Introduction
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic, progressive, and painful inflammatory rheumatic diseases [1], which often involves the sacroiliac joint and axial bone and peripheral joints. In the advanced stage of the disease, a fibrous or bony fusion of soft tissue around the spine or hip joint result in severe deformity and disability and affects the patients’ work and daily life. There is no cure for the disease, and patients often require lifelong medication, and are prone to some adverse drug reactions, such as eosinophilia, etc. [2]. AS usually starts in the second or third decade of life [3]; the incidence is significantly higher in males than females (the approximate male to female ratio is 2–3 : 1). Moreover, there is a discrepancy in different countries and regions and ethnic groups all over the world [4, 5]. China has almost 20% of the world’s population; there has not been much investigation and research on the epidemiological characteristics of AS in China. Although a few studies have been conducted, they focused on the population in a community or town, and the sample size was small. This is the first study in China to explore the epidemiological characteristics of AS among more than 50 million people. This study has taken more than 50 million indigenous residents in Guangxi Province as the research object, through statistics including the number and basic data of AS patients who had been diagnosed and hospitalized by specialists in medical and health care institutions at all levels in Guangxi Province from 2014 to 2021, and attempted to explore the epidemiological characteristics of AS in Guangxi Province of China.
Material and methods
Patients
All the patients included in this study were aboriginal residents of Guangxi Province, diagnosed and hospitalized at all levels of medical and health care institutions in Guangxi Province. The diagnostic criteria of AS were based on the New York standard revised criteria. All patients were diagnosed by specialists, which ensured the correctness of the diagnosis. The AS diagnosis was mentioned on the first page of the inpatient medical record.
Data source and ethics
In China, national health insurance was universal. The medical records of inpatients at all levels of medical and health care institutions must be reported quarterly to the National Health Statistics Network Direct Reporting System (NHSNDRS). This facilitated statistical analysis and reimbursement of medical insurance.
The data for this study were provided by Guangxi Province Health Statistical Information Center and included the number of AS patients in Guangxi Province, gender, marriage, blood type, occupation, age at diagnosis, and location of household registration data. This information excluded, all patients’ names, phone numbers, detailed addresses and other private information. This research was conducted in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration. The use of NHSNDRS Medical Research Data was authorized by Guangxi Province Health Commission, examined and approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University (approval number: 2022 KY-E-180).
Study population
This study has taken more than 50 million indigenous residents in Guangxi Province as the research object. The annual total population figures for Guangxi Province, different cities and ethnic groups were obtained from the official Statistical Yearbook of Guangxi Province.
Methods
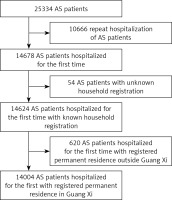
The professionals of Guangxi Health Statistical Information Center used the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) codes M45.x00(AS), M45.x03+(AS with iridocyclitis) and M40.101(AS with kyphosis), to search the database of medical records of inpatients in NHSNDRS (including all medical insurance and self-financed inpatients), and calculated the number of AS patients with one of these three codes in the main diagnosis or other diagnoses on the first page of inpatient medical records. Each patient was counted only once. Patients with repeated hospitalization, unknown place of domicile, and non-domicile in the Guangxi Province were excluded. There were 14004 patients with domicile in the Guangxi Province who are eligible to be included in the study (Figure 1, Table I).
Statistical analysis
All variables were recorded at cohort entry and were summarized using appropriate descriptive statistics: frequency (percentage (%), n) for categorical variables and mean (95% confidence interval) for continuous variables. The person-year incidence rate per 100,000 population was estimated by dividing the cases with AS by the whole population in different cities or ethnic populations, multiplied by 100,000. The mean incidence rates (per 100 000 person-years) were calculated as the number of AS in the eight-year period 2014–2021 divided by the estimated person-time in the same time period. Group analyses were performed with the Student-Newman-Keuls (SNK-q) test (normal distribution, homogeneous variance) or Tamhane T2 test (skewed distribution, unequal variance). All statistical analyses were performed with SPSS25, setting statistical significance at p < 0.05.
Results
Incidence by region
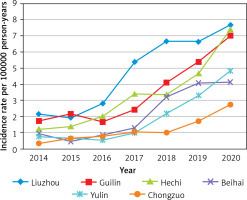
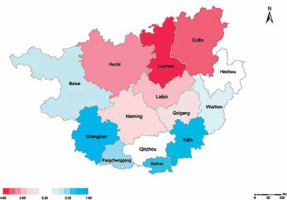
As incidence rates increased from 1.30 (95% CI: 1.20–1.40) per 100,000 person-years in 2014 to 5.71 (95% CI: 5.50–5.92) in 2020 in Guangxi Province (Figure 2), and decreased slightly in 2021. There was a constantly changing annual AS incidence rate per 100,000 person-years in different cities (Table II, Figure 3), with an overall trend of increasing year by year from 2014 to 2020 (Figure 4). There are obvious differences among different cities for mean incidence rates in the eight-year period 2014–2021 (p < 0.05). Liuzhou city was the highest (p < 0.05), followed by Guilin city and Hechi city, and Chongzuo city was the lowest (p < 0.05) (Table III, Figure 5).
