Introduction
Diabetes mellitus, encompassing both type 1 (T1D) and type 2 (T2D) diabetes, represents a significant global health challenge due to its increasing prevalence and associated complications [1]. Among these complications, diabetic nephropathy (DN) stands out as a leading cause of end-stage renal disease, contributing to substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide [2]. Understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms driving DN is crucial for developing effective therapeutic strategies and improving patient outcomes [2].
Cytokines, small proteins involved in cell signaling, have been implicated in the inflammatory processes underlying both T1D and T2D [3]. Interleukin-6 (IL-6), in particular, is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that has been shown to play a critical role in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its vascular complications [3]. Vascular complications of diabetes include a wide spectrum of conditions such as atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and an increased risk of cardiovascular events. Chronic low-grade inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development and progression of these complications, with interleukin 6 (IL-6) acting as a key mediator by promoting endothelial activation, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, and the production of adhesion molecules that facilitate leukocyte recruitment and vascular damage [3]. Elevated serum levels of IL-6 are associated with insulin resistance, β-cell dysfunction, and chronic inflammation, which are key features of diabetes [3, 4]. IL-6 is a multifunctional cytokine that mediates both acute and chronic inflammatory responses. In the context of diabetes, persistent hyperglycemia triggers the activation of immune cells such as macrophages and T-cells, leading to overproduction of IL-6. Through the JAK/STAT and MAPK signaling pathways, IL-6 amplifies the inflammatory cascade by upregulating the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators, including C-reactive protein (CRP), fibrinogen, and other acute-phase reactants. Moreover, IL-6 exacerbates vascular injury by inducing oxidative stress, impairing endothelial function, and promoting vascular remodeling, thereby contributing to the progression of diabetic vascular complications [4].
In T1D, an autoimmune disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing β cells in the pancreas. This process is marked by the release of various cytokines, including IL-6, which contributes to the inflammatory milieu [4, 5]. In T2D, a metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency, chronic low-grade inflammation is a hallmark feature [5]. IL-6, along with other pro-inflammatory cytokines, is elevated in individuals with T2D and is linked to metabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular complications [4, 5].
Diabetic nephropathy, a common microvascular complication of diabetes, involves structural and functional changes in the kidneys, including glomerular hypertrophy, basement membrane thickening, and podocyte loss [4, 5]. Inflammation plays a significant role in the progression of DN, with cytokines such as IL-6 being key mediators of renal inflammation and fibrosis. IL-6 promotes the production of extracellular matrix proteins and the activation of fibrogenic pathways, thereby exacerbating kidney damage [5]. Inflammation is a critical driver of the progression of DN. Persistent hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress and the activation of resident renal cells such as mesangial cells, podocytes, and endothelial cells, triggering the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6. This inflammatory milieu promotes leukocyte recruitment and the activation of macrophages, perpetuating the inflammatory cascade within the renal microenvironment. Over time, these processes contribute to glomerular and tubulointerstitial damage, progressive fibrosis, and functional decline of the kidneys [5]. IL-6 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that plays a central role in the pathogenesis of renal inflammation and fibrosis. Through activation of the JAK/STAT3 pathway, IL-6 induces the production of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins such as collagen and fibronectin, contributing to the accumulation of fibrotic tissue in the glomeruli and tubulointerstitial space. Additionally, IL-6 stimulates the differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, which are key effector cells in the fibrogenic process. IL-6 also upregulates the expression of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β), a master regulator of fibrosis, further amplifying ECM deposition and suppressing matrix degradation pathways. Together, these mechanisms exacerbate kidney damage and accelerate the progression of DN [4–6]. Research indicates that IL-6 levels are elevated in patients with DN compared to those without nephropathy. Studies have demonstrated a correlation between serum IL-6 levels and the severity of renal impairment, suggesting that IL-6 could serve as a biomarker for DN progression. Furthermore, IL-6 has been implicated in the modulation of endothelial function and the promotion of vascular inflammation, both of which contribute to the pathophysiology of DN [6, 7].
The primary aim of this study is to quantitatively analyze serum cytokine levels, with a specific focus on IL-6, in patients with T1D and T2D. A secondary aim is to investigate the potential correlation between IL-6 levels and the development or progression of DN. By examining these associations, this study seeks to delineate the role of IL-6 as a potential biomarker of renal inflammation and fibrosis in diabetes, offering insights into the inflammatory mechanisms underlying DN. This study is unique in its comparative evaluation of IL-6 levels in both T1D and T2D patients, providing a comprehensive understanding of inflammatory processes across different diabetes subtypes. Unlike previous studies that primarily focus on T2D, our research also addresses T1D, where the role of IL-6 in DN remains underexplored. Additionally, this study contributes to the field by correlating IL-6 levels with early and late markers of diabetic nephropathy, offering potential insights into disease progression and inflammatory mechanisms. By bridging these gaps, our findings may pave the way for the development of targeted therapies aimed at reducing renal inflammation and preventing nephropathy in diabetic patients.
