, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210009, P.R, China
3
Department of Urology, Zhongda Hospital, Southeast University, 87 Dingjiaqiao, Gulou, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
4
Department of Urology, Shanghai Children's Medical Center, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200127, P.R, China
Submission date: 2020-04-17
Final revision date: 2020-11-13
Acceptance date: 2020-11-29
Online publication date: 2021-04-09
Corresponding author
ming chen
Department of Urology, Zhongda Hospital, Southeast University, 87 Dingjiaqiao, Gulou, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Department of Urology, Zhongda Hospital, Southeast University, 87 Dingjiaqiao, Gulou, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
In this study, we validated the changes in microRNA (miRNA) expression in hypoxic human kidney 2 (HK2) cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). Additionally, we investigated the mechanism by which miRNA that are derived from EVs alleviated renal ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury.
Material and methods:
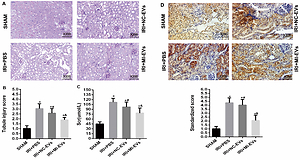
HK2 cells were treated in a hypoxic chamber (1% O2) for 12 h.EVs were obtained as supernatant from ultracentrifugation and characterized. After examining 16 differentially expressed EV-miRNAs between normoxic and hypoxic conditions by RT-PCR and bioinformatics analysis, miR-125b-5p was selected for further analysis. Normoxic and hypoxic HK2 cells-derived EVs as well as EVs that were isolated from miR-125b-5p negative control (miR-NC)-transfected or miR-125b-5p mimic (miR-MI)-transfected HK2 cells were injected in mice with renal I/R injury. The degree of renal injury was assessed by periodic acid-Schiff staining, renal tubule injury score, and plasma creatinine levels. Bioinformatics analysis was performed to determine the potential target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs. RT-PCR,western blotting, luciferase reporter assay, and immunohistochemistry were performed to investigate the relationship between miR-125b-5p and the NLR family CARD domain containing 5 (NLRC5).
Results:
RT-PCR revealed that from 16 differentially expressed miRNAs, four EV-miRNAs were upregulated. Animal study showed that miR-125b-5p overexpression in EVs alleviated renal I/R injury. Bioinformatics analysis predicted that NLRC5 was targeted by miR-125b-5p. Moreover, the relationship between miR-125b-5p and NLRC5 was also validated.
Conclusions:
There were several miRNAs that were upregulated (including miR-125b-5p) in hypoxic HK2 cells. Hypoxia induced EVs that alleviate renal IRI, can be attributed to miR-125b-5p for targeting NLRC5.
In this study, we validated the changes in microRNA (miRNA) expression in hypoxic human kidney 2 (HK2) cell-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). Additionally, we investigated the mechanism by which miRNA that are derived from EVs alleviated renal ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury.
Material and methods:
HK2 cells were treated in a hypoxic chamber (1% O2) for 12 h.EVs were obtained as supernatant from ultracentrifugation and characterized. After examining 16 differentially expressed EV-miRNAs between normoxic and hypoxic conditions by RT-PCR and bioinformatics analysis, miR-125b-5p was selected for further analysis. Normoxic and hypoxic HK2 cells-derived EVs as well as EVs that were isolated from miR-125b-5p negative control (miR-NC)-transfected or miR-125b-5p mimic (miR-MI)-transfected HK2 cells were injected in mice with renal I/R injury. The degree of renal injury was assessed by periodic acid-Schiff staining, renal tubule injury score, and plasma creatinine levels. Bioinformatics analysis was performed to determine the potential target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs. RT-PCR,western blotting, luciferase reporter assay, and immunohistochemistry were performed to investigate the relationship between miR-125b-5p and the NLR family CARD domain containing 5 (NLRC5).
Results:
RT-PCR revealed that from 16 differentially expressed miRNAs, four EV-miRNAs were upregulated. Animal study showed that miR-125b-5p overexpression in EVs alleviated renal I/R injury. Bioinformatics analysis predicted that NLRC5 was targeted by miR-125b-5p. Moreover, the relationship between miR-125b-5p and NLRC5 was also validated.
Conclusions:
There were several miRNAs that were upregulated (including miR-125b-5p) in hypoxic HK2 cells. Hypoxia induced EVs that alleviate renal IRI, can be attributed to miR-125b-5p for targeting NLRC5.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.