Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
Insights Into the Role of miR-877 and Histidine-Rich Glycoprotein in Preeclampsia
1
Clinical Biochemistry Department, Faculty of Medicine, University of Jeddah, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
2
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Egypt
3
Medical Genetics Department, Faculty of Medicine, University of Jeddah, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
4
Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine Department, College of Medicine, Alfaisal University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
5
Obstetrics & Gynecology Department, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Egypt
Submission date: 2023-11-25
Final revision date: 2024-06-29
Acceptance date: 2024-06-30
Online publication date: 2024-07-03
Corresponding author
Abeer Fouad Zakariyah
Medical Genetics Department, Faculty of Medicine, University of Jeddah, Jeddah, 23218, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Medical Genetics Department, Faculty of Medicine, University of Jeddah, Jeddah, 23218, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The clinical significance of miR-877 and histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG) in preeclampsia (PE) remains unknown. Bioinformatics analyses have identified HRG as a target for numerous micro RNAs. Based on novelty and target score, miR-877 was selected for this study to assess the clinical significance of miR-877 and HRG in placental and serum samples from patients with PE, with the aim of elucidating their potential role in disease progression.
Material and methods:
This study included 75 placental tissue samples and 75 serum samples obtained from patients with PE and normal controls. The PE group was subdivided into mild and severe cases. Relative quantification of miR-877 and HRG was performed using quantitative reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively.
Results:
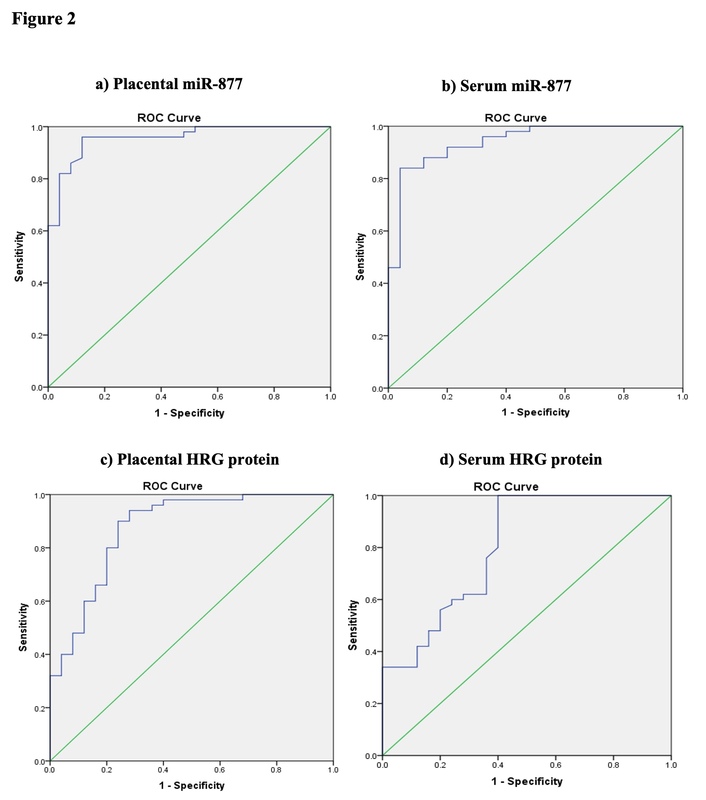
Placental and serum miR-877 levels were significantly elevated in pregnancies with PE, especially in severe cases, compared to normal controls. However, there were significant reductions in HRG serum levels along with significant increases in placental HRG levels among patients with PE. Moreover, significant differences in miR-877 and HRG levels were noted between the PE and control groups.
Conclusions:
miR-877 and HRG may play a role in the pathogenesis and progression of PE. Moreover, miR-877 potentially plays a role in the dysregulation of HRG. In addition, these molecules are potential biomarkers for the detection of PE as well as differentiation of mild and severe cases.
The clinical significance of miR-877 and histidine-rich glycoprotein (HRG) in preeclampsia (PE) remains unknown. Bioinformatics analyses have identified HRG as a target for numerous micro RNAs. Based on novelty and target score, miR-877 was selected for this study to assess the clinical significance of miR-877 and HRG in placental and serum samples from patients with PE, with the aim of elucidating their potential role in disease progression.
Material and methods:
This study included 75 placental tissue samples and 75 serum samples obtained from patients with PE and normal controls. The PE group was subdivided into mild and severe cases. Relative quantification of miR-877 and HRG was performed using quantitative reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, respectively.
Results:
Placental and serum miR-877 levels were significantly elevated in pregnancies with PE, especially in severe cases, compared to normal controls. However, there were significant reductions in HRG serum levels along with significant increases in placental HRG levels among patients with PE. Moreover, significant differences in miR-877 and HRG levels were noted between the PE and control groups.
Conclusions:
miR-877 and HRG may play a role in the pathogenesis and progression of PE. Moreover, miR-877 potentially plays a role in the dysregulation of HRG. In addition, these molecules are potential biomarkers for the detection of PE as well as differentiation of mild and severe cases.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.