Material and methods
Study design and data collection
A cross-sectional study was conducted among 200 diabetic patients diagnosed with T1D (n = 100) and T2D (n = 100) between January 2022 and December 2023 at the endocrinology and diabetes department of Madinah Hospital, Saudi Arabia. Ethical approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the General Directorate of Health Affairs in Madinah (Project Numbers: IRB22-046 and IRB022-22).
This study included male and female patients aged between 20 and 90 years, who were selected from a cohort of diabetic outpatients at the endocrinology and diabetes clinic at King Fahad Hospital in Madinah. Data were collected from patient files, including demographic information (age and sex), anthropometric measurements (height and weight), and laboratory findings (serum cytokine levels, kidney function tests, and glycemic markers). To ensure data accuracy, all patient files were reviewed by trained research staff, and standardized procedures were used for data extraction and analysis.
Anthropometric measurements
Weight and height were used to calculate the body mass index (BMI) for each participant. The World Health Organization (WHO) cut-offs were used to assess the weight status as follows: “underweight” BMI < 18.5 kg/m2; “healthy weight” 18.5 to 24.9 kg/m2; “overweight” 25.0 to 29.9 kg/m2; “obesity” ≥ 30.0 kg/m2 [8].
Laboratory analysis
The laboratory findings consisted of fasting blood glucose (FBG), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), albumin (blood and urine), creatinine (serum and urine), glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR). The data were collected from patient records and evaluated using the reference range values of the laboratories of Madinah Hospital in the Madinah area of Saudi Arabia. HbA1c is considered a standard blood test that reflects an individual’s average blood glucose levels during the past 3 months and is commonly used for diagnosis and prognosis of diabetes.
The diagnostic criteria for albuminuria were established as a spot urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of 30 mg/g or above. Albuminuria can be classified according to the UACR. Category A1 is characterized by a UACR value below 30. UACR values within the range of 30 to 300 mg/g indicate a normal to moderately elevated state, which is classified as A2. A UACR value above 300 mg/g signifies severe elevation, indicated by category A3 [9].
The GFR is usually expressed in milliliters per minute per 1.73 square meters of body surface area (ml/min/1.73 m2). The classification of GFR is essential for diagnosing the severity of kidney disease, monitoring disease progression, and guiding therapeutic interventions [10].
The stages of chronic kidney diseases (CKD) based on GFR are classified as follows [10]:
Stage 1 CKD: GFR ≥ 90 ml/min/1.73 m2, kidney damage with normal or increased GFR.
Stage 2 CKD: GFR 60–89 ml/min/1.73 m2, mildly decreased GFR.
Stage 3a CKD: GFR 45–59 ml/min/1.73 m2, mildly to moderately decreased GFR.
Stage 3b CKD: GFR 30–44 ml/min/1.73 m2, moderately to severely decreased GFR.
Stage 4 CKD: GFR 15–29 ml/min/1.73 m2, severely decreased GFR.
Stage 5 CKD: GFR < 15 ml/min/1.73 m2, kidney failure.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA)
Blood samples of 3 ml from patients were collected. The blood samples were centrifuged with a force of 1,000 times the acceleration due to gravity for a duration of 10 min at a temperature of 4°C. The plasma was subsequently extracted and divided into separate portions, which were then maintained in freezers at a temperature of –80°C until further analysis of the specific markers was conducted. The levels of IL-10, IL-6, and TNF-α were quantified using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) provided by R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). The assay methods were conducted according to the manufacturer’s instructions (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN).
Statistical analysis
All tests and graphical representations in this study were conducted using GraphPad Prism version 10 (San Diego, USA). Pearson correlation analysis was used to evaluate the strength of correlation between continuous variables, while the unpaired t-test was used to compare median values between two groups. The χ2 test was used to examine the association between two categorical variables. Simple linear regression assessed the association between FBG, HbA1c, GFR, and UACR and the level of IL-6, with the type of diabetes used for data stratification. A 95% confidence level was applied to determine the significance of the data set.
