Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
NEUROLOGY / SYSTEMATIC REVIEW/META-ANALYSIS
Cellular therapy for traumatic brain injury in adults: a meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials
1
Department of Neurosurgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, Fujian Province, China
2
Centre of Neurological and Metabolic Research, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, Fujian Province, China
3
Diabetes and Metabolism Division, Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Sydney, Australia
4
Department of Reproductive Medicine, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou, Fujian Province, China
5
Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan Province, China
6
Department of Orthopedics, Ipswich Hospital, Ipswich IP4 5PD, United Kingdom
7
Department of Interventional Radiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, Henan Province, China
Submission date: 2024-07-06
Final revision date: 2024-09-21
Acceptance date: 2024-10-12
Online publication date: 2024-10-26
Corresponding author
Shu Lin
Centre of Neurological and Metabolic Research The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University Quanzhou, Fujian Province
Centre of Neurological and Metabolic Research The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University Quanzhou, Fujian Province
Hongzhi Gao
Department of Neurosurgery The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University Quanzhou, Fujian Province China
Department of Neurosurgery The Second Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University Quanzhou, Fujian Province China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) lacks effective clinical treatment. Cellular therapy, which is the transfer of autologous or allogeneic cells or cellular material into the patient(s) for treatment or prevention of disease, has shown better outcomes in TBI in several clinical and preclinical studies. We performed a meta-analysis to synthesize and evaluate the current evidence on cellular therapy for TBI in adult patients.
Material and Methods:
We performed a meta-analysis on published articles on the topic of cellular therapy for the treatment of TBI in adult patients. The literature search was conducted via PubMed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Cochrane Library, Embase, Wan Fang Data and Google Scholar, with no restrictions on publication year. Studies were included based on selection criteria and quality assessment. The following data were extracted from included articles: author names; publication year and place; type of study; number, sex and age of participants; type of cells used; and post-treatment follow-up. The required data related to the Fugl-Meyer Motor Scale (FMMS), the Disability Rating Scale (DRS), and patients’ overall improvement were pooled and analyzed using RevMan (Ver. 5.4.1).
Results:
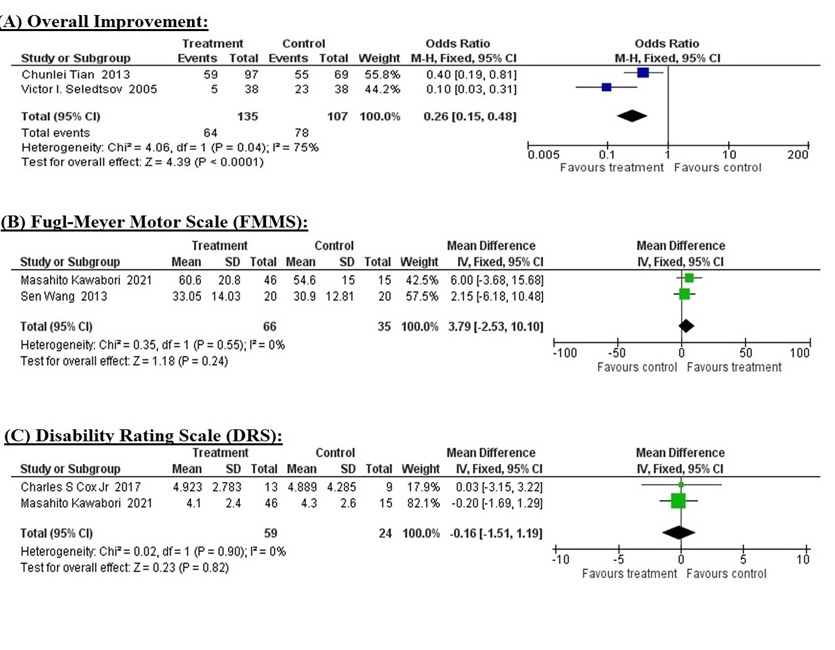
Five studies that met the selection criteria and considered as high quality, containing 367 participants, with an average follow-up time of 7.58 ±6.93 months, were included in the meta-analysis. The results showed that cellular therapy significantly improved (OR = 0.26; 95% CI = 0.15 to 0.48; p = 0.0001) the overall performance of the patients. While improvements in the FMMS (MD = 3.79; 95% CI = –2.53 to 10.10; p = 0.24) and DRS (MD = –0.16; 95% CI = –1.51 to 1.19; p = 0.82) were not statistically significant, they may still be clinically significant.
