Introduction
β-Asarone (cis-2,4,5-trimethoxy-1-allyl phenyl), which can affect the central nervous system [1–4], is a major component of Acorus tatarinowii Schott. β-Asarone could pass the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and thus enter the brain [5]. Pharmacological studies have demonstrated that β-asarone not only has nootropic and neuroprotective effects [6–11], but also has a cardiovascular protective effect [12, 13], so we supposed that it might provide cerebrovascular protection, decrease cerebral hypoperfusion and hypometabolism and treat Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Recent studies have suggested that β-asarone has anti-apoptosis activity [8, 9, 11, 14]. Moreover, β-asarone is effective against experimental models of AD [8–10, 14, 15], cerebral ischemia [16], ischemia-reperfusion-induced autophagy [17], oxygen-glucose deprivation, reperfusion-induced injury [18], and epilepsy [19].
AD is the most common form of dementia and affects millions of people worldwide. The characteristic features associated with AD patients include loss of memory-associated neurons, especially cholinergic neurons, resulting in the neurotransmitter imbalance and synaptic dysfunction [20, 21]. The pathophysiology of AD is associated with a variety of factors, including extracellular deposition of insoluble β-amyloid protein aggregates, forming senile plaques and intracellular accumulation of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), composed of hyperphosphorylated tau proteins, oxidative neuronal damage, and inflammatory cascades [22–24]. Current treatments provide only a modest benefit against clinical worsening [25, 26], so there is considerable interest in identifying new treatments for AD. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of β-asarone on neurodegeneration induced by intrahippocampal administration of β-amyloid in adult male Wistar rats.
Material and methods
Chemicals
β-amyloid and β-asarone were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO). Assay kits for superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) were purchased from Randox (Crumlin, UK). All other reagents used in this study were of analytical grade. Solutions of the drugs and chemicals were freshly prepared before use.
Animals
Male Wistar rats, initially weighing 200 to 250 g, were used in this study. The animals were housed in groups of 5 per cage in a room with controlled temperature (22 ±2°C), lighting (on, 7 AM; off, 7 PM), and relative air humidity (40–60%). The animals had free access to standard laboratory chow and tap water. The diet was purchased from Pars-Dam food service, Tehran, Iran. Experimental procedures involving the animals and their care were conducted according to institutional guidelines, which are in accordance with the national and international laws and the Guidelines for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals in Biomedical Research, as adopted and distributed by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United States National Institutes of Health 1985, no. 85-23. The experimental protocol was approved by the Research and Ethics Committee of the College of Science, Islamic Azad University.
Intrahippocampal injection of β-amyloid
β-amyloid was dissolved in DMSO to 5 mM exactly as described in the publication of Fa et al. [27]. Then 5 mM β-amyloid was diluted with sterile (1×) PBS to 100 µM on the day before surgery. The solution was mixed well by trituration and β-amyloid solution was incubated for 12 h at 4°C. Animals were anesthetized with ketamine hydrochloride (100 mg/kg, i.p.) and xylazine (5 mg/kg, i.p.). The head was placed in position in the stereotaxic apparatus and a midline sagittal incision was made in the scalp. The stereotaxic coordinates for the CA1 hippocampus [28] were measured accurately as anterio-posterior – 3.0 mm, lateral 2.25 mm and dorso-ventral, 2.8 mm ventral from the surface of the brain. The β-amyloid was prepared and slowly infused (1 µl/min) by Hamilton microsyringe in a volume of 2 µl into CA1 of the hippocampus bilaterally. Rats in the sham-operated group received an injection of the same volume of diluting DMSO in PBS [29].
Experimental design
β-Asarone was dissolved in corn oil and given orally once daily by an orogastric tube for 50 days, starting from 30 days before administration of the β-amyloid. The rats were randomly divided into 9 experimental groups of 12 animals each as follows:
– group I: Normal control rats received 1 ml of corn oil as vehicle intragastrically.
– group II: Sham-operated control rats that underwent surgery. The animals received vehicle of β-amyloid (2 µl) in CA1 of the hippocampus bilaterally and were given 1 ml of corn oil intragastrically.
– groups III–V: Normal rats received β-asarone (12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg bw) daily using an intragastric tube for 50 days.
– group VI: Alzheimer’s control rats were administered β-amyloid in a volume of 2 µl in CA1 of the hippocampus bilaterally. The animals received corn oil intragastrically, as vehicle for 20 days.