Results
Characteristics of study sample based on type of diabetes
A total of 200 patients diagnosed with either type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus were included in this study. The number of male patients was slightly higher than female patients (54%, n = 108), while more than half of the patients were aged 30–50 years (67.5%, n = 135). About 50% of patients had been diagnosed with diabetes less than 10 years ago. Forty-seven percent of patients had normal weight, while 49.5% of patients were overweight or obese. About 63.5% of patients had a reduced GFR (n = 117), while 46% of patients had albuminuria (n = 92). The detailed characteristics of the participants are presented in Table I.
Table I
Sample characteristics (n = 200)
Table II illustrates the association of the study sample stratified by type of diabetes. Significantly more type 2 diabetic patients were aged more than 50 years old compared to type 1 diabetic patients (100% vs. 0%, p < 0.0001, respectively). Moreover, most of the patients with type 1 diabetes had normal weight, while most type 2 diabetic patients were overweight or obese. The stages of kidney damage were distributed equally among both categories. In contrast, type 1 diabetic patients tended to have moderately increased albuminuria compared to type 2 diabetic patients (53% vs. 37%, p < 0.05).
Table II
Association between characteristics of the study sample and type of diabetes mellites (n = 200)
| Parameter | Type 1 diabetes (n = 100) | Type 2 diabetes (n = 100) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| 21–30 years | 9 (75.0) | 3 (25.0) | < 0.0001* | |
| 31–40 years | 29 (58.0) | 21 (42.0) | ||
| 41–50 years | 62 (72.9) | 23 (27.1) | ||
| 51–60 years | 0 (0.0) | 11 (100.0) | ||
| > 60 years | 0 (0.0) | 42 100.0) | ||
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 50 (46.3) | 58 (53.7) | 0.321 | |
| Female | 50 (54.3) | 42 (45.7) | ||
| Duration of diabetes | ||||
| 1–10 years | 4 (3.8) | 100 (96.2) | < 0.0001* | |
| 11–20 years | 21(100.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| 21–30 years | 42 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| > 30 years | 33 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Weight status | ||||
| Underweight | 6 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | < 0.0001* | |
| Healthy weight | 79 (83.2) | 16 (16.8) | ||
| Overweight | 14 (30.4) | 32 (69.6) | ||
| Obese | 1 (2.0) | 52 (98.0) | ||
| Stages of kidney damage | ||||
| G1 = Normal or elevated GFR (> 90 ml/min/1.73 m2) | 32 (48.5) | 34 (51.5) | 0.620 | |
| G2 = Slightly reduced GFR (60–89 ml/min/1.73 m2) | 35 (57.4) | 26 (42.6) | ||
| G3a = Moderately to mildly decreased GFR (45–59 ml/min/1.73 m2) | 15 (41.7) | 21 (58.3) | ||
| G3b = Moderately to drastically diminished GFR (30–44 ml/min/1.73 m2) | 14 (46.7) | 16 (53.3) | ||
| G4 = Significantly decreased GFR (15–29 ml/min/1.73 m2) | 3 (50.0) | 3 (50.0) | ||
| G5 = Renal insufficiency (GFR < 15 ml/min/1.73 m2) | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Albuminuria categories | ||||
| A1 = Normal to mildly increased (< 30 mg/g) | 47 (43.5) | 61 (56.5) | 0.036* | |
| A2 = Moderately increased (30–299 mg/g) | 53 (58.9) | 37 (41.1) | ||
| A3 = Severely increased (≥ 300 mg/g) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (100.0) | ||
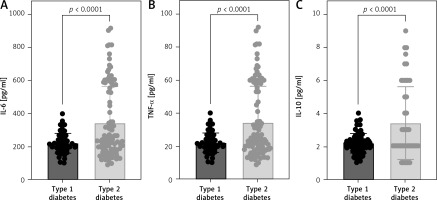
Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels among individuals with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
Serum cytokine levels including IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 were assessed in patients diagnosed with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Interestingly, the level of all studied cytokines was significantly lower among type 1 diabetic patients compared to type 2 (Figure 1). Therefore, further analysis was conducted to assess the influence of these cytokines among patients based on type of diabetes. The strength of the association between the cytokines and biomarkers such as fasting blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin, and renal function markers, including albumin (serum and urine), creatinine (serum and urine), GFR, and UACR, were assessed using Pearson correlation (Table III). IL-6, but not other cytokines, was moderately correlated with serum biomarkers observed among type 1 diabetic patients only (Table III). Both FBG and HbA1c were negatively correlated with the level of serum IL-6 in type 1 diabetic patients (r = –0.318, p < 0.01 and r = –0.319, p < 0.01, respectively). Moreover, renal dysfunction indicators such as GFR and UACR were weakly correlated with serum IL-6 (r = –0.250, p < 0.05 and r = 0.338, p < 0.001, respectively).