Conclusions:
This meta-analysis suggests that cellular therapy improves the clinical condition of TBI patients. Larger, multicenter clinical trials are required to further confirm these findings and clarify the optimal use of stem cells in TBI.
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) lacks effective clinical treatment. Cellular therapy, which is the transfer of autologous or allogeneic cells or cellular material into the patient(s) for treatment or prevention of disease, has shown better outcomes in TBI in several clinical and preclinical studies. We performed a meta-analysis to synthesize and evaluate the current evidence on cellular therapy for TBI in adult patients.
Material and Methods:
We performed a meta-analysis on published articles on the topic of cellular therapy for the treatment of TBI in adult patients. The literature search was conducted via PubMed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Cochrane Library, Embase, Wan Fang Data and Google Scholar, with no restrictions on publication year. Studies were included based on selection criteria and quality assessment. The following data were extracted from included articles: author names; publication year and place; type of study; number, sex and age of participants; type of cells used; and post-treatment follow-up. The required data related to the Fugl-Meyer Motor Scale (FMMS), the Disability Rating Scale (DRS), and patients’ overall improvement were pooled and analyzed using RevMan (Ver. 5.4.1).
Results:
Five studies that met the selection criteria and considered as high quality, containing 367 participants, with an average follow-up time of 7.58 ±6.93 months, were included in the meta-analysis. The results showed that cellular therapy significantly improved (OR = 0.26; 95% CI = 0.15 to 0.48; p = 0.0001) the overall performance of the patients. While improvements in the FMMS (MD = 3.79; 95% CI = –2.53 to 10.10; p = 0.24) and DRS (MD = –0.16; 95% CI = –1.51 to 1.19; p = 0.82) were not statistically significant, they may still be clinically significant.
Conclusions:
This meta-analysis suggests that cellular therapy improves the clinical condition of TBI patients. Larger, multicenter clinical trials are required to further confirm these findings and clarify the optimal use of stem cells in TBI.
REFERENCES (72)
1.
Sharma A, Sane H, Kulkarni P, Yadav J, Gokulchandran N, Biju H. Cell therapy attempted as a novel approach for chronic traumatic brain injury – a pilot study. SpringerPlus 2015; 4: 26.
2.
Hyder AA, Wunderlich CA, Puvanachandra P, Gururaj G, Kobusingye OC. The impact of traumatic brain injuries: a global perspective. NeuroRehabilitation 2007; 22: 341-53.
3.
Ruff RL, Riechers RG. Effective treatment of traumatic brain injury: learning from experience. JAMA 2012; 308: 2032-3.
4.
Bowman SM, Bird TM, Aitken ME, Tilford JM. Trends in hospitalizations associated with pediatric traumatic brain injuries. Pediatrics 2008; 122: 988-93.
5.
Hutchison JS, Ward RE, Lacroix J, Hébert PC, Barnes MA, Bohn DJ. Hypothermia therapy after traumatic brain injury in children. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 2447-56.
6.
Adelson PD, Ragheb J, Kanev P, Brockmeyer D, Beers SR, Brown SD. Phase II clinical trial of moderate hypothermia after severe traumatic brain injury in children. Neurosurgery 2005; 56: 740-54.
7.
Maas AIR, Menon DK, Adelson PD, Andelic N, Bell MJ, Belli A. Traumatic brain injury: integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol 2017; 16: 987-1048.
8.
Prins M, Greco T, Alexander D, Giza CC. The pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury at a glance. Dis Models Mech 2013; 6: 1307-15.
9.
Diringer MN. The evolution of the clinical use of osmotic therapy in the treatment of cerebral edema. Acta Neurochirur Suppl 2016; 121: 3-6.
10.
Shi J, Tan L, Ye J, Hu L. Hypertonic saline and mannitol in patients with traumatic brain injury: a systematic and meta-analysis. Medicine 2020; 99: e21655.
11.
Coronado VG, McGuire LC, Sarmiento K, Bell J, Lionbarger MR, Jones CD. Trends in traumatic brain injury in the U.S. and the public health response: 1995-2009. J Saf Res 2012; 43: 299-307.
12.
Wang Z, Luo Y, Chen L, Liang W. Safety of neural stem cell transplantation in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Exp Ther Med 2017; 13: 3613-8.