Table II
Incidence of AS per 100,000 person-years in different years and cities from 2014 to 2021
Table III
Incidence of AS (per 100,000 person-years) by different ethnic groups and cities
| Subgroup | Characteristic at baseline | Incidence rate per 100,000 person-years (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nationality | Bourau | 2.30 (CI: 1.15–3.45) | > 0.05* |
| Han nationality | 3.12 (CI: 0.90–5.34) | > 0.05* | |
| Other ethnic minorities | 3.14 (CI: 1.39–4.89) | > 0.05* | |
| City | Liuzhou | 4.87 (CI: 2.98–6.76) | > 0.05** |
| Guilin | 3.71 (CI: 2.03–5.39) | > 0.05** | |
| Hechi | 3.66 (CI: 1.81–5.51) | > 0.05** | |
| Laibin | 3.61 (CI: 2.23–4.99) | – | |
| Nanning | 3.41 (CI: 1.82–5.00) | – | |
| Guigang | 3.11 (CI: 2.30–3.92) | – | |
| Hezhou | 3.06 CI 1.04 - 5.08 | ------- | |
| Qinzhou | 2.91 (CI: 1.11–4.71) | – | |
| Wuzhou | 2.68 (CI: 1.50–3.86) | – | |
| Fangchenggang | 2.59 (CI: 1.41–3.77) | – | |
| Beise | 2.54 (CI: 1.40–3.68) | – | |
| Baihai | 2.30 (CI: 1.00–3.60) | < 0.05*** | |
| Yulin | 2.18 (CI: 0.72–3.64) | < 0.05*** | |
| Chongzou | 1.49 (CI: 0.50–2.48) | < 0.05*** |
* It indicates that there is no significant difference in the 8-year average incidence rate (per 100,000 person-years) between the ethnic groups (p > 0.05).
Figure 2
AS incidence rate per 100,000 person-years (95% confidence interval) in Guangxi Province from 2014 to 2021
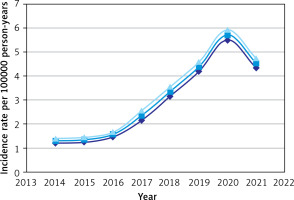
Figure 3
Comparing the incidence of AS per 100,000 person-years in different years and cities. (A to H respectively represent the years from 2014 to 2021)

Incidence by ethnic group
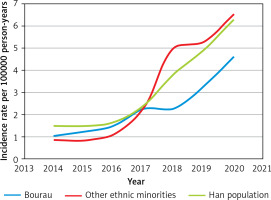
All AS patients were classified according to ethnic groups, and the AS incidence rate of each ethnic group was calculated. The results showed that the incidence rate was not significantly different between different nationalities (p > 0.05) (Table III), and the general trend increased from 2014 to 2020 (Figure 6). AS incidence rates per 100,000 person-years increased from 1.04 (95% CI: 0.94–1.14) in 2014 to 4.56 (95% CI: 4.47–5.65) in 2020 in the Bourau population, and 1.48 (95% CI: 1.38–1.58) to 6.24 (95% CI: 6.16–6.32) in Han nationality, and in other ethnic minorities from 0.85 (95% CI: 0.45–1.25) to 6.48 (95% CI: 6.22–6.74).
Age at diagnosis
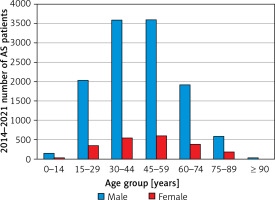
The age of diagnosis group distribution of AS patients showed that the number of male patients gradually increased from 15 to 29 years, reached the peak at the age of 30 to 44 years, and then decreased gradually. The mean age of diagnosis in male patients was 45.4 (95% CI: 45.1–45.7) years. The age of diagnosis of female patients was later than males; it gradually increased from 15 to 29 years, reached a peak at 45 to 59 years, and then decreased gradually. The mean age of diagnosis in female patients was 47.6 (95% CI: 46.8–48.4) years (Table IV, Figure 7).
