Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
CLINICAL RESEARCH
COVID-19 disease: novel clinical manifestations and therapeutic exploration
1
Department of Critical Care Medicine, Dazhou Central Hospital, Sichuan Province, China
2
Department of Critical Care Medicine, Wenjiang District People’s Hospital, Chengdu-Sichuan Province, China
3
Science and Education-Dazhou Central Hospital, Sichuan Province, China
4
Department of Respiratory Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Sichuan Province, China
5
Imaging Center, Dazhou Central Hospital, Sichuan Province, China
Submission date: 2020-05-19
Final revision date: 2020-07-16
Acceptance date: 2020-08-03
Online publication date: 2020-08-25
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
This study aims to provide further clarifications on some new clinical characteristics of COVID-19 recently discovered by our research group.
Material and methods:
In this single-centred, retrospective study, we collected all confirmed cases of COVID-19 diagnosed in Dazhou, Sichuan, China from January 23 to February 25, 2020. All the cases were either imported from Wuhan or transmitted in family clusters. We analysed general information on all patients. Meanwhile, the contents of lactic acid, Fib-C, and D-dimer in the serum of patients were detected.
Results:
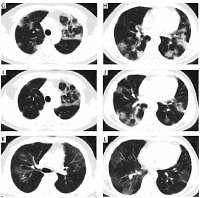
The study included 37 patients diagnosed as having COVID-19, the average age of the patients was 45.76 ±13.1 years. The average positive time of nucleic acid in pharyngeal swabs was 20.65 ±6.7 days. A total of 4 (10.8%) patients were asymptomatic. On serological examination, 33 (89.1%) patients had increased lactic acid, 17 patients had increased fibrinogen C (Fib-C), and 5 patients had increased D-dimer. Of all patients, 29 were positive for COVID-19-specific antibodies. We also detected COVID-19 nucleic acid in faecal specimens from 4 patients. Klebsiella pneumoniae was found in the sputum of 1 patient. A total of 4 patients received psychological intervention. Lopinavir/ritonavir and Abidol may not be effective in treating COVID-19.
Conclusions:
In the serum of most COVID-19-infected patients, lactic acid was higher than normal, and COVID-19-specific antibody was positive. Fib-C and D-dimer in the serum of some infected patients increased. Lopinavir/ritonavir and Abidol have little effect on shortening the positive time of viral nucleic acid in patients.
This study aims to provide further clarifications on some new clinical characteristics of COVID-19 recently discovered by our research group.
Material and methods:
In this single-centred, retrospective study, we collected all confirmed cases of COVID-19 diagnosed in Dazhou, Sichuan, China from January 23 to February 25, 2020. All the cases were either imported from Wuhan or transmitted in family clusters. We analysed general information on all patients. Meanwhile, the contents of lactic acid, Fib-C, and D-dimer in the serum of patients were detected.
Results:
The study included 37 patients diagnosed as having COVID-19, the average age of the patients was 45.76 ±13.1 years. The average positive time of nucleic acid in pharyngeal swabs was 20.65 ±6.7 days. A total of 4 (10.8%) patients were asymptomatic. On serological examination, 33 (89.1%) patients had increased lactic acid, 17 patients had increased fibrinogen C (Fib-C), and 5 patients had increased D-dimer. Of all patients, 29 were positive for COVID-19-specific antibodies. We also detected COVID-19 nucleic acid in faecal specimens from 4 patients. Klebsiella pneumoniae was found in the sputum of 1 patient. A total of 4 patients received psychological intervention. Lopinavir/ritonavir and Abidol may not be effective in treating COVID-19.
Conclusions:
In the serum of most COVID-19-infected patients, lactic acid was higher than normal, and COVID-19-specific antibody was positive. Fib-C and D-dimer in the serum of some infected patients increased. Lopinavir/ritonavir and Abidol have little effect on shortening the positive time of viral nucleic acid in patients.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.