Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
COVID-19/SARS-COV-2 / RESEARCH PAPER
Factors potentially influencing case fatality rate in different stages of COVID-19 outbreak in Europe
1
Faculty of Health Sciences, Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland
2
Institute of Process Engineering, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
3
Department of Surgical Medicine, with the Laboratory of Medical Genetics, Collegium Medicum, Jan Kochanowski University, Kielce, Poland
Submission date: 2021-01-04
Final revision date: 2021-04-22
Acceptance date: 2021-04-23
Online publication date: 2021-05-10
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The aim of this study was to analyze the changes in COVID-19 case fatality rates (CFR) in time and to examine the link between CFR and country-specific indicators referring to quality of healthcare, population and epidemiology in different stages of the COVID-19 outbreak in 30 European countries (EU27 + Switzerland, Norway and United Kingdom).
Material and methods:
We distinguished three 70-day time phases of the outbreak: 17 March–25 May; 1 June–9 August; 15 August–23 October 2020. The applied COVID-19 dataset was based on data maintained by OurWorldInData.org retrieved in November 2020. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient analysis was used to examine the link between CFR and country-specific indicators referring to population, epidemiology and quality of healthcare.
Results:
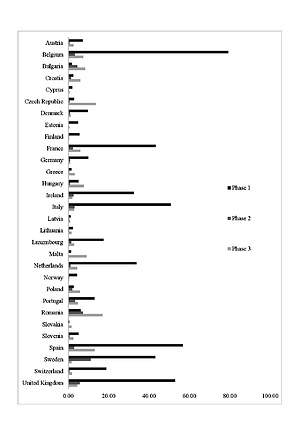
COVID-19 CFR in analyzed European countries declined from mid-March to end-October. CFR phase 1 was positively correlated with COVID-19 mortality, daily cumulative index (DCI), urbanization and proportion of the population aged > 80; CFR phase 2 was positively correlated with COVID-19 mortality and DCI; CFR phase 3 was positively correlated with COVID-19 mortality, median age, poverty, prevalence of obesity, smoking and cardiovascular disease and negatively correlated with Healthcare Access and Quality Index, Health Care Index and gross domestic product per capita.
Conclusions:
Results of our correlation analyses support the concept that the decline in CFR is real and, depending of the phase of the outbreak, different factors play a role. From the public health perspective, measures implemented to reduce the viral transmission, isolating the most vulnerable and improving the overall quality of the healthcare system are advisable.
The aim of this study was to analyze the changes in COVID-19 case fatality rates (CFR) in time and to examine the link between CFR and country-specific indicators referring to quality of healthcare, population and epidemiology in different stages of the COVID-19 outbreak in 30 European countries (EU27 + Switzerland, Norway and United Kingdom).
Material and methods:
We distinguished three 70-day time phases of the outbreak: 17 March–25 May; 1 June–9 August; 15 August–23 October 2020. The applied COVID-19 dataset was based on data maintained by OurWorldInData.org retrieved in November 2020. Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient analysis was used to examine the link between CFR and country-specific indicators referring to population, epidemiology and quality of healthcare.
Results:
COVID-19 CFR in analyzed European countries declined from mid-March to end-October. CFR phase 1 was positively correlated with COVID-19 mortality, daily cumulative index (DCI), urbanization and proportion of the population aged > 80; CFR phase 2 was positively correlated with COVID-19 mortality and DCI; CFR phase 3 was positively correlated with COVID-19 mortality, median age, poverty, prevalence of obesity, smoking and cardiovascular disease and negatively correlated with Healthcare Access and Quality Index, Health Care Index and gross domestic product per capita.
Conclusions:
Results of our correlation analyses support the concept that the decline in CFR is real and, depending of the phase of the outbreak, different factors play a role. From the public health perspective, measures implemented to reduce the viral transmission, isolating the most vulnerable and improving the overall quality of the healthcare system are advisable.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.