Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ONCOLOGY / EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH
Bioinformatics analysis and biological experiments support an emerging role of ELK3 in glioma
1
Department of Neurosurgery, First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Shihezi University, Shihezi, China
Submission date: 2020-12-29
Final revision date: 2021-07-06
Acceptance date: 2021-07-21
Online publication date: 2021-08-07
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
Glioma is a malignant tumor that recurs easily. This study aimed to investigate the biological effect of ELK3 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and its prognostic value.
Material and methods:
Bioinformatics analyses were performed to determine the expression and prognostic value of ELK3. The biological properties of glioma cells (A172 and LN229) were evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8, plate cloning and transwell assays. The Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) website was used to analyze the relationship between ELK3 expression and EMT-related markers. Western blotting was applied to detect the protein levels.
Results:
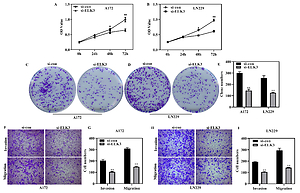
ELK3 is highly expressed in glioma and significantly associated with poor prognosis (p < 0.05), presenting promising value in the diagnosis and prognostic prediction of glioma. Further biological assays revealed that cell viability was notably reduced after down-regulating ELK3 (p < 0.01). The numbers of colonies formed by A172 (145.30 ±12.86 vs. 300.30 ±11.68) and LN229 (125.70 ±4.04 vs. 256.00 ±20.07) cells were decreased after transfection of si-ELK3 (p < 0.01). The numbers of invaded and migrated glioma cells in the si-ELK3 group were decreased by about half (p < 0.01). Moreover, ELK3 was positively correlated with N-cadherin (R = 0.21), Snail1 (R = 0.43), Slug (R = 0.6) and vimentin (R = 0.35), and depletion of ELK3 reduced the levels of these EMT-related markers more than a half (p < 0.01).
Conclusions:
Our observations illustrated that ELK3 was highly expressed in glioma and played a promoting role in the growth and mobility of glioma cells partly by modulating EMT progression.
Glioma is a malignant tumor that recurs easily. This study aimed to investigate the biological effect of ELK3 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and its prognostic value.
Material and methods:
Bioinformatics analyses were performed to determine the expression and prognostic value of ELK3. The biological properties of glioma cells (A172 and LN229) were evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8, plate cloning and transwell assays. The Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis (GEPIA) website was used to analyze the relationship between ELK3 expression and EMT-related markers. Western blotting was applied to detect the protein levels.
Results:
ELK3 is highly expressed in glioma and significantly associated with poor prognosis (p < 0.05), presenting promising value in the diagnosis and prognostic prediction of glioma. Further biological assays revealed that cell viability was notably reduced after down-regulating ELK3 (p < 0.01). The numbers of colonies formed by A172 (145.30 ±12.86 vs. 300.30 ±11.68) and LN229 (125.70 ±4.04 vs. 256.00 ±20.07) cells were decreased after transfection of si-ELK3 (p < 0.01). The numbers of invaded and migrated glioma cells in the si-ELK3 group were decreased by about half (p < 0.01). Moreover, ELK3 was positively correlated with N-cadherin (R = 0.21), Snail1 (R = 0.43), Slug (R = 0.6) and vimentin (R = 0.35), and depletion of ELK3 reduced the levels of these EMT-related markers more than a half (p < 0.01).
Conclusions:
Our observations illustrated that ELK3 was highly expressed in glioma and played a promoting role in the growth and mobility of glioma cells partly by modulating EMT progression.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.