– groups VII–IX: Alzheimeric rats received β-asarone (12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg bw) daily using an intragastric tube for 50 days, starting from 30 days before administration of the β-amyloid.
The oral administration volume was 1 ml. The animals were carefully monitored daily.
Biochemical analysis
At the end of the experiment, the animals (6 animals of each group) were anesthetized by inhalation of diethyl ether. The entire brain was then extracted and the hippocampus was dissected and used for biochemical studies. The hippocampuses were washed with chilled saline and then homogenized in chilled phosphate buffer (pH 7.4). The homogenates were centrifuged at 800 × g for 5 min at 4°C to separate the nuclear debris. The supernatant obtained was centrifuged at 10,500 × g for 20 min at 4°C, which was used to assay GPX and SOD activities.
SOD activity was measured according to the directions of the kit. A competitive inhibition assay was done using xanthine-xanthine oxidase-generated O2 to reduce nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) to blue formazan. One unit of SOD activity was determined as the amount of enzyme necessary to reduce NBT to 50% of the maximum. The maximum absorbance was read at 550 nm and the enzyme activity was expressed as units/mg protein [30].
GPX activity was measured by the method based on the reaction between GSH remaining after the action of GPX and 5,50-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid to form a complex with the maximal absorbance at 412 nm. One unit of GPX activity was defined as a 1 mol/l per min decrease in GSH in an enzymatic reaction using 1 mg of protein per min, deducting the effect of nonenzyme-catalyzed reaction [31].
Histopathological examination
At the end of the experiment, the animals (6 animals of each group) were anesthetized by inhalation of diethyl ether and perfused transcardially through the ascending aorta with 100 ml of ice cold phosphate buffered saline (PBS 0.1 M, pH 7.4) followed by 4% paraformaldehyde in cold PBS (0.1 M pH 7.4). The cortex and hippocampus were used for histological studies. The brain was post fixed in the paraformaldehyde solution for 48 h. After fixation, the tissue was dehydrated and embedded in paraffin. Coronal sections were assessed at 1.8–2.0 mm rostral to the optic chiasma. Sections (4 µm) were prepared and subjected to Bielschowsky staining as described in the protocol of the instructions. After staining, the stained hippocampus and cortex sections were examined under a light microscope (Nikon E200, Japan). Neuronal cell count with Image Analyzer version 1.36.1 software in the cortex, CA1, CA2, CA3 and dentate gyrus of the hippocampus was done.
Results
In the present study, we successfully created an experimental Alzheimeric model in rats without any mortality. Our results showed that treatment with β-asarone (12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg bw) caused no toxicity symptoms, and there was no record of death.
Biochemical findings
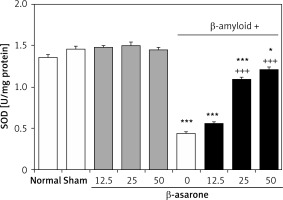
GPX and SOD activities in the hippocampus homogenates are shown in Figures 1 and 2. GPX and SOD activities in hippocampus homogenates of the Alzheimer’s control group were found to be significantly lower than those in the sham-operated and normal control group (p < 0.001). Administration of the rats with β-asarone at doses of 25 and 50 mg/kg increased the activities of both enzymes compared to the Alzheimeric control rats (p < 0.001). No significant alteration was seen in normal control rats treated only with β-asarone (Figures 1 and 2).
