Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
BASIC RESEARCH
Bidirectional causal association between type 1 diabetes and autoimmune diseases: a Mendelian randomization study
1
Department of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
2
Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
3
JingMen People’s Hospital, Jingchu University of Technology Affiliated JingMen People’s Hospital, Jingmen, China
4
Department of Dermatology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Submission date: 2024-08-12
Final revision date: 2024-12-25
Acceptance date: 2025-01-18
Online publication date: 2025-04-11
Corresponding author
Shenghao Tu
Department of Integrated Chinese Traditional and Western Medicine Tongji Hospital Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science and Technology 1095 Jiefang Avenue Qiaokou District Wuhan 430030, China
Department of Integrated Chinese Traditional and Western Medicine Tongji Hospital Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science and Technology 1095 Jiefang Avenue Qiaokou District Wuhan 430030, China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
DiabetologyGeneticsPublic HealthDiffuse Diseases of Connective TissueThyroid DiseaseHepatologyAutoimmunityEpidemiology
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
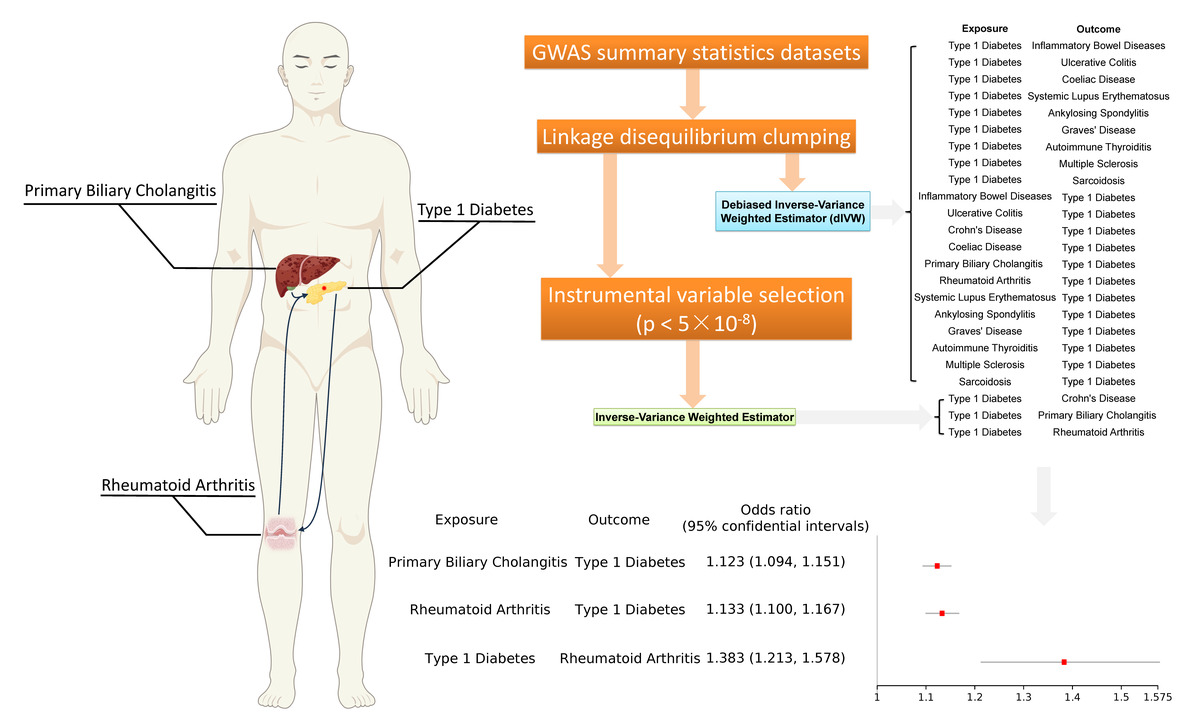
It has been reported that individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D) are at a higher risk of concomitant occurrence of other autoimmune diseases (AIDs). Currently, there is a lack of research investigating the causal relationship between T1D and other AIDs. A comprehensive Mendelian randomization (MR) study was conducted using debiased inverse-variance weighted (dIVW) and inverse-variance weighted (IVW) estimators to examine the bidirectional causal relationship between T1D and 12 AIDs.
Material and methods:
Genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics datasets related to T1D or 12 AIDs were obtained from the FinnGen study or other published cohort studies. Pruned SNPs in linkage disequilibrium (LD)-clumped single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were used as instrumental variables. For the dIVW analysis, no genome-wide significance threshold was applied for SNP selection.
