Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE / RESEARCH PAPER
Hsa_circ_0054633 regulates PDGF-BB-induced proliferation, migration and oxidative stress of vascular smooth muscle cells through miR-107/TXNIP axis
1
Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Medical University, Xi'an, Shaan’xi, China., China
2
Department of Nephrology and Endocrinology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Medical University, Xi'an, Shaan’xi, China., China
3
Department of Neurology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Medical University, Xi'an, Shaan’xi, China., China., China
4
Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Medical University, No. 167 Fangdong Street, Baqiao District 710038, Xi'an, Shaan’xi, China., China
Submission date: 2019-12-27
Final revision date: 2020-06-28
Acceptance date: 2020-07-11
Online publication date: 2021-04-15
Corresponding author
Peng Ding
Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Medical University, No. 167 Fangdong Street, Baqiao District 710038, Xi'an, Shaan’xi, China., China
Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Medical University, No. 167 Fangdong Street, Baqiao District 710038, Xi'an, Shaan’xi, China., China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Hsa_circ_0054633 has been found to be elevated in the blood of coronary artery disease (CAD) patients. However, the molecular mechanism and the role of hsa_circ_0054633 in the pathogenesis of CAD have not been reported in detail.
Material and methods:
The expression of hsa_circ_0054633, microRNA (miR)-107 and thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) mRNA was measured using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Human artery vascular smooth muscle cell (HA-VSMC) proliferation, cell cycle, and migration were detected by cell counting kit-8 assay, flow cytometry and transwell assay, respectively. The generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was analyzed by dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay. Western blot was utilized to determine the levels of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), cyclin D1, matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9), Mn-superoxide dismutase (SOD2) and TXNIP protein. The interaction between miR-107 and hsa_circ_0054633 or TXNIP was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter, RNA immunoprecipitation assay or pull-down assay.
Results:
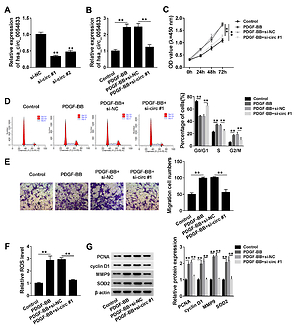
Hsa_circ_0054633 was elevated in the plasma of CAD patients, and might be a potential blood biomarker for CAD prediction. Hsa_circ_0054633 silencing reversed PDGF-BB-induced promotion on HA-VSMC proliferation, cell cycle, migration and ROS production. MiR-107 directly interacted with hsa_circ_0054633 and TXNIP, and hsa_circ_0054633 regulated TXNIP expression by sponging miR-107. Besides, rescue assay indicated that the action of hsa_circ_0054633 silencing on PDGF-BB-treated HA-VSMCs could be attenuated by miR-107 inhibition or TXNIP overexpression, respectively.
Conclusions:
Hsa_circ_0054633 knockdown protected HA-VSMCs against PDGF-BB-induced dysfunction through regulating miR-107/TXNIP axis, suggesting a potential therapeutic target for coronary atherosclerosis.
Hsa_circ_0054633 has been found to be elevated in the blood of coronary artery disease (CAD) patients. However, the molecular mechanism and the role of hsa_circ_0054633 in the pathogenesis of CAD have not been reported in detail.
Material and methods:
The expression of hsa_circ_0054633, microRNA (miR)-107 and thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) mRNA was measured using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Human artery vascular smooth muscle cell (HA-VSMC) proliferation, cell cycle, and migration were detected by cell counting kit-8 assay, flow cytometry and transwell assay, respectively. The generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) was analyzed by dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay. Western blot was utilized to determine the levels of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA), cyclin D1, matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9), Mn-superoxide dismutase (SOD2) and TXNIP protein. The interaction between miR-107 and hsa_circ_0054633 or TXNIP was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter, RNA immunoprecipitation assay or pull-down assay.
Results:
Hsa_circ_0054633 was elevated in the plasma of CAD patients, and might be a potential blood biomarker for CAD prediction. Hsa_circ_0054633 silencing reversed PDGF-BB-induced promotion on HA-VSMC proliferation, cell cycle, migration and ROS production. MiR-107 directly interacted with hsa_circ_0054633 and TXNIP, and hsa_circ_0054633 regulated TXNIP expression by sponging miR-107. Besides, rescue assay indicated that the action of hsa_circ_0054633 silencing on PDGF-BB-treated HA-VSMCs could be attenuated by miR-107 inhibition or TXNIP overexpression, respectively.
Conclusions:
Hsa_circ_0054633 knockdown protected HA-VSMCs against PDGF-BB-induced dysfunction through regulating miR-107/TXNIP axis, suggesting a potential therapeutic target for coronary atherosclerosis.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.