Introduction
Glioblastoma multiforme ranks highest in cancer-related deaths caused by intracranial malignant diseases [1]. It alone accounts for more than 30% of all the primary tumors detected in human brain globally [1]. The studies have contributed significantly in understanding the genetic and cellular basics of glioblastoma multiforme but the poor prognosis has not been overcome to date [2]. The average survival of glioblastoma multiforme patients after diagnosis has been reported as only 2 years [3]. Gliomas of low grade gradually develop into high grade with varied kinetics depending on the patient [3]. Studies on glioblastoma multiforme have led to development of novel treatment strategies such as the NovoTTF-100A system and therapeutic molecules such as temozolomide [4, 5]. These anti-glioblastoma treatment strategies are insufficient because inhibition of a single target is compensated by activation of another pro-survival signaling pathway [6]. Thus there is urgent need for a more effective chemotherapeutic strategy to target pro-survival and promote pro-apoptotic pathways for glioblastoma multiforme treatment.
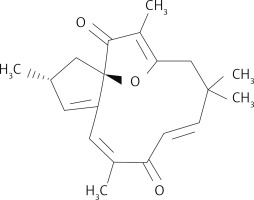
Naturally occurring compounds have shown prominent chemotherapeutic and radio sensitizing activities for various types of diseases. Resveratrol, a phenolic compound present in red grapes, has potential to inhibit growth of different types of carcinoma cells such as brain, ovary and breast cancer cells [7–9]. Saponins isolated from Ardisia pusilla inhibit lung and glioblastoma cell growth via induction of apoptosis [10, 11]. These molecules target vital enzymes associated with pro-survival pathways such as phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mTOR and NF-κB [12]. Moreover, the apoptosis inhibitors and members of the Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic protein family are also targeted by these chemotherapeutic compounds [12]. Jatrophone is a macrocyclic molecule consisting of diterpenoid structure with an oxaspiro core and many centers suitable for electrophilic attack [13–15]. The compound is a present in Jatropha isabelli and Jatropha gossypiifolia plants, which belong to the Euphorbiaceae family. Jatrophone was found to display anti-tumor, anti-malarial and anti-inflammatory activities [12–15]. The present study investigated the anti-glioblastoma potential of jatrophone (Figure 1) for U87MG and A172 cells glioma cells. The molecular mechanism associated with jatrophone-mediated inhibition of glioma cell growth was also explored.
Material and methods
Cell lines
The U87MG and A172 glioblastoma cells were purchased from the cell bank of the Fourth Military Medical University, China. The culture of cells was carried out in DMEM medium mixed with newborn calf serum (10%; Invitrogen) at 37°C in an incubator under humid atmosphere of 5% CO2 and 95% air. After 24 h, serum free medium mixed with jatrophone was put into the plates. Primary astrocytes used in the study were gifted by Dr. Zhang from the Fourth Military Medicine University.
Cell proliferation assay
Changes in primary astrocyte, U87MG and A172 cell proliferation by jatrophone were measured by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The cells were treated with 1.25, 2.5, 3.75, 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5 and 15 µM jatrophone in DMEM medium for 72 h at 37°C in an incubator. MTT solution with final concentration of 5 mg/ml was added to the plates and incubation was performed for 4 h. The medium was removed and 120 µl of DMSO was put in each well of the plate. The formation of formazan crystals from MTT was measured by microplate reader (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules. CA) at 485 nm wavelength.
Electron microscopy
Morphological changes in primary astrocytes, U87MG and A172 cells by jatrophone were detected by electron microscopy. The cells at 2.5 × 106 cells per cm2 density in T-150 flasks were treated with 4.8 µM jatrophone for 72 h. Trypsinization of cells with 0.25% trypsin was followed by centrifugation for 20 min at 1,200 xg. The cell pellets were subjected to fixing and subsequently embedded on cover slips. The 70-micron thin sections of cell layers were sliced using an ultramicrotome and stained using uranyl acetate and lead citrate dyes. The changes in morphology were detected under an electron microscope (JEM-2000EX, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan)
Hoechst 33342 staining
The apoptotic nuclear changes by jatrophone in primary astrocytes, U87MG and A172 cells were detected using Hoechst 33342 dyes. The cells put in 6-well plates at 2 × 106 cells per well distribution were treated with 4.8 µM jatrophone for 72 h. The harvested cells after washing in PBS were subjected to fixing for 3 h in 70% ethyl alcohol at 4°C. Then cells were incubated for 5 min with Hoechst 33342 dye at 25°C, washed in PBS and visualized under a fluorescence microscope (Wetzlar, Germany) for apoptotic nuclear changes.