Results:
For each 1-unit increase in the log-transformed odds ratio (OR) of patients with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) or rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the ORs of T1D were 1.123 (95% CI: 1.094–1.151) and 1.133 (95% CI: 1.100–1.167), respectively. Conversely, for each 1-unit increase in the log-transformed OR of T1D, the OR of RA was 1.383 (95% CI: 1.213–-1.578). No bidirectional associations were found between T1D and other AIDs.
Conclusions:
Patients with RA or PBC have a higher risk of developing T1D, and those with T1D also have an increased risk of developing RA. These findings highlight the importance of regular screening for individuals with T1D, RA, or PBC.
It has been reported that individuals with type 1 diabetes (T1D) are at a higher risk of concomitant occurrence of other autoimmune diseases (AIDs). Currently, there is a lack of research investigating the causal relationship between T1D and other AIDs. A comprehensive Mendelian randomization (MR) study was conducted using debiased inverse-variance weighted (dIVW) and inverse-variance weighted (IVW) estimators to examine the bidirectional causal relationship between T1D and 12 AIDs.
Material and methods:
Genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics datasets related to T1D or 12 AIDs were obtained from the FinnGen study or other published cohort studies. Pruned SNPs in linkage disequilibrium (LD)-clumped single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were used as instrumental variables. For the dIVW analysis, no genome-wide significance threshold was applied for SNP selection.
Results:
For each 1-unit increase in the log-transformed odds ratio (OR) of patients with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) or rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the ORs of T1D were 1.123 (95% CI: 1.094–1.151) and 1.133 (95% CI: 1.100–1.167), respectively. Conversely, for each 1-unit increase in the log-transformed OR of T1D, the OR of RA was 1.383 (95% CI: 1.213–-1.578). No bidirectional associations were found between T1D and other AIDs.
Conclusions:
Patients with RA or PBC have a higher risk of developing T1D, and those with T1D also have an increased risk of developing RA. These findings highlight the importance of regular screening for individuals with T1D, RA, or PBC.
REFERENCES (62)
1.
Mayer-Davis EJ, Lawrence JM, Dabelea D, et al. Incidence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes among youths, 2002-2012. N Engl J Med 2017; 376: 1419-29.
3.
Katsarou A, Gudbjörnsdottir S, Rawshani A, et al. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2017; 3: 17016.
4.
Green A, Hede SM, Patterson CC, et al. Type 1 diabetes in 2017: global estimates of incident and prevalent cases in children and adults. Diabetologia 2021; 64: 2741-50.
5.
Lawrence JM, Divers J, Isom S, et al. Trends in prevalence of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in the US, 2001-2017. JAMA 2021; 326: 717-27.
6.
Li Y, Qian K, Wu D, et al. Incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in beijing during 2011-2020 and predicted incidence for 2025-2035: a multicenter, hospitalization-based study. Diabetes Ther 2023; 14: 519-29.
7.
Zhao Z, Sun C, Wang C, et al. Rapidly rising incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in Chinese population: epidemiology in Shanghai during 1997-2011. Acta Diabetol 2014; 51: 947-53.
8.
Wu HB, Zhong JM, Hu RY, et al. Rapidly rising incidence of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents aged 0-19 years in Zhejiang, China, 2007 to 2013. Diabet Med 2016; 33: 1339-46.
9.
Pathak V, Pathak NM, O’Neill CL, et al. Therapies for type 1 diabetes: current scenario and future perspectives. Clin Med Insights Endocrinol Diabetes 2019; 12: 1179551419844521.
10.
von Scholten BJ, Kreiner FF, Gough SCL, et al. Current and future therapies for type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2021; 64: 1037-48.
11.
Triolo TM, Armstrong TK, McFann K, et al. Additional autoimmune disease found in 33% of patients at type 1 diabetes onset. Diabetes Care 2011; 34: 1211-3.
12.
Liao KP, Gunnarsson M, Källberg H, et al. Specific association of type 1 diabetes mellitus with anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide-positive rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2009; 60: 653-60.
13.
Bar Yehuda S, Axlerod R, Toker O, et al. The association of inflammatory bowel diseases with autoimmune disorders: a report from the epi-IIRN. J Crohns Colitis 2019; 13: 324-9.
14.
Barker JM. Clinical review: type 1 diabetes-associated autoimmunity: natural history, genetic associations, and screening. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006; 91: 1210-7.
15.
