Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
BASIC RESEARCH
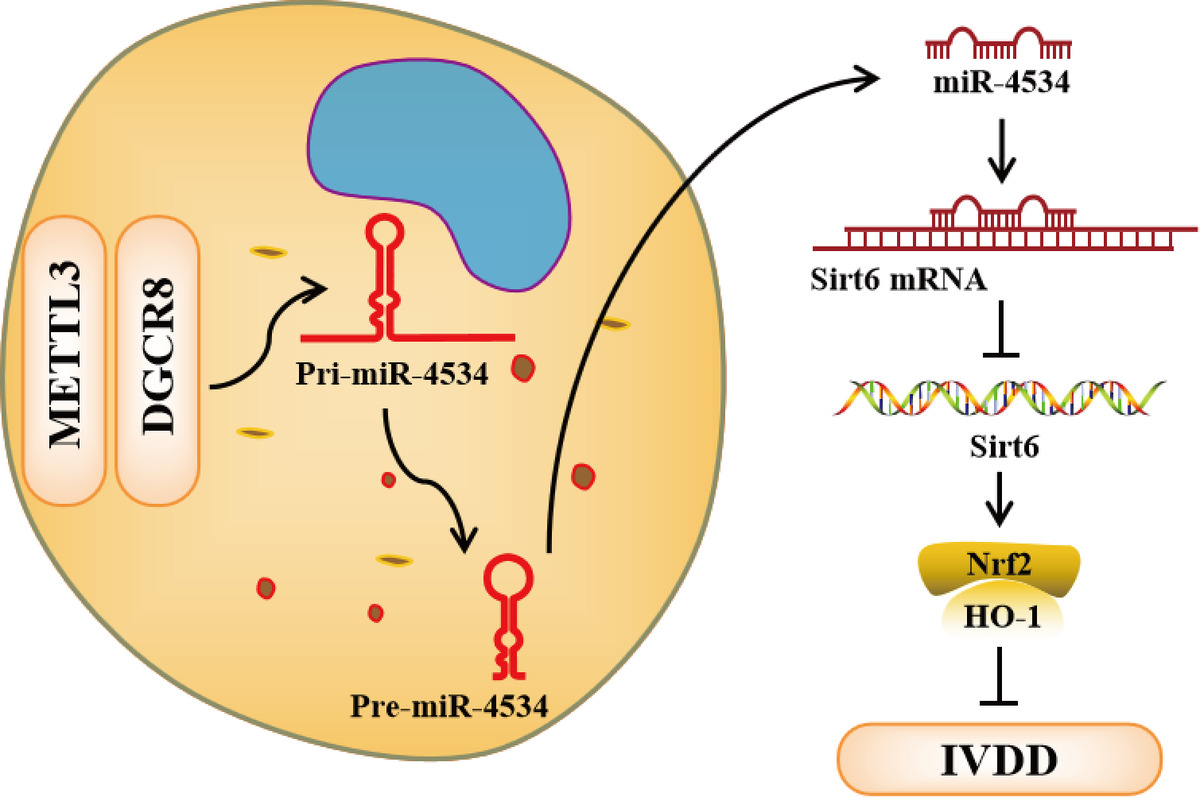
METTL3-mediated miR-4534 maturation promotes IVDD progression by targeting the Sirt6-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 pathway
1
The Second District of Spinal Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Yangjiang, Jiangcheng District, Yangjiang City, Guangdong Province, China
Submission date: 2023-08-18
Final revision date: 2023-10-11
Acceptance date: 2023-11-19
Online publication date: 2024-08-17
Corresponding author
Bo Ran
The Second District of Spinal Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Yangjiang, No. 14 Dongshan Road Jiangcheng District, Yangjiang City, Guangdong Province, China, Phone: +86 15150026910
The Second District of Spinal Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Yangjiang, No. 14 Dongshan Road Jiangcheng District, Yangjiang City, Guangdong Province, China, Phone: +86 15150026910
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) is a significant contributor to the development of discogenic low back pain and impairment. Apoptosis and degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) have also been reported to be major factors in IVDD. However, current treatments are unable to cure it, and the exact mechanisms are not fully understood.
Material and methods:
Nucleus pulposus (NP) tissues were collected from individuals diagnosed with either IVDD or lumbar vertebral fractures, whereas nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) were isolated from non-degenerative, healthy NP tissues. The IVDD cell model was established by treating NPCs with IL-1β at a concentration of 20 ng/ml, and an animal model was induced through annulus fibrosus puncture surgery. Histological examination of NP tissues was performed using HE staining. Analysis of mRNA and protein expression was performed using qRT-PCR and western blot techniques. Cellular viability was assessed using the CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry and TUNEL assays were employed to evaluate cellular apoptosis, the binding interaction between miR-4534 and Sirt6 was confirmed via a dual-luciferase reporter system, and we utilized RIP and Me-RIP methods to provide evidence of m6A modification in pri-miR-4534.