Figure 1
Effect of oral administration of β-asarone at doses of 12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg body weight on GPX activities in hippocampal homogenates of normal and Alzheimeric rats. Each column represents mean ± SEM for six rats. Normal control rats administered with corn oil as a vehicle. ***P < 0.001 significantly different from the normal control group. +++P < 0.001 significantly different from the Alzheimeric control group
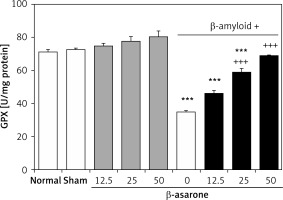
Figure 2
Effect of oral administration of β-asarone at doses of 12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg body weight on SOD activities in hippocampal homogenates of normal and Alzheimeric rats. Each column represents mean ± S.E.M. for six rats. Normal control rats administered with corn oil as a vehicle. *P < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 significantly different from the normal control group. +++P < 0.001 significantly different from the Alzheimeric control group
Histopathological findings
Bielschowsky staining was used to detect histomorphological changes in cerebral cortex and hippocampal neurons following β-amyloid administration (Figure 3). In Alzheimeric control rats, Bielschowsky staining revealed cell loss and neuronal necrosis with accumulation of astrocytes as gliosis, NFTs and neuritic plaques in the cerebral cortex. There are on average 3 neuritic plaques in each high power field (HPF). In addition, there are on average 12 NFTs in HPF in the cortex and the hippocampus. Neuronal loss, especially in the CA1 area, was seen in the hippocampus of the Alzheimer’s control rats. Compared to the Alzheimer’s control rats, administration of β-asarone at 25 and 50 mg/kg increased the number of surviving neurons and decreased NFTs (Figure 3). Our results showed that the number of neurons was normal in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Also, our findings showed cell loss in these zones after administration of β-amyloid in rats. Administration of β-asarone at doses of 25 and 50 mg/kg significantly decreased cell loss in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus (Table I).
Figure 3
Bielschowsky staining in cerebral cortex and CA1 region of hippocampus. Cerebral cortex in normal control group (A) showed normal neuronal cell body (arrow) and vessels (arrowhead). CA1 of hippocampus in normal control group (B) showed normal neuronal cell (arrowhead) population. Sham-operated group (C) revealed normal neuron (arrowhead) in the cortex. Normal rats administered β-asarone at doses of 12.5 (D), 25 (E), and 50 (F) mg/kg revealed a normal neuronal cell body (arrowhead). Alzheimer’s control group revealed neuritic plaques (arrow) in cerebral cortex (G) and in CA1 (H). Also, loss of neuronal cell population (arrow) and neurofibrillary tangles (arrowhead) was seen. β-asarone at dose of 12.5 mg/kg (I) led to moderate neurofibrillary tangles (arrowhead) and neuronal necrosis (arrow) in Alzheimeric rats. Administration of β-asarone at doses of 25 (J), 50 (L) mg/kg revealed few neurofibrillary tangles (arrow) in cortex, improved neuronal population (arrowhead) and decreased neuronal necrosis (arrow) in CA1 (K, M)
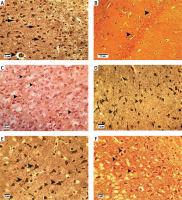
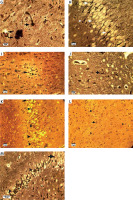
Table I
Effect of β-asarone at doses of 12.5, 25, and 50 mg/kg bw on neuron numbers in normal and Alzheimeric ratsa
| Groups | Neuron numbers | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex | CA1 | CA2 | CA3 | Dentate gyrus | |
| Group I(Normal control) | 83.50 ±2.17 | 125.16 ±0.83 | 53.66 ±1.33 | 75.00 ±1.32 | 192.5 ±2.11 |
| Group II (sham-operated control) | 85.66 ±1.65 | 125.16 ±0.60 | 51.83 ±1.52 | 75.33 ±1.31 | 193.33 ±1.38 |
| Group III (Normal + β-asarone (12.5 mg/kg)) | 81.00 ±1.18 | 124.66 ±0.84 | 49.00 ±1.68 | 74.16 ±0.94 | 191.83 ±0.79 |
| Group IV (Normal + β-asarone (25 mg/kg)) | 78.66 ±1.35 | 120.83 ±0.75 | 49.00 ±2.21 | 72.83 ±1.38 | 193.66 ±1.38 |
| Group V (Normal + β-asarone (50 mg/kg)) | 82.00 ±1.71 | 126.00 ±1.57 | 51.5 ±1.46 | 72.16 ±1.01 | 187.33 ±4.15 |
| Group VI (Alzheimeric control) | 38.16 ±1.30*** | 42.16 ±1.45*** | 42.4 ±1.03*** | 55.66 ±1.63*** | 93.16 ±1.97*** |
| Group VII (Alzheimeric + β-asarone (12.5 mg/kg)) | 45.16 ±2.14*** | 53.83 ±1.14*** | 46.83 ±0.60** | 59.60 ±1.09*** | 107.83 ±1.88*** |
| Group VIII (Alzheimeric + β-asarone (25 mg/kg)) | 69.33 ±1.80***+++ | 109.17 ±2.52***+++ | 48.33 ±0.86*+ | 71.83 ±1.35+++ | 182.33 ±1.61**+++ |
| Group IX (Alzheimeric + β-asarone (50 mg/kg)) | 80.16 ±2.70+++ | 123.00 ±1.41+++ | 49.33 ±1.26++ | 75.00 ±1.16+++ | 187.83 ±1.70+++ |
Discussion
In the present study, we found that β-asarone dose-dependently increased activities of GPX, and SOD, and attenuated brain architecture damage in Alzheimeric rats. Based on our data, administration of β-asarone caused histological and biochemical improvements in Alzheimeric rats. There were no significant alterations in normal rats treated with β-asarone.