13.
Aertker BM, Bedi S, Cox CS Jr. Strategies for CNS repair following TBI. Exp Neurol 2016; 275: 411-26.
14.
Walker PA, Shah SK, Harting MT, Cox CS Jr. Progenitor cell therapies for traumatic brain injury: barriers and opportunities in translation. Dis Models Mech 2009; 2: 23-38.
15.
Sharma A, Gokulchandran N, Chopra G, Kulkarni P, Lohia M, Badhe P. Administration of autologous bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells in children with incurable neurological disorders and injury is safe and improves their quality of life. Cell Transpl 2012; 21 Suppl 1: S79-90.
16.
Sharma A, Sane H, Paranjape A, Gokulchandran N, Kulkarni P, Nagrajan A. Positron emission tomography-computer tomography scan used as a monitoring tool following cellular therapy in cerebral palsy and mental retardation-a case report. Case Rep Neurol Med 2013; 2013: 141983.
17.
Sharma A, Gokulchandran N, Sane H, Nagrajan A, Paranjape A, Kulkarni P. Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy for autism: an open label proof of concept study. Stem Cells Int 2013; 2013: 623875.
18.
Kim HJ, Lee JH, Kim SH. Therapeutic effects of human mesenchymal stem cells on traumatic brain injury in rats: secretion of neurotrophic factors and inhibition of apoptosis. J Neurotrauma 2010; 27: 131-8.
19.
Ul Hassan A, Hassan G, Rasool Z. Role of stem cells in treatment of neurological disorder. Int J Health Sci 2009; 3: 227-33.
20.
Liu S, Qu Y, Stewart TJ, Howard MJ, Chakrabortty S, Holekamp TF. Embryonic stem cells differentiate into oligodendrocytes and myelinate in culture and after spinal cord transplantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 6126-31.
21.
Zhao LR, Duan WM, Reyes M, Keene CD, Verfaillie CM, Low WC. Human bone marrow stem cells exhibit neural phenotypes and ameliorate neurological deficits after grafting into the ischemic brain of rats. Exp Neurol 2002; 174: 11-20.
22.
Hsu YC, Chen SL, Wang DY, Chiu IM. Stem cell-based therapy in neural repair. Biomed J 2013; 36: 98-105.
23.
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zou J, Cao F. A meta-analysis of cohort studies: traumatic brain injury and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 2021; 16: e0253206.
24.
Goebell PJ, Kamat AM, Sylvester RJ, Black P, Droller M, Godoy G. Assessing the quality of studies on the diagnostic accuracy of tumor markers. Urol Oncol 2014; 32: 1051-60.
25.
Oremus M, Oremus C, Hall GB, McKinnon MC. Inter-rater and test-retest reliability of quality assessments by novice student raters using the Jadad and Newcastle-Ottawa Scales. BMJ Open 2012; 2: e001368.
26.
Zheng F, Dong Y, Xia P, Mpotsaris A, Stavrinou P, Brinker G. Is clipping better than coiling in the treatment of patients with oculomotor nerve palsies induced by posterior communicating artery aneurysms? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2017; 153: 20-6.
27.
Kawabori M, Weintraub AH, Imai H, Zinkevych I, McAllister P, Steinberg GK. Cell therapy for chronic TBI: interim analysis of the randomized controlled STEMTRA trial. Neurology 2021; 96: e1202-14.
28.
Wiesner K, Schwarz A, Meya L, Kaufmann JE, Traenka C, Luft AR. Interrater reliability of the Fugl-Meyer Motor assessment in stroke patients: a quality management project within the ESTREL study. Front Neurol 2024; 15: 1335375.
29.
Nichol AD, Higgins AM, Gabbe BJ, Murray LJ, Cooper DJ, Cameron PA. Measuring functional and quality of life outcomes following major head injury: common scales and checklists. Injury 2011; 42: 281-7.
30.
Tian C, Wang X, Wang X, Wang L, Wang X, Wu S. Autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell therapy in the subacute stage of traumatic brain injury by lumbar puncture. Exp Clin Transplant 2013; 11: 176-81.
31.
Seledtsov VI, Rabinovich SS, Parlyuk OV, Kafanova MY, Astrakov SV, Seledtsova GV. Cell transplantation therapy in re-animating severely head-injured patients. Biomed Pharmacother 2005; 59: 415-20.
