The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) epidemic, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), poses unprecedented challenges to global healthcare systems. As of 13 October 2024, over 776 million confirmed cases and over 7 million deaths have been reported globally [1]. The main manifestations of COVID-19 are fever, cough and weakness [2], and acute hypoxic respiratory failure is a common and more serious complication of severe COVID-19 (SCOVID-19), the mortality rate of which can be as high as 45% [3]. Autopsies of patients who died from COVID-19 showed a high rate of microthrombus formation in the pulmonary capillaries [4], which might explain the prominent hypoxemia in SCOVID-19 patients. Coagulation dysfunction is thought to occur throughout the pathogenesis of SCOVID-19, with studies confirming the presence of thrombocytopenia and increased D-dimer aggregates in up to 57.7% and 59.6% of patients with SCOVID-19, respectively [5]. As a key regulatory gene in the coagulation system, ADAMTS13 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, member 13) encoded by the ADAMTS13 gene is an enzyme produced in the liver whose main function is to regulate the size of von Willebrand factor (VWF), thereby avoiding unnecessary platelet aggregation and thrombosis [6]. Genome-wide association studies have revealed that some genetic variations are associated with an increased risk of SCOVID-19. For example, research has found that the gene group on chromosome 3p21.31 is associated with worsening COVID-19 symptoms [7]. ADAMTS13 has been shown to play a critical role in the development of thromboembolism in SCOVID-19. In addition to inflammation-induced inhibition of ADAMTS13 activity in SCOVID-19 [8], the host genetic determinants of this susceptibility to ADAMTS13 are still unclear, especially in the Han Chinese population.
The aim of this study was to investigate whether ADAMTS13 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are associated with SCOVID-19 in the Chinese Han population and compared with severe pneumonia due to pathogens other than SARS-CoV-2 (non-S-SP).
Methods. The study followed a case-control design and included 370 severe pneumonia (SP) patients and 500 healthy controls from January 1 to September 30, 2023. The sample size was calculated using PASS15, and the sample size of the two groups in the study was sufficient. The participants or their guardians received detailed study information and signed an informed consent form. This research was conducted in compliance with the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki, and its plan was approved by the Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital Committee (opinion no. 581/2023).
Study population. The inclusion criteria of SP were as follows: (1) age ranging from 18 to 85 years; (2) all participants were of Han Chinese ethnicity; (3) SCOVID-19 and non-S-SP must meet the diagnostic criteria for SP according to the American Thoracic Society guidelines for community-acquired pneumonia and have clear corresponding pathogens (SARS-CoV-2 or other pathogens) [9]. Patients with other special infectious diseases of the lung such as tuberculosis, parasitic infection as well as those with severe liver and kidney diseases, cancer, HIV, long-term use of hormones and immunosuppressant, or history of drug abuse, were excluded from the study.
Genotyping. We used the NCBI 1000 Genome Project (http://browser.1000genome) database to identify ADAMTS13 haplotype-tagged SNPs (TagSNPs). The selection of TagSNPs was based on a minor allele frequency (MAF) of ≥ 5% and linkage disequilibrium (LD) r2 cut-off values of 0.8–1.0. Ultimately, three TagSNPs (rs3118667, rs3124768, and rs652600) were selected for our investigation. Five milliliters of peripheral blood was collected from all participants and was anticoagulated with EDTA. DNA extraction was performed according to the steps described in the Tiangen kit manual (Tiangen Biotech Beijing, Co., Ltd, China). Multiple SNP typing was performed using the SNPscan method, which involved synthesizing specific primers based on the SNP information provided and optimizing the linkage reaction system (Cat #: G0104K, Genesky Inc. Shanghai, China).
Collection of clinical data. The clinical information collected included demographics, underlying illnesses, APACHE II scores and complications. The treatment decisions were based on the corresponding diagnosis and treatment guidelines [9].