It has previously been demonstrated that infusion of β-amyloid in rats resulted in significant decrease of the antioxidant capacity [32, 33]. Oxidative stress and related degeneration of cholinergic neurons is one of the most common sharing pathways involved in neurodegenerative disorders such as AD [34–36]. The brain is more susceptible to reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated injury because its cellular membranes are preferentially enriched in oxyradical-sensitive polyunsaturated fatty acids that are the substrates of lipid peroxidation. It has also been reported in earlier reports that AD brains exhibit a marked increase in malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitrite levels and decreased activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione, catalase, and SOD [37–39]. During oxidative stress, β-amyloid can pass through the neuronal membrane bilayer and induce overproduction of ROS. Moreover, SOD and GPX are the two main antioxidant enzymes involved in cellular protection against damage induced by free radicals [40]. Levels of both have been shown to be decreased in the brains of patients with AD [41, 42]. Therefore, measurements of the activity of antioxidant enzymes are important when comparing the alterations induced by β-amyloid with those found in AD patients. In our study, β-amyloid alone-treated rats exhibited a decrease of SOD and GPX activity in the hippocampal homogenates.
Furthermore, our results showed that β-asarone (25 and 50 mg/kg bw) increased the activity of SOD and GPX in the hippocampal homogenates of β-amyloid-treated rats. The present study supports the hypothesis that β-asarone possesses strong antioxidant properties. β-asarone can exert neuroprotective effects in both in vivo and in vitro AD models [8, 10, 11]. Our previous study proved that β-asarone could reduce neuronal apoptosis and improve memory deficits in AD-model mice [14]. It is reported that β-asarone could protect cerebral ischemia via increasing antioxidants activity. β-asarone could pass the BBB and is well distributed in the brain [5, 43, 44]. Other investigators have shown that β-asarone is capable of protecting cultured cortical neurons from glutamate toxicity [6, 45]. Pharmacological studies have demonstrated that β-asarone not only has nootropic and neuroprotective effects [6–9, 11, 46], but also has a cardiovascular protective effect [12, 13], so it is supposed that it might provide cerebrovascular protection, decrease cerebral hypoperfusion and hypometabolism and treat AD.
Our results showed that intrahippocampal administration of β-amyloid decreased the number of neurons in both the hippocampus and cortex. Also, β-amyloid caused extensive injuries, characterized by moderate to severe neuronal degeneration and necrosis. NFTs and accumulation of astrocytes in the form of gliosis were observed. However, our results showed that the brain lesions induced by intrahippocampal administration of β-amyloid were significantly reduced in rats that received concomitant β-asarone. Neurodegeneration in AD is associated with oxidative stress, dysfunction of mitochondria, impaired energy metabolism, progressive β-amyloid agglutination, and formation of NFTs [47]. The effectiveness of β-asarone in this β-amyloid model of dementia also indicates the possible antioxidant activity of β-asarone, since the β-amyloid model is predominantly based on free radical production [48].
In this study, toxicokinetic study of β-asarone in the blood of animals administered β-asarone was not performed. This would provide other information regarding the kinetic of this compound in rats and potentially could help to correlate the Tmax with the dosage, histopathology findings, and/or SOD/GPX measurements. Also, other organs and tissues have not been evaluated histopathologically and by the clinical pathology assessment to investigate potential toxicity of this compound in other organs such as the heart, liver, kidney, and lymphoid tissues.
In conclusion, the present results demonstrate that β-amyloid induces memory impairments in rats, while β-asarone treatment significantly improves biochemical and neuronal histopathology parameters in Alzheimeric rats.