Molano-González N, Rojas M, Monsalve DM, et al. Cluster analysis of autoimmune rheumatic diseases based on autoantibodies. New insights for polyautoimmunity. J Autoimmun 2019; 98: 24-32.
16.
Glastras SJ, Craig ME, Verge CF, et al. The role of autoimmunity at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes in the development of thyroid and celiac disease and microvascular complications. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 2170-5.
17.
Frommer L, Kahaly GJ. Type 1 diabetes and associated autoimmune diseases. World J Diabetes 2020; 11: 527-39.
18.
Jensen AH, Winther-Sørensen M, Burisch J, et al. Autoimmune liver diseases and diabetes: a propensity score matched analysis and a proportional meta-analysis. Liver Int 2023; 43: 2479-91.
19.
Ismail AMA, Abd Elfatah Abo Saif HF, El-Moatasem Mohamed AM. Effect of Jyoti-Trataka on intraocular pressure, autonomic control, and blood glucose in diabetic patients with high-tension primary open-angle glaucoma: a randomized-controlled trial. J Complement Integr Med 2022; 19: 1013-8.
20.
Ismail AMA, Hamed DE. Erectile dysfunction and metabolic syndrome components in obese men with psoriasis: response to a 12-week randomized controlled lifestyle modification program (exercise with diet restriction). Ir J Med Sci 2024; 193: 523-9.
21.
Ismail AMA, El-Azeim ASA. Short-term intraocular pressure response to the combined effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation over acupoint (Acu-TENS) and yoga ocular exercise in type 2 diabetic patients with primary open-angle glaucoma: a randomized controlled trial. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 2021; 14: 193-9.
22.
Ismail AMA, Abd El-Azeim AS. Response of erectile dysfunction to extracorporeal shock wave therapy in type 2 diabetic men. Physiother Quart 2022; 30: 77-80.
23.
Ye T, Shao J, Kang H. Debiased inverse-variance weighted estimator in two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization. Ann Stat 2021; 49: 2079-100.
24.
Zhao Q, Wang J, Hemani G, et al. Statistical inference in two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization using robust adjusted profile score. Ann Stat 2020; 48: 1742-69.
25.
Xu S, Wang P, Fung WK, et al. A novel penalized inverse-variance weighted estimator for Mendelian randomization with applications to COVID-19 outcomes. Biometrics 2023; 79: 2184-95.
26.
Kurki MI, Karjalainen J, Palta P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023; 613: 508-18.
27.
Forgetta V, Manousaki D, Istomine R, et al. Rare genetic variants of large effect influence risk of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2020; 69: 784-95.
28.
Inshaw JRJ, Sidore C, Cucca F, et al. Analysis of overlapping genetic association in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2021; 64: 1342-7.
29.
Kamat MA, Blackshaw JA, Young R, et al. PhenoScanner V2: an expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics 2019; 35: 4851-3.
30.
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, et al. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet 2018; 50: 693-8.
31.
Chelala C, Duchatelet S, Joffret ML, et al. PTPN22 R620W functional variant in type 1 diabetes and autoimmunity related traits. Diabetes 2007; 56: 522-6.
32.
Barton A, Eyre S, Ke X, et al. Identification of AF4/FMR2 family, member 3 (AFF3) as a novel rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility locus and confirmation of two further pan-autoimmune susceptibility genes. Hum Mol Genet 2009; 18: 2518-22.
33.
Eyre S, Hinks A, Bowes J, et al. Overlapping genetic susceptibility variants between three autoimmune disorders: rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes and coeliac disease. Arthritis Res Ther 2010; 12: R175.
34.
Hemani G, Zheng J, Elsworth B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife 2018; 7: e34408.
35.
Yavorska OO, Burgess S. MendelianRandomization: an R package for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data. Int J Epidemiol 2017; 46: 1734-9.
36.
Liu X, Xu H, Zhan M, et al. The potential effects of diabetes mellitus on liver fibrosis in patients with primary biliary cholangitis. Med Sci Monit 2019; 25: 6174-80.
37.
Chapman MH, Thorburn D, Hirschfield GM, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology and UK-PSC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut 2019; 68: 1356-78.
38.
Cummings BP, Bettaieb A, Graham JL, et al. Bile-acid-mediated decrease in endoplasmic reticulum stress: a potential contributor to the metabolic benefits of ileal interposition surgery in UCD-T2DM rats. Dis Model Mech 2013; 6: 443-56.
39.
