Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
PHARMACOLOGY AND PHARMACY / EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH
Describing a novel chemotherapeutic drug formulated with diosmin for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and diabetes mellitus
1
Department of Hematology, The Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
2
Department of Geriatrics, Nanjing Gaochun Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
3
Department of Endocrinology, Aerospace Center Hospital, Beijing, China
4
Department of Blood Transfusion, Xi’an Children’s Hospital, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
Submission date: 2021-10-16
Final revision date: 2021-11-15
Acceptance date: 2021-11-17
Online publication date: 2021-12-08
Corresponding author
Qian Hou
Deparment of Blood Transfusion, Xi'an Children's Hospital, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710003, China, China
Deparment of Blood Transfusion, Xi'an Children's Hospital, Xi'an, Shaanxi, 710003, China, China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Diosmin is a natural citrus flavone with remarkable antioxidant and anti-inflammatory features. Acute leukemia is a common type of cancer that is caused in the blood.
Material and methods:
α-Amylase activity was determined by a method adapted from the work of Taha et al.
Results:
In this study, we examined its effect on some important enzymes, the IC50 values were 196.07 for Aldose reductase, and 76.40 for α-Amylase. The molecular docking study was performed to assess the binding affinity and biological activities of diosmin in the presence of alpha amylase and aldose reductase.
Discussion:
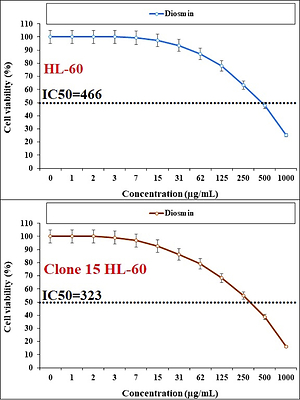
The results of the docking study indicated that diosmin has a remarkable binding affinity to these enzymes with a docking score of –9.768 and –140469 for α-amylase and aldose reductase, respectively. Therefore, this compound could be used as a potential inhibitor for these enzymes. In the cellular and molecular part of the recent study, the cells treated with diosmin were assessed by MTT assay for 48 h regarding the cytotoxicity and anti-human acute lymphoblastic leukemia properties on HL-60, Clone 15 HL-60, HL-60/MX1, and HL-60/MX2 cell lines. The IC50 values of diosmin were 466, 323, 502, and 537 µg/ml against HL-60, Clone 15 HL-60, HL-60/MX1, and HL-60/MX2 cell lines, respectively.
Conclussions:
The viability of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines decreased dose-dependently in the presence of diosmin. It appears that the anti-human acute lymphoblastic leukemia effect of diosmin is due to its antioxidant effects.
Diosmin is a natural citrus flavone with remarkable antioxidant and anti-inflammatory features. Acute leukemia is a common type of cancer that is caused in the blood.
Material and methods:
α-Amylase activity was determined by a method adapted from the work of Taha et al.
Results:
In this study, we examined its effect on some important enzymes, the IC50 values were 196.07 for Aldose reductase, and 76.40 for α-Amylase. The molecular docking study was performed to assess the binding affinity and biological activities of diosmin in the presence of alpha amylase and aldose reductase.
Discussion:
The results of the docking study indicated that diosmin has a remarkable binding affinity to these enzymes with a docking score of –9.768 and –140469 for α-amylase and aldose reductase, respectively. Therefore, this compound could be used as a potential inhibitor for these enzymes. In the cellular and molecular part of the recent study, the cells treated with diosmin were assessed by MTT assay for 48 h regarding the cytotoxicity and anti-human acute lymphoblastic leukemia properties on HL-60, Clone 15 HL-60, HL-60/MX1, and HL-60/MX2 cell lines. The IC50 values of diosmin were 466, 323, 502, and 537 µg/ml against HL-60, Clone 15 HL-60, HL-60/MX1, and HL-60/MX2 cell lines, respectively.
Conclussions:
The viability of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines decreased dose-dependently in the presence of diosmin. It appears that the anti-human acute lymphoblastic leukemia effect of diosmin is due to its antioxidant effects.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.