Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
OBSTETRICS AND GYNAECOLOGY / CLINICAL RESEARCH
CBX3 promotes ovarian cancer progression by regulating p53/p21-mediated glucose metabolism via inhibiting NCOR2
1
Department of Gynecology, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia, China
2
Department of Anesthesiology, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia, China
3
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Ningxia Peoples Hospital, Yinchuan, Ningxia, China
Submission date: 2021-08-13
Final revision date: 2022-04-07
Acceptance date: 2022-04-22
Online publication date: 2022-08-03
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Chromobox protein homolog 3 (CBX3) has been reported to play an oncogenic role in various tumors. Nevertheless, the role of CBX3 in ovarian cancer remains vague.
Material and methods:
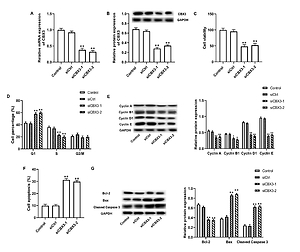
Chromobox protein homolog 3 expression was determined by qRT-PCR and western blotting in ovarian cancer tissues and cell lines. Cell proliferation, cycle and apoptosis were detected using CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry. Transwell and wound healing assays were used to determine cell invasion and migration. Furthermore, the modulatory effects of CBX3 on NCOR2 expression and p53/p21-mediated glycolysis were confirmed.
Results:
The expression of CBX3 was significant elevated in ovarian cancer tissues and cell lines. CBX3 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation, invasion and migration, while it promoted G1/S phase blockade and cell apoptosis. Mechanism analysis verified that CBX3 downregulation increased NCOR2 expression and blocked subsequent p53/p21-mediated glycolysis. NCOR2 silencing and p53/p21 inhibitor treatment reversed the inhibitory effects of CBX3 knockdown on ovarian cancer cellular function.
Conclusions:
CBX3 promoted ovarian cancer progression by promoting p53/p21-mediated glycolysis via inhibiting NCOR2.
Chromobox protein homolog 3 (CBX3) has been reported to play an oncogenic role in various tumors. Nevertheless, the role of CBX3 in ovarian cancer remains vague.
Material and methods:
Chromobox protein homolog 3 expression was determined by qRT-PCR and western blotting in ovarian cancer tissues and cell lines. Cell proliferation, cycle and apoptosis were detected using CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry. Transwell and wound healing assays were used to determine cell invasion and migration. Furthermore, the modulatory effects of CBX3 on NCOR2 expression and p53/p21-mediated glycolysis were confirmed.
Results:
The expression of CBX3 was significant elevated in ovarian cancer tissues and cell lines. CBX3 knockdown inhibited cell proliferation, invasion and migration, while it promoted G1/S phase blockade and cell apoptosis. Mechanism analysis verified that CBX3 downregulation increased NCOR2 expression and blocked subsequent p53/p21-mediated glycolysis. NCOR2 silencing and p53/p21 inhibitor treatment reversed the inhibitory effects of CBX3 knockdown on ovarian cancer cellular function.
Conclusions:
CBX3 promoted ovarian cancer progression by promoting p53/p21-mediated glycolysis via inhibiting NCOR2.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE