Understanding the correlation between autophagy rate and cardiomyocyte survival could be beneficial for preventing and treating cardiovascular diseases [1]. Uncontrolled autophagy can induce a type of cell death called autosis [2]. Different stress-induced conditions promote cardiomyocyte autosis and myocardial injury [3]. Some evidence points to the essential role of sodium/potassium-adenosine triphosphates (Na+/K+-ATPase) in autosis because, along with autophagy inhibitors, Na+/K+-ATPase antagonists prevent autosis [2, 4]. Moreover, Na+/K+-ATPase interacts with the autophagy protein Beclin-1 when autosis occurs [2, 4].
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) is one of the potent regulators of Na+/K+-ATPase activity, as demonstrated by us and other authors [5, 6]. The actions of IGF-1 are mediated through IGF receptors (IGFR), insulin receptor (IR), and a hybrid receptor composed of components from both the IGFR and the IR (IGFR/IR) [7]. The protein kinase B (Akt) pathway is recognized as one of the signaling pathways via which the effects of IGF-1 are mediated. The involvement of Akt in autophagy regulation is dominantly through the regulation of forkhead box O (FOXO) transcription factor [8]. Additionally, IGF-1 regulates nutrient-sensitive signaling molecules such as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which is important in autophagy regulation [9]. FOXO1 and AMPK regulate Beclin-1, an essential autophagy molecule whose role depends on association with different proteins, enabling the cell response to diverse autophagy stimuli [10, 11]. Despite the ineffectiveness of therapeutic strategies targeting various types of cell death in treating myocardial injury, the suppression of autosis resulted in reduced infarct size, suggesting the importance of autosis regulation in stress-induced damage in the heart. Since signaling mechanisms involved in autosis are distinct from those governing apoptosis and necrosis, a comprehensive investigation of signaling pathways involved in autosis and the underlying mechanism by which IGF-1 influences autosis in cardiac tissue is of great importance. Furthermore, considering the autocrine/paracrine actions of locally produced IGF-1, examining the distinct signaling molecules involved in the IGF-1 transduction cascade, which are associated with the cardiomyocyte autosis, may yield valuable insights for developing novel therapeutic approaches.
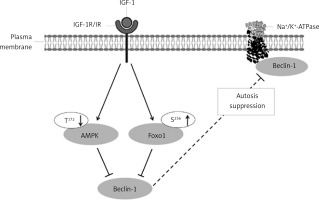
This study hypothesized that IGF-1 might directly affect cardiac autosis by reducing Na+/K+-ATPase and Beclin-1 interaction by activating IGF-1R/IR and suppressing AMPK and FOXO1 signaling (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Potential mechanism for the in vivo effects of IGF-1 on the modulation of autosis in the rat heart. IGF-1 binds to the receptor at the plasma membrane, which induces autophosphorylation and activation. Activated receptor regulates downstream molecules such as AMPK and FOXO-1 and Beclin-1 and Na+/K+-ATPase interaction
AMPK – AMP-activated protein kinase, FOXO1 – forkhead box protein O1, IGF-1 – insulin-like growth factor-1, IGF-1R/IR – IGF-1 receptor β/insulin receptor β receptor, Na+/K+-ATP-ase – sodium/potassium adenosine triphosphatase, PI3K – phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase, S – serine, T – threonine, ↓ – decrease, ↑ – increase, ⊥ – inhibition.
Methods
In order to test our hypothesis, we used the hearts of adult male Wistar rats, fed with a balanced diet for laboratory rats and water ad libitum. A total of 14 animals were divided into 2 groups (n = 7). Half of the rats were treated intraperitoneally with a bolus injection of 50 µg/kg of IGF-1 (Sigma-Aldrich) dissolved in saline (IGF-1 group), while another half of the rats were injected with saline (CONT group). After 24 h, animals were euthanized with 80 mg/kg of ketamine and 12 mg/kg xylazine. The hearts of the rats were excised and homogenized for further analysis. The Vinca Institute’s official Ethics Committee for Experimental Animals approved the experimental treatment (Veterinary Directorate – No. 323-07-02710/2017-05).
The interaction of Beclin-1 with the α1 subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase in the heart tissue of rats was measured by co-immunoprecipitation. Heart plasma membrane fractions (500 µg of protein) were incubated overnight at 4°C with 2 µg of antibody against Beclin-1 (Santa Cruz). Immunocomplexes were absorbed with protein A/G-Sepharose, incubated overnight at 4°C, and then recovered by centrifugation at maximum speed for 5 min. Pellets were centrifuged, washed three times with buffer, and separated on SDS-PAGE gel. After separation, immunocomplexes were transferred to the polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane and probed with an antibody against the α1 subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase (Santa Cruz). Membranes were subsequently washed, incubated with an appropriate secondary antibody and used for detection using an electrochemiluminescence method. Scanned films were quantified using Image J 1.45s software (National Institutes of Health, USA).
In order to obtain a deeper understanding of the mechanism via which IGF-1 regulates the interplay between Na+/K+-ATPase and Beclin-1 in the cardiac tissue of rats, we conducted an analysis utilizing Western blotting to quantify the phosphorylation levels of IGF-1R/IR, FOXO1, and AMPK proteins. Total protein lysates and plasma membrane protein fractions were separated using SDS-PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes. Membranes were probed with antibodies (Cell Signaling) directed against phospho-IGF-1Rβ (Tyr1131)/IR β (Tyr1146), IR β, FOXO1 and phospho-FOXO1 (Ser256), AMPK and phospho-AMPK (Thr172). The blots were reprobed with mouse monoclonal anti-β-actin (Santa Cruz) antibody to ensure equal loading. The signals were quantified using Image J 1.45s software.
Results
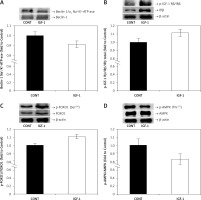
Autosis occurs in the heart in different physiological and pathophysiological conditions; therefore, suppression of autosis may reduce cardiomyocyte death and minimize myocardial injury. Although the molecular mechanism of autosis is currently under extensive research, the association of the autophagy protein Beclin-1 and Na+/K+-ATPase is required [2–4]. Our study was designed to explore the role of IGF-1 in autosis regulation and the potential mechanism of Na+/K+-ATPase engagement. Thus, we examined the in vivo effect of IGF-1 on the association of Beclin-1 with the α1 subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase. The results showed that the association of Beclin-1 and the α1 subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase was lower (p < 0.05) in IGF-1-treated rats compared to control rats (Figure 2 A). Since IGF-1 initiates a signaling pathway in the cell after binding to its receptor at the plasma membrane, some evidence suggests that IGF-1 binds to the IGF/IR hybrid receptor with high affinity, probably making it the dominant activator [7]. Thus, we investigated whether IGF-1 treatment affects the protein expression of p-IGF-1Rβ (Tyr1131)/IRβ (Tyr1146). We found that the p-IGF-1R/IR/IR ratio was increased (p < 0.05) in IGF-1-treated rats compared to non-treated rats (Figure 2 B). Beclin-1 is a central factor of autophagy that forms complexes with different proteins and is regulated by various signaling molecules, including FOXO-1 and AMPK [12, 13]. We further examined the phosphorylation of FOXO1 and AMPK, important autophagy-related signaling molecules, in the heart of IGF-1-treated rats. The phosphorylation of FOXO1 on Ser256 leads to nuclear exclusion of the cytoplasm, resulting in the eventual inactivation of FOXO1. Our results indicate that the phosphorylation of FOXO1 on Ser256 was increased (p < 0.01) (Figure 2 C), while AMPK on Thr172 was decreased (p < 0.01) in IGF-1-treated rats compared to control rats (Figure 2 D).
Figure 2
Effects of IGF-1 on the association of the α1 subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase with Beclin-1 and phosphorylation of IGF-1R/IR, FOXO1 and AMPK in rat hearts. A – The y-axis represents the association level between Beclin-1 and Na+/K+-ATP-ase, and the x-axis represents treatment. Inserts: representative western blots. B – The y-axis represents p-IGF-Rβ/IRβ as fold changes vs. protein expression of IRβ, and the x-axis represents treatment. Inserts: representative western blots. C – The y-axis represents FOXO1 phosphorylated on Ser256 as fold changes vs. total FOXO1, and the x-axis represents treatment. Inserts: representative western blots. D – The y-axis represents AMPK phosphorylated on Thr172 as fold changes vs. total AMPK, and the x-axis represents treatment. Inserts: representative western blots. The results for phosphorylation and expression are expressed as a percentage of the value obtained for the control and represent mean ± SEM (CONT: arbitrarily set at 1)
AMPK – AMP-activated protein kinase, CONT – control group, FOXO1 – forkhead box protein, IGF-1 – insulin-like growth factor-1 treated group, Na+/K+-ATP-ase – sodium/potassium adenosine triphosphatase, p-IGF-1Rβ/IRβ – phospho-IGF-I receptor β (Tyr1131)/insulin receptor β (Tyr1146), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Discussion
Following an injury, the heart has a limited potential for regeneration, increasing the risk of cardiomyocyte loss and decreased cardiac function. Due to the low regenerative capacity of cardiomyocytes, the important function of IGF-1 in promoting cell survival becomes evident in the heart, where diverse stresses can induce autosis and subsequent cardiomyocyte death [14]. Moreover, IGF-1 protects against the disruption of cardiac autophagy induced by various stressful conditions. Na+/K+-ATPase is a membrane protein that is required for normal cellular function. Cardiomyocyte function primarily relies on the activity of Na+/K+-ATPase. Additionally, Na+/K+-ATPase acts as a scaffolding and signaling molecule since exposing cells to Na+/K+-ATPase antagonists induces activation of various signaling pathways [15]. Tight regulation of Na+/K+-ATPase is significant in the heart since numerous pathologies correlate with aberrant Na+/K+-ATPase activity [15]. The literature data suggest that Na+/K+-ATPase plays a crucial role in the regulation of autophagy and is necessary for autosis to occur [3]. Autosis occurs in different stress-induced conditions, which subsequently lead to myocardial injury [3, 4]. In physiological conditions such as starvation or exercise, the interaction of Na+/K+-ATPase and the autophagy protein Beclin-1 was elevated, suggesting an increased autotic cell death rate. In addition, autosis occurs during the late phase of reperfusion following a period of ischemia, contributing to myocardial injury. Based on the results obtained from our study, it was observed that the interaction between Na+/K+-ATPase and Beclin-1 exhibited a reduction in the cardiac tissues of rats subjected to IGF-1 treatment. Considering that Na+/K+-ATPase and Beclin-1 association is essential for autosis, our results indicate that IGF-1 may be a potent antagonist for cardiac autosis.
In order to gain a better understanding of how IGF-1 regulates autosis, we conducted additional research into the potential mechanisms by which IGF-1 has this effect. Some data suggest that IGF-1 binds to IGF-1R/IR with high affinity, making it the primary activator of IGF-1 [7]. Our results indicate that exogenous IGF-1 recruits IGF-1R/IR by increasing its phosphorylation in the plasma membrane fraction of rat hearts. Because this particular form of the hybrid receptor is considered specific for IGF-1 [7], the influence on autosis in the hearts of IGF-1-treated rats is a consequence of this action. To gain more insight into the mechanism of autosis regulation by IGF-1, we further examined the involvement of FOXO1 and AMPK – key molecules involved in different autophagy stages – in IGF-1 regulation of autosis [8–10]. Beclin-1 is a crucial component in autophagy; it forms complexes with various proteins, and its activity is controlled by several different signaling molecules, including AMPK and FOXO1 [10, 11]. In MDA-MB-231 cells treated with an autophagy stimulant (paclitaxel), knocking down FOXO1 expression decreased Beclin-1 gene expression and the autophagy rate [12]. According to these results, FOXO1 is vital in autophagy initiation and regulation of Beclin-1 expression and influences autosis. Based on our results showing that IGF-1 treatment decreased FOXO1 activity by phosphorylating it, we assume that this IGF-1 action also decreased Beclin-1’s interaction with Na+/K+-ATPase, which affected autosis. According to other studies that confirmed the abolishing effect of IGF-1 on AMPK activity in vitro in diverse cells, the decreased AMPK activation in response to IGF-1 treatment shown in our study aligns with these findings [9, 13]. According to the current study’s findings, the protective effect of IGF-1 in cardiomyocytes may be due to its capacity to reduce AMPK phosphorylation. This is significant because AMPK plays a vital role in regulating many physiological processes to maintain cardiomyocyte homeostasis, and its overexpression has been associated with heart failure [10]. Furthermore, a study with HEK293T cells, challenged with glucose starvation and pretreated with AMPK inhibitors, showed suppressed Beclin-1 activation [13]. These results suggest the importance of AMPK regulation of Beclin-1, and therefore in autosis, which can be related to our results showing that IGF-1 via decreasing AMPK activation reduced interaction of Na+/K+-ATPase with Beclin-1 and suppressed autosis [14].
Na+/K+-ATPase is considered as a promising therapeutic target [15]. Cardiotonic steroids are one of the most commonly used drugs that induce Na+/K+-ATPase inhibition and a subsequent positive inotropic effect. Cardiotonic steroids are used for treating various conditions such as persistent heart failure symptoms, heart rate management, hypertension, renal failure and cardiovascular disease. Among innovative drugs, the DRm217 antibody targets the DR extracellular region of the Na+/K+-ATPase α1 subunit and enhances Na+/K+-ATPase activity, providing a protective effect against ischemic injury and cardiac remodeling. In addition, genetic silencing and pharmacological inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase are deleterious for autosis in vitro [3].
Even though the requirement of Na+/K+-ATPase in autosis is established, additional investigation is necessary to unravel the molecular mechanisms of Na+/K+-ATPase involvement in autosis. Investigating the modulation of myocardial Na+/K+-ATPase activity and expression in the presence of different agents in animal models could contribute to better understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying autosis associated with Na+/K+-ATPase. Since IGF-1 has positive effects on the cardiovascular system and is one of the most potent Na+/K+-ATPase stimulators, additional basic and human intervention studies are required in order to enhance understanding and elucidate the potential relevance and safety considerations of IGF-1 effects in autosis.
In conclusion, the current study is the first to investigate how exogenous IGF-1 impacts rat cardiac autosis by diminishing the association of Beclin-1 with the α1 subunit of Na+/K+-ATPase in the rat heart. We propose that this outcome is achieved by activating IGF-1R/IR, a hybrid receptor, while simultaneously suppressing the signaling pathways of AMPK and FOXO-1. Thus, our results indicate that the administration of IGF-1 may help prevent autosis in cardiac tissue.