Table IV
Age of diagnosis group distribution of all AS patients
Distribution gender, marriage, and blood type
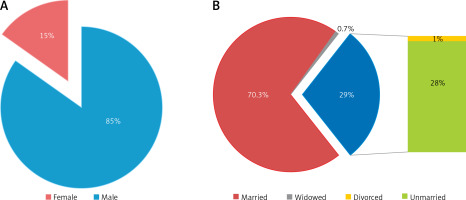
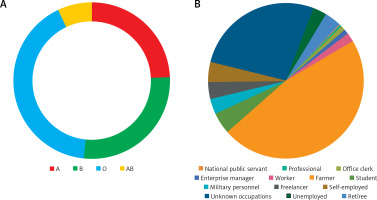
A total of 14004 patients were diagnosed with AS during hospitalization in Guangxi Province from 2014 to 2021, including 11866 males, 2113 females, and 25 of them with unknown gender. The ratio of males to females was 5.61 : 1. Male patients accounted for about 85% (Figure 8 A). The marital status of 780 people was unknown, 70.30% were married, 28% were unmarried, 0.7% were widowed, and 1% were divorced (Figure 8 B). 6158 patients did not check their blood type during hospitalization, and 7846 patients were examined, of whom 24% had blood group A, 27.6% had group B, 41.4% had group O blood, and 7% had group AB (Figure 9 A).
Occupation
The occupation data of these AS patients showed 4208 with unknown occupations and unemployed. Among the 9796 patients whose occupations were known, farmer occupation was the most frequent, accounting for 47% of all patients, followed by office clerk (4.6%) and student (3.9%). The least common occupations were enterprise managers (0.4%) and military personnel (0.07%) (Figure 9 B).
Discussion
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a complex chronic autoimmune disease that affects the axial joints, which often causes limitation of functional capacity, decreased ability to work, and reduced quality of life. Incidence of AS varies in different countries and regions, different races and genders. Usually, in the northern hemisphere it is higher than in the southern hemisphere in males it is higher than in females, and in rural populations it is higher than in cities [4, 5]. A population-based study from Finland found an AS incidence rate of 6.9 per 100,000 person-years [6]. Incidence of AS in northwestern Greece was estimated to be 1.5 per 100,000 person-years [7], and in Caucasian populations it was 6–7 per 100,000 persons [8]. Research based on hospital records in Rochester, Minnesota, found the incidence rate of primary AS to be 6.3 per 100,000 person-years, that of primary and secondary AS together to be 7.3 per 100,000 person-years [8]. The estimated incidence of all types of spondyloarthropathies in the Japanese population was 0.48 per 100,000 person-years [9].
AS had been neglected in China before and was thought to be a less common disease among Chinese [10]. Until the last two decades, some Chinese scholars have started to conduct some research on the incidence of AS. Ng et al. [11] reviewed eight surveys among civilian communities in the Chinese mainland and two surveys among military communities and determined that the comprehensive prevalence rate of AS in civilian and military communities was 0.23% and 0.24%, respectively. Liao et al. [12] used a questionnaire developed in France in 1999 and conducted a face-to-face survey among the Han population in Dalang Town, Yangshan County, Guangdong Province. The results showed that the prevalence rate of spondyloarthropathy (SPA) in southern China was 0.782%. Chou et al. [13] conducted an epidemiological survey of communities in Taiwan and found that the prevalence rate of AS in Taiwan was 0.38%. Different studies have shown that the prevalence of AS in the Chinese population was different. Until now, a study with a large sample size on the incidence of AS among millions of people in China has not been reported. The use of a comprehensive population-based healthcare register with diagnoses by physicians offers a promising opportunity to estimate the prevalence of AS.
Our study revealed that the incidence rate per 100,000 person-years of AS in Guangxi Province of China increased from 1.30 (95% CI: 1.20–1.40) in 2014 to 5.71 (95% CI: 5.50–5.92) in 2020. The incidence of AS increases year by year, which was estimated to be the result of multiple factors, and genetic factors should come first. According to previous studies, the prevalence of HLA-B27 in the Chinese population ranges from 2% to 9% [14], with 4% to 8% being the most common [15], compared to 10% in the white population and 1% in the Japanese population [16]. The prevalence of HLA-B27 in Chinese AS is 90–95%, which is comparable to the prevalence in the white population. In a study of regional differences, AS patients from southern China were found to have a higher prevalence of HLA-B27 than those from northern China (96.5% vs. 83.5%) [17]. In addition to genetic factors [18–21], environmental factors, living habits [22] and pathogen infection [21–26] are important. In recent years, with the rapid development of China’s industrialization, the problem of environmental pollution has become increasingly serious. Liuzhou was the most important industrial city in Guangxi Province, with a developed industry and the most serious environmental pollution. In the past, Liuzhou City often experienced acid rain. In this study, the incidence of AS in Liuzhou City had been ranked first for a long time, and the contribution of environmental pollution was an indispensable factor. In addition, with the accelerated pace of people’s lives, fast food and street food became popular in China. These foods were cheap, the quality was difficult to guarantee, the processing time was very short, the pathogens cannot be effectively removed, and the environment was relatively simple, predisposing to proliferation of Escherichia coli and Bacteroides species. Moreover, the habit of eating raw fish fillets and snail powder was becoming more and more popular among people in southwest China. It is well known that various fish and snails which live in different oceans, rivers, lakes and fish ponds can carry many pathogenic microorganisms. Eating such foods could easily cause intestinal infectious diseases, thereby increasing the risk of AS.