Results:
MiR-4534 was found to be upregulated in NP tissues affected by IVDD, and it promoted apoptosis of NPCs and ECM degradation by inhibiting Sirt6 expression and inactivating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Furthermore, this upregulation was attributed to m6A epigenetic modification of pri-miR-4534, facilitated by METTL3, and the knockdown of METTL3 alleviated the progression of IVDD.
Conclusions:
MiR-4534, upregulated through METTL3-mediated m6A modification, functions by suppressing Sirt6 and deactivating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which, in turn, promotes apoptosis of NPCs and contributes to ECM degradation, thereby facilitating the progression of IVDD.
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) is a significant contributor to the development of discogenic low back pain and impairment. Apoptosis and degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) have also been reported to be major factors in IVDD. However, current treatments are unable to cure it, and the exact mechanisms are not fully understood.
Material and methods:
Nucleus pulposus (NP) tissues were collected from individuals diagnosed with either IVDD or lumbar vertebral fractures, whereas nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) were isolated from non-degenerative, healthy NP tissues. The IVDD cell model was established by treating NPCs with IL-1β at a concentration of 20 ng/ml, and an animal model was induced through annulus fibrosus puncture surgery. Histological examination of NP tissues was performed using HE staining. Analysis of mRNA and protein expression was performed using qRT-PCR and western blot techniques. Cellular viability was assessed using the CCK-8 assay, flow cytometry and TUNEL assays were employed to evaluate cellular apoptosis, the binding interaction between miR-4534 and Sirt6 was confirmed via a dual-luciferase reporter system, and we utilized RIP and Me-RIP methods to provide evidence of m6A modification in pri-miR-4534.
Results:
MiR-4534 was found to be upregulated in NP tissues affected by IVDD, and it promoted apoptosis of NPCs and ECM degradation by inhibiting Sirt6 expression and inactivating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Furthermore, this upregulation was attributed to m6A epigenetic modification of pri-miR-4534, facilitated by METTL3, and the knockdown of METTL3 alleviated the progression of IVDD.
Conclusions:
MiR-4534, upregulated through METTL3-mediated m6A modification, functions by suppressing Sirt6 and deactivating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which, in turn, promotes apoptosis of NPCs and contributes to ECM degradation, thereby facilitating the progression of IVDD.
REFERENCES (39)
1.
Shen FH, Samartzis D, Andersson GB. Nonsurgical management of acute and chronic low back pain. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2006; 14: 477-87.
2.
Mohd Isa IL, Teoh SL, Mohd Nor NH, Mokhtar SA. Discogenic low back pain: anatomy, pathophysiology and treatments of intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Sci 2022; 24: 208.
3.
Raj PP. Intervertebral disc: anatomy-physiology-pathophysiology-treatment. Pain Pract 2008; 8: 18-44.
4.
Tu J, Li W, Yang S, et al. Single-cell transcriptome profiling reveals multicellular ecosystem of nucleus pulposus during degeneration progression. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2022; 9: e2103631.
5.
Zhang Y, Han S, Kong M, Tu Q, Zhang L, Ma X. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis identifies unique chondrocyte subsets and reveals involvement of ferroptosis in human intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2021; 29: 1324-34.
6.
Mern DS, Beierfuss A, Thome C, Hegewald AA. Enhancing human nucleus pulposus cells for biological treatment approaches of degenerative intervertebral disc diseases: a systematic review. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2014; 8: 925-36.
7.
Sun K, Jiang J, Wang Y, et al. The role of nerve fibers and their neurotransmitters in regulating intervertebral disc degeneration. Ageing Res Rev 2022; 81: 101733.
8.
Zhang CY, Hu XC, Zhang GZ, Liu MQ, Chen HW, Kang XW. Role of Nrf2 and HO-1 in intervertebral disc degeneration. Connect Tissue Res 2022; 63: 559-76.
9.
Hu B, Shi C, Xu C, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 attenuates IL-1beta induced alteration of anabolic and catabolic activities in intervertebral disc degeneration. Sci Rep 2016; 6: 21190.
10.
Sudan K, Vijayan V, Madyaningrana K, et al. TLR4 activation alters labile heme levels to regulate BACH1 and heme oxygenase-1 expression in macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med 2019; 137: 131-42.
11.
Wang R, Luo D, Li Z, Han H. Dimethyl fumarate ameliorates nucleus pulposus cell dysfunction through activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration. Comput Math Methods Med 2021; 2021: 6021763.
12.
Anderson KA, Green MF, Huynh FK, Wagner GR, Hirschey MD. SnapShot: mammalian sirtuins. Cell 2014; 159: 956-6e951.
13.
Liu Y, Li Y, Huang ZN, et al. The effect of intervertebral disc degenerative change on biological characteristics of nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cell: an in vitro study in rats. Connect Tissue Res 2019; 60: 376-88.
14.