Statistical analysis. Data analysis was conducted using the statistical software SPSS 22.0. Continuous variables were presented as mean and standard deviation (SD) or median and interquartile range (IQR). Categorical variables were presented as counts and percentages. Univariate analyses were performed with the t-test or Mann-Whitney test for continuous variables and the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables, as appropriate. Logistic regression and haplotype analyses were performed to analyze the gene polymorphisms. The SHEsis online software platform [10] was used to evaluate LD and perform haplotype analysis between SNPs. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
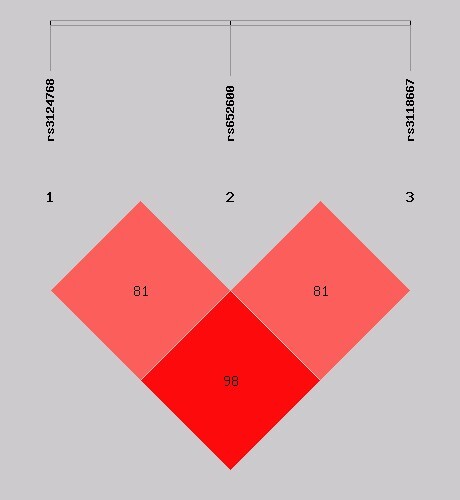
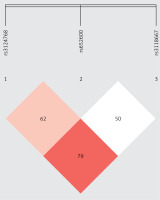
Results. The demographic characteristics of SP patients and healthy controls were balanced (Additional file 1: Supplementary Table SI). The 370 SP patients included 95 with SCOVID-19 and 275 with non-S-SP. There were no statistically significant differences in body mass index (BMI), sex, age, underlying disease, APACHE II score, or 28-day mortality between the two groups, but the SCOVID-19 group showed higher respiratory rates, thrombotic events, invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) days, and acute kidney injury (AKI) incidence than the non-S-SP group (Supplementary Table SII). Table I presents the association between ADAMTS13 SNPs and susceptibility to SCOVID-19 or non-S-SP group. Our analysis demonstrated that, after adjusting for sex and age, the distribution frequencies of the C allele (OR = 0.630, 95% CI: 0.459–0.864, p = 0.004) and the CC genotype (OR = 0.188, 95% CI: 0.043–0.825, p = 0.027), as well as the recessive genetic model (OR = 0.208, 95% CI: 0.048–0.908, p = 0.037) and the additive genetic model (OR = 0.632, 95% CI: 0.460–0.868, p = 0.005) of rs3118667 were significantly associated with a decreased risk of susceptibility in the non-S-SP group. Similarly, the distribution frequencies of the A allele (OR = 0.722, 95% CI: 0.539–0.966, p = 0.029) and the additive genetic model (OR = 0.726, 95% CI: 0.543–0.700, p = 0.031) of rs3124768 also exhibited a significant association with reduced susceptibility risk. However, no association was found between susceptibility and the selected ADAMTS13 SNPs in the SCOVID-19 group. We further conducted a comparative analysis between the SCOVID-19 group and the non-S-SP group. The results indicated that the C allele of rs3118667 was associated with an increased risk of SCOVID-19 after adjusting for potential confounding variables (OR = 1.638, 95% CI: 1.026–2.613, p = 0.039). Additionally, the additive genetic model demonstrated a similar association (OR = 1.694, 95% CI: 1.041–2.757, p = 0.034), as detailed in Table II. Figure 1 illustrates the LD analysis between the ADAMTS13 SNPs investigated (rs3118667, rs3124768, rs652600). The r2 values between the three TagSNPs indicated a relatively high level of LD. Four haplotypes were identified: AAC, AGC, GAT, and GGT. The haplotype AGC was significantly associated with an increased risk of contracting SCOVID-19 compared to non-S-SP (OR = 3.254, 95% CI: 1.096–9.659, p = 0.025) (Supplementary Table SIII).