Annexin V/propidium iodide assay
The apoptotic cell fraction was subjected to semi-quantification by flow cytometry using Annexin V-FITC/PI Kit (Immunotech Co., Marseille, France). The primary astrocytes, U87MG and A172 cells were distributed in 60-mm dishes at 1 × 105 cells per dish concentration and treated with 4.8 µM jatrophone for 72 h. After harvesting, the cells were rinsed in PBS and then incubated for 20 min with Annexin-V (5 µl) and PI (5 µl) dyes (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) under darkness. The apoptotic cells were detected by flow cytometry and data analyzed using Modfit software (House, Inc., Topsham, ME).
Immunocytochemical analysis
The immune-reactive score for expression of nuclear NF-κB p65 was evaluated using immunocytochemistry as previously reported [15]. Briefly, primary astrocytes, U87MG and A172 cells were treated with 4.8 µM jatrophone. Following treatment, the cells were subjected to incubation with anti-NF-κB p65 rat monoclonal antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) for 2 h and then with biotinylated rabbit anti-mouse IgG secondary antibodies.
Western blot analysis
Primary astrocytes, U87MG and A172 cells were treated with 4.8 µM jatrophone for 72 h and the lysed in RIPA buffer (sodium chloride (150 mM), NP-40 (1%), sodium deoxycholate (0.5%), SDS (0.2%), tris-hydrochloride (50 mM at pH 8.0), EDTA (10 mM) and PMSF (1 mM; Sigma, Chemical, St. Louis, MO) for 45 min at 4°C. The lysate clarification was carried out by centrifugation at 14,000 xg for 25 min followed by determination of protein concentration using the BCA protein Assay Kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL). The equal protein quantities were resolved by electrophoresis on 12% SDS-PAGE and then transferred onto PVDF membranes (Millipore, MA, USA). Blocking of the membranes was performed by incubation at room temperature with TBS containing Tween-20 (0.1%) and 5% milk. Incubation with primary antibodies was carried out at 4°C overnight. Then PBS washed membranes were incubated for 2 h with HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibodies. Immunoreactive protein bands were subjected to visualization using an ECL Advance Detection kit (GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences, Tokyo, Japan). The following primary antibodies were used: anti-p65 (1 : 300, mouse monoclonal), anti-survivin (1 : 300, mouse monoclonal), anti-XIAP (1 : 300, mouse monoclonal), anti-Bax (1 : 600, rabbit polyclonal), anti-Bcl-2 (1 : 600, rabbit polyclonal), anti-cleaved caspase-9 (1 : 600, rabbit polyclonal), anti-cleaved caspase-3 p11 (1 : 600, rabbit polyclonal), and anti-β-actin (1 : 600, rabbit polyclonal).
Determination of nuclear NF-κB
The fractionation of cellular lysate was performed using a Qproteome Nuclear Kit (Qiagen) to obtain the nuclear and cytosolic fractions in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The protein content in the fractions was quantified and then detected for NF-κB level by western blotting using anti-p65 antibodies.
Statistical analysis
The data presented are mean ± standard deviation (SD) of triplicate experiments. The data comparison was performed statistically by Student’s t-test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Bonferroni multiple test. Analysis of the data was performed statistically using the SPSS 13.0 software. The level of p < 0.05 was taken to represent statistically significance differences.
Results
Suppression of U87MG and A172 cell viability by jatrophone
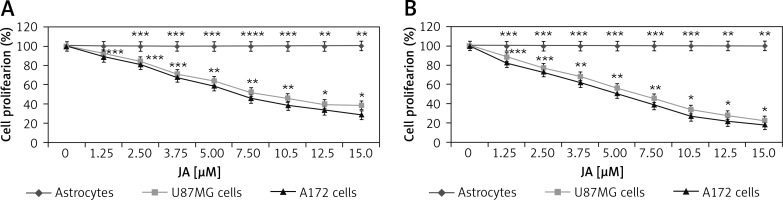
Cytotoxicity of jatrophone on U87MG and A172 cells was measured at 24 and 72 h on treatment with 1.25, 2.5, 3.75, 5.0, 7.5, 10, 12.5 and 15 µM by MTT assay (Figure 2). The proliferative potential of U87MG and A172 cells was suppressed by jatrophone significantly depending on dose and treatment duration. Suppression of proliferation by jatrophone was slightly more prominent in A172 cells relative to U87MG cells. Treatment with jatrophone (15 µM) suppressed U87MG and A172 cell proliferation to 38.7 ±1.2 and 29.4 ±0.8%, respectively at 24 h. The IC50 of jatrophone for U87MG and A172 cells at 24 h was 7.8 and 6.5 µM, respectively. Jatrophone (15 µM) treatment for 72 h suppressed proliferation of U87MG and A172 cells to 22.5 ±0.8 (IC50 4.8 µM) and 18.6 ±0.4% (IC50 3.8 µM), respectively. Moreover, jatrophone treatment for 72 h could not change the proliferation of primary astrocytes.