Table III
Correlation between the concentration of cytokines and other biomarkers according to the type of diabetes (n = 200)
The impact of IL-6 on the level of FBG and percentage of HbA1c
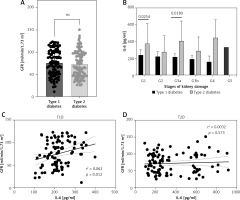
The level of FBG was assessed in both type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients. Interestingly, type 2 diabetic patients had a lower level of FBG compared to type 1 diabetic patients (Figure 2 A). The reduced level of serum IL-6 was associated with a 10% increase in the level of FBG among type 1 diabetic patients (Figure 2 B). However, this was not the case in type 2 diabetic patients (Figure 2 C).
Figure 2
The level of serum IL-6 among type 1 diabetic patients is negatively associated with level of fasting blood glucose (FBG) and percentage of HbA1c
Conversely, HbA1c was significantly reduced in patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes (Figure 2 D). However, the reduced level of serum IL-6 was associated with a 10% increase in the percentage of HbA1c observed only in type 1 diabetic patients (Figure 2 E).
Reduced serum IL-6 level in type 1 diabetic patients is associated with normal kidney function
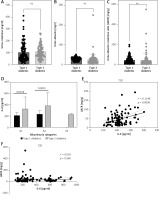
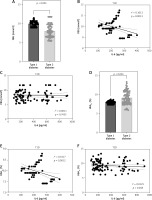
The GFR showed similar levels among patients with both types of diabetes mellitus (Figure 3 A). Although the level of IL-6 was lower among all stages of kidney damage in type 1 compared to type 2 diabetic patients, in stages G1 and G3a the difference was statistically significant (Figure 3 B). The correlation between GFR and IL-6 in type 1 diabetic patients was weak (Table III) but statistically significant (Figure 3 C). Furthermore, urine creatinine and albumin levels did not differ significantly between patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes (Figures 4 A, B). The level of UACR was not signficantly different between type 1 and type 2 patients (Figure 4 C). All the categories of albuminuria in type 1 diabetes showed a lower level of serum IL-6 compared to type 2 diabetic patients (Figure 4 D). Interestingly, the level of IL-6 was significantly positively associated with the level of albuminuria only among type 1 diabetic patients (Figures 4 E, F).
Discussion
This study provides valuable insights into the relationship between serum cytokine levels, particularly IL-6, and DN in patients with T1D and T2D. The cohort demographics, metabolic profiles, and kidney function parameters highlight significant differences between the two diabetes types and their potential implications for diabetic complications. The cohort consisted of a slightly higher proportion of male patients (54%) and was predominantly aged between 30 and 50 years (67.5%). The observation that approximately half of the patients were diagnosed with diabetes less than 10 years ago is consistent with the rising incidence of diabetes and its early diagnosis in younger populations. Weight distribution analysis revealed that nearly half of the patients had a normal weight, while the other half were overweight or obese, reflecting the well-documented association between obesity and T2D. The significant finding that all T2D patients were over 50 years old compared to none in the T1D group (p < 0.0001) underscores the age-related risk factors and pathophysiological differences between T1D and T2D. T1D is primarily an autoimmune condition often diagnosed in younger individuals, while T2D is more commonly associated with aging and lifestyle factors, such as obesity and physical inactivity. A reduced GFR was observed in 63.5% of patients, and 46% exhibited albuminuria, indicating a substantial burden of kidney damage among the cohort. The equal distribution of kidney damage stages between T1D and T2D patients suggests that both groups are equally susceptible to DN, despite their differing etiologies. However, the higher prevalence of moderately increased albuminuria in T1D patients (53% vs. 37%, p < 0.05) may indicate more pronounced early glomerular injury in T1D, potentially due to the autoimmune nature of the disease and its impact on the renal microvasculature [11, 12]. Previous studies have shown that albuminuria is a critical predictor of DN progression and cardiovascular events in both T1D and T2D patients. For instance, Gross et al. reported that albuminuria prevalence is higher in T1D patients, which aligns with our findings [12]. Furthermore, Perkins et al. found that early albuminuria in T1D patients often precedes more severe nephropathy, underscoring the importance of early detection and management [13].
Serum cytokine analysis revealed significantly lower levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 in T1D patients compared to T2D patients. IL-6 levels showed moderate negative correlations with FBG (r = –0.318, p < 0.01) and HbA1c (r = –0.319, p < 0.01) in T1D patients, indicating that higher glucose levels are associated with lower IL-6 levels in T1D. Additionally, IL-6 is weakly correlated with renal function indicators, such as GFR and urine UACR, suggesting that IL-6 may have a role in renal dysfunction in T1D patients.