Table I
Analysis of ADAMTS13 gene SNPs in association with susceptibility to SCOVID-19 and non-S-SP
| SNPs | Genetic models | Allele/genotype | SP group [N (%)] | Healthy group [N (%)] | SCOVID-19 vs. Healthy control group | Non-S-SP group vs. Healy control group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORa (95% CI) | P-valuea | ORa (95% CI) | P-valuea | |||||
| rs3118667 (T>C) | T | 633 (85.5) | 825 (82.5) | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | |
| C | 93 (12.6) | 165 (16.5) | 1.036 (0.682–1.573) | 0.869 | 0.630 (0.459–0.864) | 0.004 | ||
| TT | 274 (74.1) | 347 (69.4) | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | ||
| CT | 85 (23.0) | 131 (26.2) | 1.174 (0.719–1.919) | 0.521 | 0.703 (0.491–1.007) | 0.055 | ||
| CC | 4 (1.0) | 17 (3.4) | 0.637 (0.143–2.839) | 0.554 | 0.188 (0.043–0.825) | 0.027 | ||
| Recessive | CC vs.TT + CT | 0.624 (0.141–2.757) | 0.534 | 0.208 (0.048–0.908) | 0.037 | |||
| Additive | 2CC + CT vs. TT | 1.035 (0.685–1.565) | 0.870 | 0.632 (0.460–0.868) | 0.005 | |||
| rs652600 (G>A) | G | 95 (12.8) | 423 (42.3) | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | |
| A | 640 (86.5) | 569 (56.9) | 0.997 (0.653–1.52) | 0.987 | 0.913 (0.685–1.216) | 0.534 | ||
| GG | 264 (71.4) | 334 (66.8) | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | ||
| GA | 92 (24.9) | 141 (28.2) | 0.818 (0.489–1.37) | 0.445 | 0.823 (0.586–1.157) | 0.263 | ||
| AA | 12 (32.4) | 20 (4.0) | 1.007 (0.332–3.058) | 0.990 | 0.671(0.290–1.557) | 0.353 | ||
| Recessive | AA vs. GG + GA | 1.074 (0.358–3.229) | 0.898 | 0.710 (0.308–1.636) | 0.421 | |||
| Additive | 2AA + GA vs. GG | 0.893 (0.593–1.345) | 0.587 | 0.824 (0.624–1.089) | 0.174 | |||
| rs3124768 (G>A) | G | 633 (85.5) | 825 (82.5) | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | |
| A | 93 (12.6) | 165 (16.5) | 0.985 (0.656–1.480) | 0.944 | 0.722 (0.539–0.966) | 0.029 | ||
| GG | 263 (71.1) | 332 (66.4) | 1 | Reference | 1 | Reference | ||
| GA | 95 (25.7) | 142 (28.4) | 1.043 (0.640–1.701) | 0.865 | 0.775 (0.550–1.091) | 0.144 | ||
| AA | 8 (2.2) | 20 (4.0) | 0.498 (0.215–1.151) | 0.103 | 0.393 (0.144-1.072) | 0.068 | ||
| Recessive | AA vs. GG + GA | 0.798 (0.231–2.754) | 0.721 | 0.426 (0.157–1.155) | 0.094 | |||
| Additive | 2AA + GA vs. GG | 0.986 (0.660–1.473) | 0.994 | 0.726 (0.543–0.700) | 0.031 | |||
Table II
Comparison of ADAMTS13 polymorphisms between the SCOVID-19 group and the non-S-SP group
| SNPs | Genetic models | Allele/genotype | SCOVID-19 group [N (%)] | Non-S-SP group [N (%)] | SCOVID-19 group vs. | Non-S-SP group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ORa (95% CI) | P-valuea | |||||
| rs3118667 (T>C) | T | 158 (83.2) | 475 (86.4) | 1 | Reference | |
| C | 32 (16.8) | 61 (11.1) | 1.638 (1.026–2.613) | 0.039 | ||
| TT | 65 (68.4) | 209 (75.0) | 1 | Reference | ||
| CT | 28 (29.5) | 57 (20.7) | 1.651 (0.966–2.823) | 0.067 | ||
| CC | 2 (2.1) | 2 (0.7) | 3.580 (0.486–26.367) | 0.211 | ||
| Recessive | CC vs. TT + CT | 3.126 (0.429–22.777) | 0.261 | |||
| Additive | 2CC + CT vs. TT | 1.694 (1.041–2.757) | 0.034 | |||
| rs652600 (G>A) | G | 159 (83.7) | 461 (83.8) | 1 | Reference | |
| A | 31 (16.3) | 85 (15.6) | 1.085 (0.691–1.704) | 0.722 | ||
| GG | 68 (71.6) | 196 (71.3) | 1 | Reference | ||
| GA | 23 (24.2) | 69 (25.1) | 0.996 (0.574–1.726) | 0.987 | ||
| AA | 4 (4.2) | 8 (2.9) | 1.530 (0.443–5.282) | 0.501 | ||
| Recessive | AA vs. GG + GA | 1.503 (0.440–5.142) | 0.516 | |||
| Additive | 2AA + GA vs. GG | 1.081 (0.697–1.676) | 0.729 | |||
| rs3124768 (G>A) | G | 156 (82.1) | 465 (84.5) | 1 | Reference | |
| A | 34 (17.9) | 77 (14.0) | 1.353 (0.868–2.111) | 0.182 | ||
| GG | 64 (67.4) | 199 (72.4) | 1 | Reference | ||
| GA | 28 (29.5) | 64 (23.3) | 1.341 (0.792–2.271) | 0.276 | ||
| AA | 3 (3.2) | 5 (1.8) | 2.014 (0.463–8.773) | 0.351 | ||
| Recessive | AA vs. GG + GA | 1.829 (0.425–7.869) | 0.418 | |||
| Additive | 2AA + GA vs .GG | 1.360 (0.868–2.133) | 0.180 |
Figure 1
The r2 between rs3124768 and rs652600 was 0.626 and the r2 value between rs3124768 and rs3118667 was 0.793, indicating a relatively strong level of LD. Finally, the r2 between rs6526000 and rs3118667 was 0.508, indicating a moderate level of LD as well