Zhang GZ, Deng YJ, Xie QQ, et al. Sirtuins and intervertebral disc degeneration: roles in inflammation, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial function. Clin Chim Acta 2020; 508: 33-42.
15.
Li L, Zhang H, Chen B, et al. BaZiBuShen alleviates cognitive deficits and regulates Sirt6/NRF2/HO-1 and Sirt6/P53-PGC-1alpha-TERT signaling pathways in aging mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2022; 282: 114653.
16.
Wang C, Cui L, Gu Q, et al. The mechanism and function of miRNA in intervertebral disc degeneration. Orthop Surg 2022; 14: 463-71.
17.
Liu J, Li R, Lv P. Identification and verification of key miRNAs associated with intervertebral disc degeneration. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 2023; 26: 1766-74.
18.
Han X, Guo J, Fan Z. Interactions between m6A modification and miRNAs in malignant tumors. Cell Death Dis 2021; 12: 598.
19.
Zhu B, Chen HX, Li S, et al. Comprehensive analysis of N6-methyladenosine (m(6)A) modification during the degeneration of lumbar intervertebral disc in mice. J Orthop Translat 2021; 31: 126-38.
20.
Gao D, Hu B, Ding B, Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Xiao L. N6-Methyladenosine-induced miR-143-3p promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating SOX5. Bone 2022; 163: 116503.
21.
Chen PB, Shi GX, Liu T, et al. Oxidative stress aggravates apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells through m(6)A modification of MAT2A Pre-mRNA by METTL16. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022; 2022: 4036274.
22.
Bai X, Jiang M, Wang J, et al. Cyanidin attenuates the apoptosis of rat nucleus pulposus cells and the degeneration of intervertebral disc via the JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway in vitro and in vivo. Pharm Biol 2022; 60: 427-36.
23.
Chen F, Jiang G, Liu H, et al. Melatonin alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by disrupting the IL-1beta/NF-kappaB-NLRP3 inflammasome positive feedback loop. Bone Res 2020; 8: 10.
24.
Wan J, Zhang G, Li X, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 3: a promoting and destabilizing factor in the pathogenesis of disease and cell differentiation. Front Physiol 2021; 12: 663978.
25.
Sun Y, Zhang W, Li X. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells deliver exogenous miR-105-5p via small extracellular vesicles to rejuvenate senescent nucleus pulposus cells and attenuate intervertebral disc degeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021; 12: 286.
26.
Fan Y, Cheng J, Yang Q, et al. Sirt6-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 activation alleviates angiotensin II-induced DNA DSBs and apoptosis in podocytes. Food Funct 2021; 12: 7867-82.
27.
Chen Y, Zheng Z, Wang J, et al. Berberine suppresses apoptosis and extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation in nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates disc degeneration in a rodent model. Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14: 682-92.
28.
Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, He C. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2017; 18: 31-42.
29.
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol 2011; 7: 885-7.
30.
Yang Q, Guo XP, Cheng YL, Wang Y. MicroRNA-143-5p targeting eEF2 gene mediates intervertebral disc degeneration through the AMPK signaling pathway. Arthritis Res Ther 2019; 21: 97.
31.
Ji ML, Jiang H, Zhang XJ, et al. Preclinical development of a microRNA-based therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Commun 2018; 9: 5051.
32.
Yang X, Liu H, Zhang Q, et al. MiR-96 promotes apoptosis of nucleus pulpous cells by targeting FRS2. Hum Cell 2020; 33: 1017-25.
33.
Wang J, Liu X, Sun B, Du W, Zheng Y, Sun Y. Upregulated miR-154 promotes ECM degradation in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Biochem 2019; 120: 11900-7.
34.
Tan H, Zhao L, Song R, Liu Y, Wang L. microRNA-665 promotes the proliferation and matrix degradation of nucleus pulposus through targeting GDF5 in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Cell Biochem 2018; 119: 7218-25.
35.
Liu W, Zhang Y, Xia P, et al.MicroRNA-7 regulates IL-1beta-induced extracellular matrix degeneration by targeting GDF5 in human nucleus pulposus cells. Biomed Pharmacother 2016; 83: 1414-21.
36.
Chen J, Xie JJ, Jin MY, et al. Sirt6 overexpression suppresses senescence and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells by inducing autophagy in a model of intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Death Dis 2018; 9: 56.
37.
Lu J, Miao Z, Jiang Y, et al. Chrysophanol prevents IL-1beta-Induced inflammation and ECM degradation in osteoarthritis via the Sirt6/NF-kappaB and Nrf2/NF-kappaB axis. Biochem Pharmacol 2023; 208: 115402.
38.
Kang L, Hu J, Weng Y, Jia J, Zhang Y. Sirtuin 6 prevents matrix degradation through inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Cell Res 2017; 352: 322-32.
39.
Jiao F, Zhang Z, Hu H, Zhang Y, Xiong Y. SIRT6 activator UBCS039 inhibits thioacetamide-induced hepatic injury in vitro and in vivo. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 837544.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.