32.
Wang S, Cheng H, Dai G, Wang X, Hua R, Liu X. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation significantly improves neurological function in patients with sequelae of traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 2013; 1532: 76-84.
33.
Cox CS Jr, Hetz RA, Liao GP, Aertker BM, Ewing-Cobbs L, Juranek J. Treatment of severe adult traumatic brain injury using bone marrow mononuclear cells. Stem Cells 2017; 35: 1065-79.
34.
Smith DH, Chen XH, Pierce JE, Wolf JA, Trojanowski JQ, Graham DI. Progressive atrophy and neuron death for one year following brain trauma in the rat. J Neurotrauma 1997; 14: 715-27.
35.
Bramlett HM, Dietrich WD. Progressive damage after brain and spinal cord injury: pathomechanisms and treatment strategies. Progress Brain Res 2007; 161: 125-41.
36.
Peng X, Zhu P, Zhang Q, Li J. The prognostic value of cancer stem cell markers in thyroid cancer: a systematic review. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 686-90.
37.
Jorge RE, Starkstein SE. Pathophysiologic aspects of major depression following traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil 2005; 20: 475-87.
38.
Schwarzbold M, Diaz A, Martins ET, Rufino A, Amante LN, Thais ME. Psychiatric disorders and traumatic brain injury. Neuropsych Dis Treat 2008; 4: 797-816.
39.
Yin L, Ouyang D, Lin L, Xin X, Ji Y. Salidroside regulates imbalance of Th17/Treg and promotes ischemic tolerance by targeting STAT-3 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Arch Med Sci 2021; 17: 523-34.
40.
Kraus MF, Susmaras T, Caughlin BP, Walker CJ, Sweeney JA, Little DM. White matter integrity and cognition in chronic traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain 2007; 130: 2508-19.
41.
Tajiri N, Duncan K, Antoine A, Pabon M, Acosta SA, de la Pena I. Stem cell-paved biobridge facilitates neural repair in traumatic brain injury. Front Systems Neurosci 2014; 8: 116.
42.
Lee JA, Kim BI, Jo CH, Choi CW, Kim EK, Kim HS. Mesenchymal stem-cell transplantation for hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rat model. Pediatr Res 2010; 67: 42-6.
43.
Guo S, Zhen Y, Wang A. Transplantation of bone mesenchymal stem cells promotes angiogenesis and improves neurological function after traumatic brain injury in mouse. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2017; 13: 2757-65.
44.
Anbari F, Khalili MA, Bahrami AR, Khoradmehr A, Sadeghian F, Fesahat F. Intravenous transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promotes neural regeneration after traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen Res 2014; 9: 919-23.
45.
Acosta SA, Tajiri N, Hoover J, Kaneko Y, Borlongan CV. Intravenous bone marrow stem cell grafts preferentially migrate to spleen and abrogate chronic inflammation in stroke. Stroke 2015; 46: 2616-27.
46.
Wennersten A, Meier X, Holmin S, Wahlberg L, Mathiesen T. Proliferation, migration, and differentiation of human neural stem/progenitor cells after transplantation into a rat model of traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 2004; 100: 88-96.
47.
Yan ZJ, Zhang P, Hu YQ, Zhang HT, Hong SQ, Zhou HL. Neural stem-like cells derived from human amnion tissue are effective in treating traumatic brain injury in rat. Neurochem Res 2013; 38: 1022-33.
48.
Gao M, Chen Y, Zhai F, Liu Z, Liu Q, Wang Z. The effect of cultured autologous oral mucosal epithelial cells on ocular surface reconstruction. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 813-21.
49.
Sawicka OP, Kocięba-Łaciak AH, Gałuszka D, Ślusarczyk K, Kasperowicz J. Parents’ attitudes towards children’s transplantology. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 326-31.
50.
Lenzlinger PM, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Laurer HL, McIntosh TK. The duality of the inflammatory response to traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol 2001; 24: 169-81.
51.
Modo M, Stroemer RP, Tang E, Patel S, Hodges H. Effects of implantation site of stem cell grafts on behavioral recovery from stroke damage. Stroke 2002; 33: 2270-8.
52.
Zhang ZX, Guan LX, Zhang K, Zhang Q, Dai LJ. A combined procedure to deliver autologous mesenchymal stromal cells to patients with traumatic brain injury. Cytotherapy 2008; 10: 134-9.