Sahin GS, Lee H, Engin F. An accomplice more than a mere victim: the impact of -cell ER stress on type 1 diabetes pathogenesis. Mol Metab 2021; 54: 101365.
40.
Lally FJ, Ratcliff H, Bone AJ. Apoptosis and disease progression in the spontaneously diabetic BB/S rat. Diabetologia 2001; 44: 320-4.
41.
Hunt L, Hensor EM, Nam J, et al. T cell subsets: an immunological biomarker to predict progression to clinical arthritis in ACPA-positive individuals. Ann Rheum Dis 2016; 75: 1884-9.
42.
Lehuen A, Diana J, Zaccone P, et al. Immune cell crosstalk in type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Immunol 2010; 10: 501-13.
43.
Gerlag DM, Safy M, Maijer KI, et al. Effects of B-cell directed therapy on the preclinical stage of rheumatoid arthritis: the PRAIRI study. Ann Rheum Dis 2019; 78: 179-85.
44.
Pescovitz MD, Greenbaum CJ, Krause-Steinrauf H, et al. Rituximab, B-lymphocyte depletion, and preservation of beta-cell function. N Engl J Med 2009; 361: 2143-52.
45.
Leete P, Mallone R, Richardson SJ, et al. The effect of age on the progression and severity of type 1 diabetes: potential effects on disease mechanisms. Curr Diab Rep 2018; 18: 115.
46.
Zheng Y, Liu Q, Goronzy JJ, et al. Immune aging - a mechanism in autoimmune disease. Semin Immunol 2023; 69: 101814.
47.
Eizirik DL, Colli ML, Ortis F. The role of inflammation in insulitis and beta-cell loss in type 1 diabetes. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2009; 5: 219-26.
48.
Brennan FM, McInnes IB. Evidence that cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 2008; 118: 3537-45.
49.
Rogers MAM, Wei MY, Kim C, et al. Sex differences in autoimmune multimorbidity in type 1 diabetes mellitus and the risk of cardiovascular and renal disease: a longitudinal study in the United States, 2001-2017. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2020; 29: 511-9.
50.
Halling ML, Kjeldsen J, Knudsen T, et al. Patients with inflammatory bowel disease have increased risk of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23: 6137-46.
51.
Nielsen NM, Westergaard T, Frisch M, et al. Type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis: a Danish population-based cohort study. Arch Neurol 2006; 63: 1001-4.
52.
Mäkimattila S, Harjutsalo V, Forsblom C, et al. Every fifth individual with type 1 diabetes suffers from an additional autoimmune disease: a Finnish Nationwide Study. Diabetes Care 2020; 43: 1041-7.
53.
Gimenez-Perez G, Vlacho B, Navas E, et al. Comorbid autoimmune diseases and burden of diabetes-related complications in patients with type 1 diabetes from a Mediterranean area. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022; 191: 110031.
54.
Su K, Jia Z, Wu Y, et al. A network causal relationship between type-1 diabetes mellitus, 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and systemic lupus erythematosus: Mendelian randomization study. PLoS One 2023; 18: e0285915.
55.
Zhang J, Qi J, Li Y, et al. Association between type 1 diabetes mellitus and ankylosing spondylitis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front Immunol 2023; 14: 1289104.
56.
Su T, Gan Y, Ma S, et al. Causal association between type 1 diabetes mellitus and inflammatory bowel disease: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Res Square 2023; https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.....
57.
Sims EK, Besser REJ, Dayan C, et al. Screening for type 1 diabetes in the general population: a status report and perspective. Diabetes 2022; 71: 610-23.
58.
Veigas B, Matias A, Calmeiro T, et al. Antibody modified gold nanoparticles for fast colorimetric screening of rheumatoid arthritis. Analyst 2019; 144: 3613-9.
59.
Liu H, Norman GL, Shums Z, et al. PBC screen: an IgG/IgA dual isotype ELISA detecting multiple mitochondrial and nuclear autoantibodies specific for primary biliary cirrhosis. J Autoimmun 2010; 35: 436-42.
60.
Quinn LM, Wong FS, Narendran P. Environmental determinants of type 1 diabetes: from association to proving causality. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 737964.
61.
Deane KD, Demoruelle MK, Kelmenson LB, et al. Genetic and environmental risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 2017; 31: 3-18.
62.
Jiang T, Gill D, Butterworth AS, et al. An empirical investigation into the impact of winner’s curse on estimates from Mendelian randomization. Int J Epidemiol 2023; 52: 1209-19.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.