Tuberculosis (TB) caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is a lethal manifestation of TB with suboptimal treatment options and accounts for approximately 2–5% of TB cases each year [1]. The clinical presentation of TBM is characterized by nonspecific symptoms, such as fever, lethargy, and weight loss. Consequently, TBM may advance to severe complications, including coma, cranial nerve palsies, and fatality [2]. WHO guidelines recommend a two-month four-drug regimen for TBM, followed by two drugs for 7–10 months [3]. Isoniazid and pyrazinamide penetrate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) well, but rifampin’s effectiveness is limited by high protein binding and poor blood-brain barrier penetration [4, 5]. Furthermore, the penetration of CSF diminishes after the resolution of meningeal inflammation with the use of streptomycin and ethambutol [2]. Consequently, there is a need for improved management strategies in the treatment of TBM. Cohort studies suggest that adding linezolid (LZD) to conventional TB therapy for TBM can be effective, with better outcomes in a randomized controlled trial [6–8]. However, the majority of these studies were retrospective in nature and utilized small sample sizes. Therefore, it is imperative to thoroughly assess the effectiveness and safety of linezolid in the management of TBM. We conducted a meta-analysis of all related published studies to evaluate the efficacy and safety of therapy regimens containing linezolid during the intensive phase of treatment.
Methods
The meta-analysis was prepared based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines for systematic reviews and meta-analyses [9]. As the study involved the synthesis of existing articles and did not involve the handling of individual patient data, ethical approval was deemed unnecessary.
Search strategy and study selection
The PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE and Cochrane Library databases were searched to identify relevant studies (Supplementary Table SI). English-language studies published with no time restriction were retrieved using the following keywords: “tuberculous meningitis”, or “linezolid”, and their synonyms or similar words. Two independent reviewers (DY and XS) read and assessed the titles and abstracts of all articles identified by the search strategy. The full-text study reports of all potentially eligible studies were also independently screened by two review authors (DY and XS) according to a standardized form containing the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Studies were considered eligible based on the following criteria: (1) inclusion of individuals diagnosed with TBM, confirmed through clinical, microbiological, molecular, imaging, and immunodiagnostic methods; (2) administration of linezolid to the intervention group, either intravenously or orally, in comparison to the control group receiving standard anti-TBM treatment without linezolid; (3) the control group received anti-TBM treatment without linezolid; (4) the study included retrospective, randomized controlled trial, or prospective cohort studies.
Assessment of methodological quality
Each study included in the meta-analysis underwent independent quality assessment by two reviewers, with further analysis conducted on high-quality studies. For randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the Jadad scale [10] was utilized by the two review authors to evaluate methodological quality based on criteria such as randomization, allocation concealment, blinding, and follow-up. A maximum score of five points was possible, with a score of ≥ 3 indicating high quality (Supplementary Table SII). In cohort studies, the methodological quality of the research was evaluated using a modified version of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) (http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp) by two independent reviewers (Supplementary Table SIII). The assessment criteria included participant selection, comparability of study groups, and ascertainment of outcomes. The NOS assigns a maximum of nine points, with a score exceeding seven indicative of high quality.
Data extraction
Two authors (DY and XS) independently extracted data on study characteristics, participant characteristics, intervention details, and treatment outcomes. Disagreements were resolved by a third author (Min).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted utilizing Review Manager 5.4 to assess the impact of linezolid on TBM. Meta-analysis calculations were carried out using individual patient data with defined treatment outcomes, including treatment success (comprising cure or treatment completion) and all-cause mortality. The risk ratio (RR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) were utilized as indicators of treatment efficacy. The I 2 test [11] was employed to assess between-study heterogeneity, while publication bias was evaluated using a funnel plot (Supplementary Figure S1).
Results
Study flow diagram
Out of 201 citations, 16 articles were relevant for full-text analysis, and 4 were included in the meta-analysis [6–8, 12] (Figure 1 A).
Figure 1
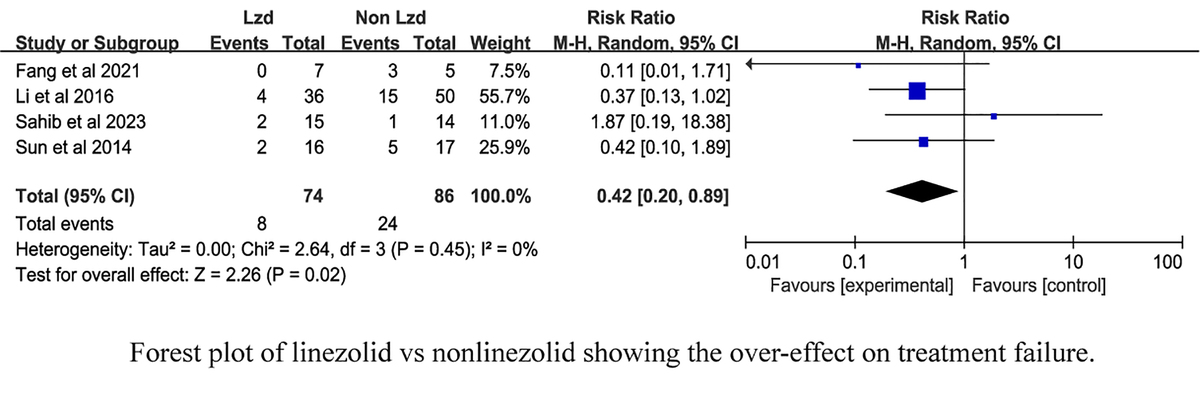
Meta-analysis of efficacy of LZD in the treatment of TBM. A – Study flow diagram. B – Forest plot of linezolid vs non-linezolid showing the overall effect on treatment failure. C – Forest plot of linezolid vs. non-linezolid showing the overall effect on the temperature recovery. D – Forest plot of linezolid vs. non-linezolid showing the overall effect on adverse events
Characteristics of included studies
The characteristics of the studies and the number of cases analyzed in the systematic review and meta-analysis are summarized in Supplementary Table SIV The 3 retrospective cohort studies were all conducted in China and published in 2021, 2016 and 2014, and 1 randomized control trial was conducted in India and published in 2023.