Previous research supports the differential expression of cytokines in T1D and T2D [3, 14, 15]. These studies highlighted that T2D is often characterized by a chronic low-grade inflammatory state with elevated cytokine levels, including IL-6, which is linked to insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction. By contrast, in T1D, the autoimmune destruction of β-cells triggers an initial inflammatory response, but chronic inflammation may not be as pronounced, which could explain the lower IL-6 levels observed in our study. The role of IL-6 in T1D is complex and involves both pro-inflammatory and regulatory functions. For example, during the autoimmune attack on pancreatic β-cells, IL-6 is produced by immune cells infiltrating the islets. It contributes to the inflammatory milieu that accelerates β-cell destruction. Elevated levels of IL-6 have been observed in the sera of newly diagnosed T1D patients, indicating its role in the early stages of the disease. Also, IL-6 influences glucose metabolism by affecting insulin sensitivity. In T1D, despite its involvement in β-cell destruction, IL-6’s impact on peripheral tissues’ insulin sensitivity remains an area of active research, with studies indicating both positive and negative effects on glucose uptake and metabolism [16–18].
Interestingly, T2D patients exhibited lower FBG levels compared to T1D patients, and the reduced IL-6 level was associated with a 10% increase in FBG and HbA1c among T1D patients. This relationship was not observed in T2D patients, highlighting distinct inflammatory and metabolic dynamics between the two diabetes types. The weak correlation between GFR and IL-6 in T1D patients, despite statistical significance, further emphasizes the complexity of cytokine interactions in diabetic nephropathy. Furthermore, IL-6 plays a significant role in the development and progression of diabetic complications, particularly DN. IL-6 contributes to the pathogenesis of DN by promoting inflammation and fibrosis in the kidneys. Elevated IL-6 levels have been linked to increased albuminuria and a decreased GFR, key markers of kidney damage in diabetes. The comparable levels of urine creatinine and albumin between T1D and T2D patients, along with similar UACR levels, suggest that traditional markers of renal function may not fully capture the inflammatory nuances associated with DN [19–21]. The significantly lower IL-6 levels in T1D patients across all albuminuria categories point to a potentially protective role of IL-6 against albuminuria in T1D. However, this protective aspect appears to be overshadowed by IL-6’s pro-inflammatory role in the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Given its central role in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy, IL-6 is a potential therapeutic target. IL-6 inhibitors, such as tocilizumab, have shown promise in reducing inflammation and fibrosis in preclinical models of diabetic nephropathy, and clinical trials are underway to evaluate their efficacy in patients [22]. While preclinical studies have demonstrated the therapeutic potential of targeting IL-6 in DN, several challenges need to be addressed before these strategies can be translated into clinical practice. Collectively, these findings support the hypothesis that IL-6 plays a critical role in the development of diabetic nephropathy, particularly in T1D patients. The moderate correlation of IL-6 with glucose control markers and its weak association with renal dysfunction indicators underscore its complex role in the inflammatory pathways contributing to diabetic complications. Future studies should focus on elucidating the precise mechanisms by which IL-6 modulates renal pathology in diabetes and explore targeted interventions that may mitigate its deleterious effects.
Study limitations. While the study provides valuable insights into the association between IL-6 levels and DN in patients with T1D and T2D, several limitations should be acknowledged: the cross-sectional design of the study limits the ability to establish causality between IL-6 levels and diabetic nephropathy. Longitudinal studies are needed to assess the temporal relationship and determine whether changes in IL-6 levels precede or follow the development of diabetic kidney disease. Moreover, the modest sample size in this study may limit the generalizability of our findings. While our results provide valuable insights, particularly regarding IL-6 levels, larger cohort studies are required to validate these findings and strengthen the conclusions. A larger, multicenter cohort with a diverse patient population would provide more robust and representative results. The study did not account for potential confounding factors that may influence IL-6 levels and diabetic nephropathy, such as comorbidities (e.g., hypertension), medication use (e.g., anti-inflammatory drugs), and lifestyle factors (e.g., smoking, diet). Addressing these limitations in future research would strengthen the evidence base and enhance our understanding of the role of IL-6 in the pathogenesis and progression of diabetic kidney disease.
In conclusion, IL-6 plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of DN by promoting renal inflammation, fibrosis, and endothelial dysfunction. Strategies aimed at reducing IL-6 levels or blocking its downstream signaling pathways hold promise for the prevention and treatment of DN. However, further preclinical and clinical studies are needed to fully elucidate the therapeutic potential of IL-6 inhibition in diabetic kidney disease.