Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
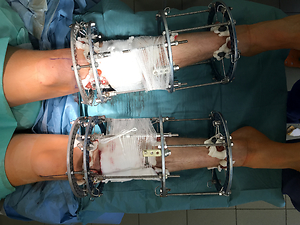
Changes in the quality of life of patients with Blount’s disease undergoing simultaneous bilateral varus deformity correction with the use of the Ilizarov method.
1
Warsaw Medical University, Poland
2
Medical University of Wrocław, Poland
3
University of Opole, Poland
Submission date: 2021-01-02
Final revision date: 2021-04-20
Acceptance date: 2021-04-20
Online publication date: 2021-04-23
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Blount’s disease is a growth disorder of the proximal tibia, which leads to the varus deformity and internal rotation of this bone. The treatment is mainly surgical and involves proximal tibial osteotomy and deformity correction. The aim of this study was to assess the change in the quality of life of patients with tibia vara deformity who underwent correction via the Ilizarov method.
Material and methods:
A total of 23 Blount’s disease patients who had undergone bilateral varus deformity correction with the Ilizarov method were included in this study. The following parameters were assessed retrospectively: duration of treatment with Ilizarov frames, baseline and postoperative values of the medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) and mechanical axis deviation (MAD). The quality of life was assessed with a Short Form (SF)-36 survey.
Results:
The study population comprised 13 females and 10 males (mean age of 28.43), in whom the Ilizarov fixators were kept for an average duration of 106.65 days. MAD values diminished significantly after the surgery. We also observed significant increases in the MPTA values. The SF-36 scores increased across all of the questionnaire’s domains, which indicates a significant improvement in the postoperative quality of life.
Conclusions:
Simultaneous bilateral correction of the varus deformity with Ilizarov external fixators is a safe and effective treatment method. It helps reduce pain and improve gait, which translates to improving the quality of life in all its aspects. The duration of treatment depends to a large extent on the degree of patient cooperation, their attitude, and self-discipline.
Blount’s disease is a growth disorder of the proximal tibia, which leads to the varus deformity and internal rotation of this bone. The treatment is mainly surgical and involves proximal tibial osteotomy and deformity correction. The aim of this study was to assess the change in the quality of life of patients with tibia vara deformity who underwent correction via the Ilizarov method.
Material and methods:
A total of 23 Blount’s disease patients who had undergone bilateral varus deformity correction with the Ilizarov method were included in this study. The following parameters were assessed retrospectively: duration of treatment with Ilizarov frames, baseline and postoperative values of the medial proximal tibial angle (MPTA) and mechanical axis deviation (MAD). The quality of life was assessed with a Short Form (SF)-36 survey.
Results:
The study population comprised 13 females and 10 males (mean age of 28.43), in whom the Ilizarov fixators were kept for an average duration of 106.65 days. MAD values diminished significantly after the surgery. We also observed significant increases in the MPTA values. The SF-36 scores increased across all of the questionnaire’s domains, which indicates a significant improvement in the postoperative quality of life.
Conclusions:
Simultaneous bilateral correction of the varus deformity with Ilizarov external fixators is a safe and effective treatment method. It helps reduce pain and improve gait, which translates to improving the quality of life in all its aspects. The duration of treatment depends to a large extent on the degree of patient cooperation, their attitude, and self-discipline.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.