Treatment outcomes
Four studies, including 160 subjects, were included in the meta-analysis to evaluate the association between linezolid therapy and the risk of treatment failure among patients with TBM. Treatment failure was defined as death, coma, fever after 2 months of treatment, and severe neurological deficits. The overall effect size using the random-effects model (I2 = 0%, p = 0.45) demonstrated a significant protective effect of linezolid against TBM, with a 58% lower risk compared with non-linezolid patients with TBM (RR = 0.42, 95% CI: [0.20, 0.89]; p = 0.02) (Figure 1 B).
Two studies evaluated the case fatality rate during the treatment of TBM and assessed the impact of linezolid on the case fatality rate of TBM. The pooled results showed no statistically significant difference in the early case fatality rate between the two groups (RR = 0.33, 95% CI: [0.09, 1.26]; p = 0.11) after a random-effects model (I2 = 0%, p = 0.35) (Supplementary Figure S2).
Two studies involved temperature recovery during anti-tuberculosis treatment and evaluated the effect of linezolid on the recovery of body temperature in patients within the first month of treatment. The pooled results showed a medium difference (RR = 1.56, 95% CI: [1.21, 2.02]; p < 0.001) after a random-effects model (I2 = 5%, p = 0.31) (Figure 1 C).
Three studies recorded adverse events, including hematological, neurological and visual dysfunction. The pooled results showed that there was no significant difference under a random-effects model (RR = 1.73, 95% CI: [0.35, 8.51], p = 0.50) (Figure 1 D). The heterogeneity was described as an I2 of 46% (p = 0.16); therefore, we considered that there was no statistical heterogeneity in this analysis.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis to investigate the effects of linezolid on patients with TBM. We analyzed data from 4 studies, including 160 patients. The results of this meta-analysis revealed the efficacy of linezolid in the treatment of TBM. Primary data show that linezolid use is associated with a 58% lower risk of treatment failure and can achieve temperature recovery more effectively compared with the non-linezolid use among TBM patients. However, regarding the early case fatality rate of tuberculous meningitis, our analysis showed no statistically significant difference between the linezolid group and the non-linezolid group. In addition, there was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse events in the linezolid and non-linezolid arms, which was uncertain due to the small sample size.
Linezolid is a licensed oxazolidinone antibiotic repurposed for the treatment of tuberculosis and elevated to Group A (medicines prioritized for inclusion in regimens) in evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of multidrug-resistant TB [13, 14]. Linezolid’s ability to penetrate the CSF suggests that it could be a beneficial treatment for patients with TBM. Two additional ongoing clinical trials (NCT03537495 and NCT04021121) should help clarify its role in TBM treatment, including optimal duration and dose. Our study revealed that the administration of linezolid in patients with TBM can lead to a higher treatment success rate and more efficient temporary recovery. Our analysis suggests that the use of linezolid in patients with TBM demonstrates better therapeutic effects and faster recovery of body temperature; however, it does not seem to improve the early case fatality rate of TBM. This is similar to the conclusions of Davis’s study, which indicated that the combination of high-dose rifampicin with linezolid did not significantly improve the fatality rate of TBM. Furthermore, Davis’s study confirmed the safety of linezolid in TBM treatment [15]. Currently, the Mazanhanga team has developed a method for measuring the concentration of linezolid in cerebrospinal fluid, thus providing a foundation for monitoring the pharmacokinetics of linezolid in the future [16]. The utilization of linezolid may represent a significant advancement in the management of TBM, potentially playing a crucial role in limiting the transmission of the disease and reducing mortality rates. Despite reports that there are currently strains of tuberculosis that are resistant to linezolid, linezolid may still be an effective treatment option in specific circumstances [17].
There are many adverse reactions to linezolid, such as gastrointestinal disturbance, hepatotoxicity, rash, peripheral neuropathy, and myelosuppression. A multicenter, randomized controlled clinical trial found that adverse events presumably due to linezolid occurred in 64.7% of treated patients (mainly anemia) [18]. It is thought that most patients treated with linezolid will have adverse drug reactions but not necessitating treatment interruption with long-term use of linezolid 600 mg/day, and the safety of linezolid in the treatment of TBM has also been demonstrated in Davis’s study [15, 19].
However, the present analysis has several limitations. First, only four studies were included in this meta-analysis. Second, the included studies had many nonuniform confounding variables, such as age, sex, body mass index, comorbidities, and the severity of TBM, which could not be adjusted. Third, most of the included studies were retrospectively designed, which may have resulted in recall and selection bias, although each study had a low risk of bias based on the NOS. Fourth, due to the small number of studies included in the meta-analysis, this may suggest the presence of publication bias. However, upon visual inspection of the funnel plot, its shape appears relatively symmetrical, indicating that publication bias is within an acceptable range (Supplementary Figure S1). Finally, we did not analyze the two groups separately because the reduced sample size after separation could lead to insufficient power in statistical tests, making it difficult to detect true effects, and the conclusions drawn from separate analyses would be harder to generalize to the entire population. Therefore, well-designed RCTs are warranted to better define the efficacy and safety of linezolid in the treatment of TBM.
In conclusion, the first meta-analysis examining the association between linezolid and TBM suggests that the use of linezolid is associated with improved therapeutic outcomes in TBM, contributes to the recovery of body temperature, and does not appear to result in a significant increase in adverse effects.