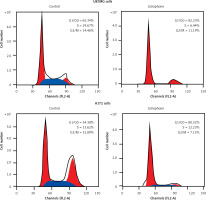
Jatrophone-induced apoptosis in U87MG and A172 cells
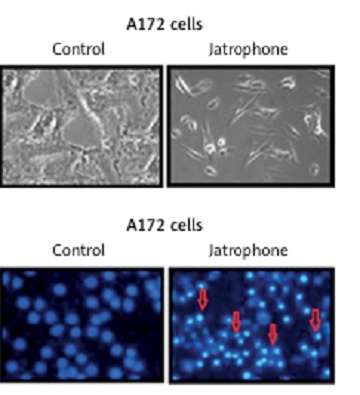
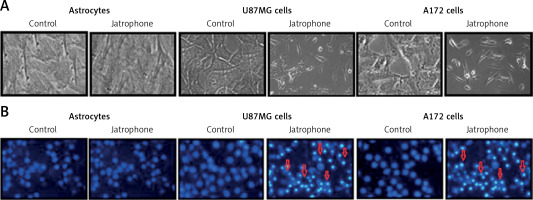
Treatment with jatrophone (4.8 µM) for 72 h significantly induced apoptosis in U87MG and A172 cells (Figure 3 A). The morphological features of jatrophone-treated U87MG and A172 cells showed apoptotic changes such as shrinking, cell detachment and aggregation. Apoptotic changes were not seen in the primary astrocytes treated with jatrophone for 72 h. Induction of apoptosis by jatrophone treatment in U87MG and A172 cells was also confirmed using Hoechst 33342 staining (Figure 3 B).
Figure 3
Effect of jatrophone on U87MG and A172 cell apoptosis. The vehicle-control or jatrophone-treated cells were observed for apoptotic changes morphologically. A – The morphological changes in U87MG and A172 cells were observed using inverted microscopy. B – The nuclear apoptotic changes were detected using Hoechst 33342 staining by flow cytometry
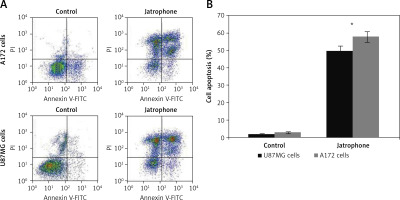
The jatrophone-induced apoptotic changes in U87MG and A172 cells were semi-quantified using AnnexinV/PI assay (Figures 4 A, B). Treatment with jatrophone (4.8 µM) for 72 h increased apoptosis in U87MG and A172 cells to 49.5 ±2.3 and 57.7 ±2.6%, respectively. The apoptotic fraction of vehicle control U87MG and A172 cells was 1.89 ±0.2 and 2.87 ±0.4%, respectively.
Jatrophone caused cell cycle arrest in U87MG and A172 cells
In jatrophone (4.8 µM) treated U87MG and A172 cells the G1/G0 phase cell population was significantly (p < 0.05) increased (Figure 5). Flow cytometry of jatrophone-treated U87MG and A172 cells showed a decrease in the S and G2/M phase cell population compared to control cells. This revealed that jatrophone arrests cell cycle in U87MG and A172 cells in G1/G0 phase.
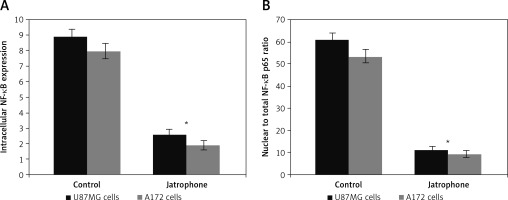
Jatrophone reduced NF-κB expression and its nuclear translocation
The intracellular NF-κB p65 level in U87MG and A172 cells was suppressed significantly on treatment with jatrophone at 72 h (Figure 6 A). The intracellular NF-κB p65 score in U87MG cells was decreased to 2.6 ±0.4 on treatment with jatrophone compared to 8.9 ±0.9 in vehicle control. Similarly, in A172 cells the score was decreased to 1.9 ±0.4 by jatrophone treatment relative to 8.0 ±0.8 in the vehicle control. The score of nuclear to total NF-κB p65 ratio in U87MG cells was suppressed by jatrophone from 61.2 ±2.8 to 11.3 ±0.9%. In A172 cells the score of nuclear to total NF-κB p65 ratio was reduced from 53.5 ±2.7 to 9.5 ±0.7% by jatrophone treatment (Figure 6 B).