There is another important factor, the widespread use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in diagnosis has improved the early diagnosis rate of AS. MRI, which is better than radiography for detection of early sacroiliitis, can be performed if radiographs are negative in patients with clinical signs of AS [27–29]. In the past, MRI was only available in tertiary first-class hospitals in China. In the last 10 years, it has gradually become popular in second-class and primary hospitals. The change of MRI signal of the sacroiliac joint in AS patients is significantly earlier than that of computed tomography (CT) or X-ray. The widespread use of MRI in hospitals at all levels is conducive to early diagnosis of AS, thus improving the diagnosis rate of AS in the short term. The incidence rate of AS in 2021 was lower than in 2020; the author speculates that the 2021 incidence of the population in southwest China may be close to the actual incidence level, and no longer showed a significant upward trend, and began to fluctuate in a small range in a stable state. At present, the annual incidence of AS in Guangxi Province of China in higher than in Japan and Greece [7, 9], and lower than in Finland, the Caucasus and Minnesota in North America [6, 8].
We classified all AS patients in the study by gender and found that there was a difference in the incidence rate of AS between males and females, and in males it was significantly higher than in females. The results were consistent with most previous studies [4, 5, 30], despite some methodological differences. The ratio of the incidence of AS among males to females was 5.61 : 1, which was similar to that reported in other series [4, 5, 30]. The mean age of diagnosis in males is 45.4 (95% CI: 45.1–45.7) years, and in females is 47.6 (95% CI: 46.8–48.4) years. These results indicated that the age of diagnosis of AS in the Guangxi population was delayed, in comparison with Germany [31], Taiwan and other parts of mainland China [32, 33].
In Guangxi Province of China, there are more than ten local ethnic groups. We categorized all AS patients by ethnicity, in an attempt to explore the incidence rates of different ethnic groups. The survey showed that the AS incidence rate was not significantly different between different ethnic groups (p > 0.05), which may be related to the similar prevalence of HLA-B27 among different ethnic groups in southwest China [14, 15]. In this research we analyzed the occupations of AS patients among whom 9796 people have jobs, with farmers accounting for 47% of the total. This might be related to the environment in which the farmers live, pathogenic infections, living standards, and manual labor [34]. Currently, the average annual income of farmers is significantly lower than that of people in other industries [34]. There is still a gap between rural and urban living conditions [35]. Healthcare knowledge among farmers still needs to be improved, and the probability of pathogenic infection is high [36–39]. These factors, coupled with long-term heavy manual labor, might be the reasons for the increased incidence of AS.
According to the geographical area that AS patients inhabit, we calculated the eight-year average incidence rates of each city in Guangxi Province based on their administrative jurisdiction, and compared the three cities with the highest incidence and the three with the lowest. The results showed that the top three cities with the highest average incidence rates were all located in the northern part of Guangxi Province, with adjacent borders. There was no significant difference between the three cities with the top three incidence rates (p > 0.05). There are obvious differences between the three cities with the lowest incidence and Liuzhou with the highest incidence (p < 0.05), which may be related to the different environments, eating habits and lifestyles of the population living in different cities. For example, in Liuzhou City, where industry was developed and environmental pollution was relatively heavy, the indigenous people generally like to eat sashimi and snail noodles. The research indicates that the incidence of AS in southwestern China had obvious regional discrepancy, showing a local and regional aggregation.
This study has several limitations. First, as this was a retrospective study, selection bias cannot be ruled out. Second, some patients diagnosed in outpatient clinics have not been hospitalized, resulting in a relatively small number of patients. The AS incidence rate per 100,000 person-years was slightly lower than actual. Third, some patients were diagnosed before their first hospitalization, resulting in a difference from the year included. Finally, diagnostic coding in the National Health Statistics Network Direct Reporting System (NHSNDRS) may not be accurate. In this study, almost all diagnoses of AS were made by specialists, which ensured the correctness of the diagnosis. Although this study has the above shortcomings, due to the large population base, this small number of patients should have a little impact on the overall study results. The findings of this study basically revealed the epidemiological characteristics of AS in the Guangxi Province population.
In conclusion, the AS incidence rate per 100,000 person-years in Guangxi Province of China was increasing year-on-year. This was related to genetic factors, environmental factors, lifestyle habits, pathogen infection and early MRI diagnosis. There are obvious gender and regional differences, showing the characteristics of local area aggregation.