Discussion. In addition to influencing the development of thromboembolism, hypercoagulability induced by SARS-CoV-2 causes direct damage to lung and endothelial cells, as well as interactions with local and systemic inflammatory responses, further contributing to increased disease severity and high mortality rates [8]. SNPs are closely associated with susceptibility to and development of SCOVID-19 [7], and some risk variants map near genes specifically involved in hemostatic regulation [11]. However, few studies have explored SNPs related to coagulation in SCOVID-19 patients, and research on ADAMTS13 polymorphisms in the Chinese Han population with SCOVID-19 is lacking, especially in contrast to non-S-SP.
In comparison with healthy populations, we found that the ADAMTS13 SNPs (rs3118667, rs3124768, rs652600) are not associated with susceptibility to SCOVID-19, but rs3118667 and rs3124768 were associated with a reduced susceptibility risk of the non-S-SP group. Specifically, individuals carrying the C allele and the additive genetic model of rs3118667 exhibited a higher risk of SCOVID-19 than non-S-SP. Furthermore, haplotype analysis indicated that the AGC haplotype was significantly associated with an elevated risk of SCOVID-19. Rs3118667 is a synonymous SNP of the ADAMTS13 gene, which has been reported to be associated with an increase in ADAMTS13 activity [12] and has a protective effect against deep vein thrombosis onset [13]. A haplotype is a physical grouping of genomic variants (or polymorphisms) that tend to be inherited together [14], and the haplotype AGC confirms the association between ADAMTS13 gene polymorphisms and a high risk of SCOVID-19. This is precisely because of the reduced susceptibility to non-S-SP in the Chinese Han population, which theoretically exhibits a higher risk of SCOVID-19 caused by ADAMTS13 polymorphisms. SARS-CoV-2 affects all components of hemostasis, including primary hemostasis (i.e., platelets, VWF, and endothelium) [15], due to direct virus-induced endothelial damage and secondary inflammation caused by cytokine storms [16]. Data from the multicenter GEN-COVID study allow us to define the prevalence of ADAMTS13 mutations in a SARS-CoV-2-positive population by affecting the expression of ADAMTS13 [17]. Owing to the lack of protection from rs3118667, SCOVID-19 may result in more pulmonary and extrapulmonary microthrombi due to weakened ADAMTS13 activity [18], leading to pulmonary arterial hypertension, extrapulmonary organ involvement, even right heart dysfunction [19]. Our clinical data also indicate that SCOVID-19 patients experienced more thrombus events, longer ventilator time, and higher incidence of AKI, which is consistent with the above speculation. Further research is required to improve the detection of serum ADAMTS13 levels to support this hypothesis.
This is the first report on the association of coagulation-associated ADAMTS13 polymorphisms with SCOVID-19 in the Han Chinese population. Interestingly, our research revealed that for Han Chinese individuals, there was no significant association between ADAMTS13 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility of SCOVID-19, but the risk of SCOVID-19 was greater in individuals carrying rs3118667 than that of non-S-SP. This may explain why coagulation dysfunction in SCOVID-19 is more prominent than that in SP caused by other pathogens. Our study has several shortcomings, as follows: 1. ADAMTS13 activity was not monitored in the patients included in the study. 2. The three SNPs included in the study (rs3118667, rs3124768, and rs652600) were not representative of the full range of genetic variants in ADAMTS13. 3. Caution should be exercised when generalizing these findings to other ethnic groups. 4. Future research should consider conducting longitudinal studies and expanding the scope of SNP analyses to encompass functional assessments and examinations across diverse populations. Moreover, detection of serum ADAMTS13 activity and further functional studies are required to confirm these conclusions.