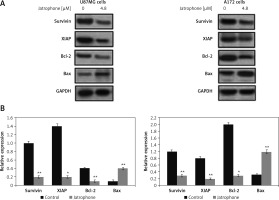
Jatrophone suppressed IAPs
The expression of survivin and XIAP in U87MG and A172 cells was reduced markedly by jatrophone treatment at 4.8 µM (Figure 7). The level of endogenous Bcl-2 was markedly higher and Bax expression very weak in U87MG and A172 cells. Treatment with jatrophone suppressed Bcl-2 and elevated Bax expression in U87MG and A172 cells. The Bcl-2/Bax ratio in U87MG and A172 cells was decreased by treatment with jatrophone. However, no change in Bcl-2/Bax ratio in U87MG and A172 cells was observed on treatment with jatrophone in primary astrocytes.
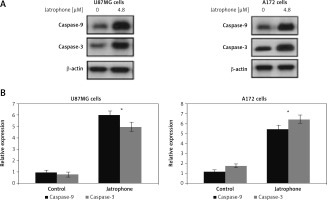
Jatrophone-induced activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9
The jatrophone-induced activation of caspase-9 and caspase-3 in primary astrocytes, U87MG and A172 cells was assessed by western blot assay (Figure 8). Treatment with jatrophone did not induce cleavage of caspase-3 and -9 in primary astrocytes. In U87MG and A172 cells caspase-3 and -9 cleavage was promoted markedly by treatment with jatrophone.
Discussion
Glioblastoma resection is the most difficult and challenging surgery in neuro-oncology; therefore it is treated by surgery, radio and chemotherapies in combination. Various studies have been conducted to understand the mechanism of neurological disorders to develop effective treatment strategies [16–19]. There has been some improvement in overall survival by temozolomide and irinotecan, but nearly half of the glioma patients are not benefitting due to cellular resistance [20]. The present study showed that jatrophone exhibits an anti-proliferative effect on U87MG and A172 glioma cells by inducing apoptosis and inhibition of NF-κB expression. Jatrophone showed no inhibitory effect on proliferation of primary astrocytes, which comprise a major portion of the brain parenchyma. In glioblastoma cells the proteins of the NF-κB pathway are activated constitutively as a genetic feature [21]. The NF-κB has a key role as a mediator for various survival signaling pathways which regulate activation of genes associated with cellular survival and growth [22]. In glioblastoma cells NF-κB present in the nucleus has a major role in maintaining the malignant phenotype of cells [23]. It is reported that NF-κB expression impacts average survival of glioma patients and it is believed to be an unfavorable factor for prognosis [24]. NF-κB inhibition by bortezomib has been found to improve the anti-tumor activity of docetaxel for glioma cells by preventing chemoresistance [25]. In the present study jatrophone suppressed U87MG and A172 glioma cell viability specifically without any toxicity for primary astrocytes. The jatrophone-induced anti-proliferative effect for U87MG and A172 cells was associated with activation of apoptosis. The data from western blotting demonstrated that jatrophone down-regulated expression of NF-κB in U87MG and A172 cells. This suggested that jatrophone exhibited an anti-proliferative effect on glioma cells by targeting NF-κB expression, which is involved in cell viability. Apoptosis inhibitors, survivin and XIAP are components of the pro-survival pathway which counter pro-apoptotic signals induced by chemotherapeutic molecules [26]. Studies have found that targeting these apoptosis inhibitors leads to death of some glioma cells [27, 28]. Studies on glioblastoma specimens have demonstrated that the poor average survival of glioma patients is probably related to over-expression of survivin [29]. It is reported that expression of survivin shows gradual enhancement with the increase in pathological grade of glioma [30]. The spontaneous induction of apoptosis has been found to be inversely related to the expression of survivin in glioblastoma cells, which highlights its role as a target for treatment strategies [31]. The survivin protein is believed to be linked with the chemoresistance of not only glioblastomas but also various other cancer cells [32]. The present study showed that survivin and XIAP expression in U87MG and A172 cells is suppressed by jatrophone. These finding indicate that jatrophone eliminates chemoresistance of U87MG and A172 cells by targeting survivin and XIAP. Inhibition of survivin can lead to apoptosis by promotion of Bax and inhibition of Bcl-2 proteins [33]. The data from the present study confirmed that jatrophone decrease increased Bax and suppressed Bcl-2 expression in U87MG and A172 cells.
In conclusion, jatrophone inhibits cellular growth by inducing apoptosis in U87MG and A172 glioblastoma cells. The anti-glioblastoma potential of jatrophone is associated with suppression of NF-κB expression, targeting apoptosis inhibitors and promotion of pro-apoptotic proteins. Thus, jatrophone has potential to inhibit glioblastoma and therefore may be used to develop anti-glioblastoma treatment.