SAPHO syndrome and adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) are both rare polygenic auto-inflammatory diseases. SAPHO syndrome was initially described by the rheumatologist Chamot in 1987 and is characterized by osteitis, synovitis, bone hypertrophy, pustulosis, and acne vulgaris [1], with skin involvement and bone and joint damage being the primary clinical features [2]. SAPHO syndrome was found to be more common in middle-aged women [3]. The etiology of AOSD remains unknown, and its clinical presentation includes a typical triad of high fever, joint pain/arthritis, and rash, often accompanied by hyperlipidemia, lymphadenopathy, and leukocytosis [4]. Here, we report a case of a 39-year-old woman who presented with SAPHO syndrome 4 years after diagnosis of AOSD.
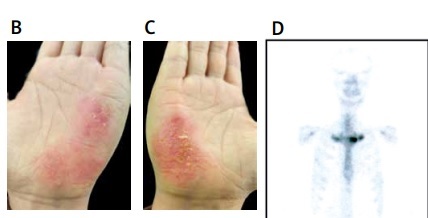
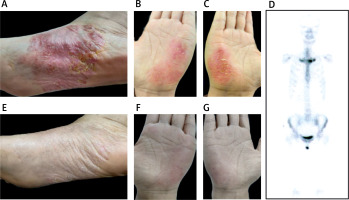
A female patient, aged 39, presented with a 5-year history of AOSD. In 2018, she developed characteristic intermittent high-grade fever, with a body temperature often above 39°C, accompanied by wrist and knee pain, and rash. Subsequently, the patient was diagnosed with AOSD and initiated on prednisone 30 mg once daily, which resulted in a significant improvement in the rash. Following 1 month of full-dose treatment, the dosage was gradually tapered by 5 mg every 2 weeks, and ultimately maintained at 10 mg daily until July 2022. Two months after discontinuing medication, the patient presented with typical yellow pustules on the palmaris major pisiformis and metatarsal arches, accompanied by sternoclavicular joint pain (Figures 1 A–C). A bone scan was performed, revealing accumulation at the sternoclavicular joint, leading to a diagnosis of SAPHO syndrome (Figure 1 D). The patient was prescribed tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily, resulting in significant improvement of the rash and bone pain symptoms after 2 months (Figures 1 E–G).
Figure 1
Bone scintigraphy and rash images of the patient with SAPHO and AOSD syndrome. A–C – The patient exhibited recurrent erythematous skin lesions and yellowish pustules on both palmar aspects of the hands and plantar aspects of the feet, accompanied by desquamation in the form of bran-like scales. D – Technetium 99m-methyl diphosphonate whole body bone scintigraphy showed abnormal accumulation of radioactivity in bilateral sternoclavicular joints. E–G – After treatment, the pustules gradually subsided, and the desquamation characterized by bran-like scales also improved
Tofacitinib is a novel small molecule inhibitor of the JAK signaling pathway, predominantly targeting JAK1 and JAK3, capable of modulating the Th17/Treg balance and reducing disease activity by inhibiting the interaction between JAK and STAT [5]. There have been reported cases of successful treatment of SAPHO syndrome and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis with tofacitinib [5, 6]. In a prospective study with a single-center, open-label, single-arm design that lasted 12 weeks, it was found that tofacitinib alleviated nail lesions and pustular palmoplantar psoriasis (PPP) in patients with SAPHO syndrome, while also improving inflammatory markers and the quality of life for these patients [7].
SAPHO syndrome and AOSD are rare systemic auto-inflammatory diseases that belong to the category of polygenic disorders, and may be associated with HLA class II genes. AOSD is typically described as the adult type of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA), which is characterized by a combination of autoimmune and auto-inflammatory conditions. Studies have suggested that HLA-DRB1*11 and variant major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II genes contribute to JIA development, while the “shared epitope” encoded by HLA-DRB1 alleles is associated with typical JIA characteristics [8]. Genetic testing conducted by Li et al. has revealed significant susceptibility loci for AOSD in the HLA class II region among Chinese AOSD patients [9]. Previous studies have demonstrated the presence of the HLA-B27 gene in up to 30% of patients with SAPHO syndrome [10]. Genetic susceptibility and familial clustering have been reported in pairs of monozygotic twins and in siblings [11]. Additionally, it has been found that in several instances the affected siblings shared numerous human leukocyte antigens (HLA) phenotypes [12].
Since both AOSD and SAPHO syndrome are inflammatory diseases, it is possible that their occurrence and development are related to abnormalities in the immune system. Similar pathogenesis may explain the particular association between these two conditions. The pathogenesis of AOSD remains unclear; however, previous studies have suggested that it may be a result of a combination of inflammatory immune cells and cytokines, influenced by genetic factors [4]. Recent studies have shown that cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6 and IL-18 jointly drive the occurrence and development of AOSD [13]. Inflammatory cytokines also play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of SAPHO syndrome. Recently, it has been found that the imbalance of the immune system can lead to a strong humoral and cellular pro-inflammatory response, which in turn triggers SAPHO syndrome [14]. The elevation of cytokines such as IL-1, IL-8, IL-17 and IL-18 also supports the idea of an inflammatory origin of SAPHO syndrome [15], and that cytokines, such as IL-8 and IL-18, may be responsible for maintaining the clinical manifestations of SAPHO syndrome [11].
Th17 cells, which are named after their signature cytokine, IL-17, play a significant role in mediating numerous inflammatory and autoimmune reactions. Briefly, IL-17 exerts potent proinflammatory actions and augments recruitment of monocytes and neutrophils to inflammatory foci by elevating production of chemokines, such as IL-8 and MCP-1. It also bolsters T-cell infiltration and activation through the induction of intercellular adhesion molecule-1, and intensifies immune responses via the stimulation of diverse immunological mediators, such as IL-6 and PGE2 [16]. Chen et al. observed an increase in circulating Th17 cells, which correlates with disease activity in AOSD, suggesting that the dysregulation of Th17 cells may represent a significant mechanism underlying the pathogenesis of AOSD [17]. Similarly, Davide et al. found an increase in Th17 cells in the peripheral blood of individuals with SAPHO syndrome, implying a significant role for these cells in the disease’s pathogenesis [18]. This similar phenomenon may also be related to the coexistence of AOSD and SAPHO. In a multicenter retrospective study, researchers found that adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD)/systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA) and spondyloarthritis (SpA) can coexist within the same patient. SAPHO syndrome can also be considered as a type of SpA. Among the cases, 1 patient developed symptoms associated with SpA 5 years after the diagnosis of AOSD and met the diagnostic criteria for SAPHO syndrome. The study proposed a hypothesis that the ‘cytokine burst’ during an SJIA/AOSD flare may trigger, via overexpression of these cytokines, a form of SpA [19]. This perspective is similar to our proposed viewpoint regarding the inflammatory pathways. But there is a dearth of direct research concerning the genetic and immunological overlap between SAPHO syndrome and AOSD. Further in-depth research is necessary and beneficial in the future to provide direct and compelling evidence for the potential association between the two conditions.
In conclusion, our group described a case of the co-occurrence of AOSD and SAPHO syndrome, which may be associated with inflammatory pathways of genetic susceptibility. Further investigation is needed to elucidate the potential association between SAPHO syndrome and AOSD and its genetic basis.