53.
Cox CS Jr, Baumgartner JE, Harting MT, Worth LL, Walker PA, Shah SK. Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell therapy for severe traumatic brain injury in children. Neurosurgery 2011; 68: 588-600.
54.
Liao GP, Harting MT, Hetz RA, Walker PA, Shah SK, Corkins CJ. Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells reduce therapeutic intensity for severe traumatic brain injury in children. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2015; 16: 245-55.
55.
Wang L, Zhao J, Zhu B, Shen J, Ye Z, Peng Q. Microglia polarization in heat-induced early neural injury. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 1307-13.
56.
Riess P, Zhang C, Saatman KE, Laurer HL, Longhi LG, Raghupathi R. Transplanted neural stem cells survive, differentiate, and improve neurological motor function after experimental traumatic brain injury. Neurosurgery 2002; 51: 1043-52.
57.
Shear DA, Tate MC, Archer DR, Hoffman SW, Hulce VD, Laplaca MC. Neural progenitor cell transplants promote long-term functional recovery after traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 2004; 1026: 11-22.
58.
Skardelly M, Gaber K, Burdack S, Scheidt F, Hilbig H, Boltze J. Long-term benefit of human fetal neuronal progenitor cell transplantation in a clinically adapted model after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 2011; 28: 401-14.
59.
Fujiwara Y, Tanaka N, Ishida O, Fujimoto Y, Murakami T, Kajihara H. Intravenously injected neural progenitor cells of transgenic rats can migrate to the injured spinal cord and differentiate into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Neurosci Letters 2004; 366: 287-91.
60.
Harting MT, Sloan LE, Jimenez F, Baumgartner J, Cox CS Jr. Subacute neural stem cell therapy for traumatic brain injury. J Surg Res 2009; 153: 188-94.
61.
Karimi-Abdolrezaee S, Eftekharpour E, Wang J, Morshead CM, Fehlings MG. Delayed transplantation of adult neural precursor cells promotes remyelination and functional neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 3377-89.
62.
Chu K, Kim M, Park KI, Jeong SW, Park HK, Jung KH. Human neural stem cells improve sensorimotor deficits in the adult rat brain with experimental focal ischemia. Brain Res 2004; 1016: 145-53.
63.
Zhang Z, Sui R, Xia D. A variant in microRNA-124 is involved in the control of neural cell apoptosis and associated with recovery after spinal cord injury (SCI). Arch Med Sci 2022; 18: 1399-403.
64.
Lladó J, Haenggeli C, Maragakis NJ, Snyder EY, Rothstein JD. Neural stem cells protect against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity and promote survival of injured motor neurons through the secretion of neurotrophic factors. Mol Cell Neurosci 2004; 27: 322-31.
65.
Chen J, Lu Y, Xu J, Hua Z. Clinical evaluation of maxillary sinus floor elevation with or without bone grafts: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials with trial sequential analysis. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 384-401.
66.
Caplan AI. Adult mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering versus regenerative medicine. J Cell Physiol 2007; 213: 341-7.
67.
Harting MT, Baumgartner JE, Worth LL, Ewing-Cobbs L, Gee AP, Day MC. Cell therapies for traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg Focus 2008; 24: E18.
68.
Maegele M, Schaefer U. Stem cell-based cellular replacement strategies following traumatic brain injury (TBI). Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 2008; 17: 119-31.
69.
Schouten JW, Fulp CT, Royo NC, Saatman KE, Watson DJ, Snyder EY. A review and rationale for the use of cellular transplantation as a therapeutic strategy for traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 2004; 21: 1501-38.
70.
Gao J, Prough DS, McAdoo DJ, Grady JJ, Parsley MO, Ma L. Transplantation of primed human fetal neural stem cells improves cognitive function in rats after traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol 2006; 201: 281-92.
71.
Lu P, Jones LL, Snyder EY, Tuszynski MH. Neural stem cells constitutively secrete neurotrophic factors and promote extensive host axonal growth after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 2003; 181: 115-29.
72.
Ma H, Yu B, Kong L, Zhang Y, Shi Y. Transplantation of neural stem cells enhances expression of synaptic protein and promotes functional recovery in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Mol Med Rep 2011; 4: 849-56.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.