Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ONCOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
Association between inflammatory cytokines and prostate cancer
1
Ningbo Medical Centre LiHuiLi Hospital, China
2
Xiuzhou District People's Hospital of Jiaxing, China
Submission date: 2024-03-02
Final revision date: 2024-07-01
Acceptance date: 2024-07-04
Online publication date: 2024-07-28
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
We conducted bidirectional two-sample Mendelian Randomization (MR) analysis to investigate the causal relationship between 91 inflammatory cytokines and prostate cancer (PCa).
Material and methods:
The Inverse Variance Weighted (IVW) model served as the primary two-sample MR analysis method, utilized to estimate the causal effect of exposure on the outcome. The Weighted Median (WM) and MR Egger methods were additionally employed to complement the IVW model. Sensitivity analyses were performed using Cochran's Q test for both the IVW and MR Egger methods. To assess the presence of horizontal pleiotropy, the instrumental variables (IVs) were subjected to the MR-Egger intercept test.
Results:
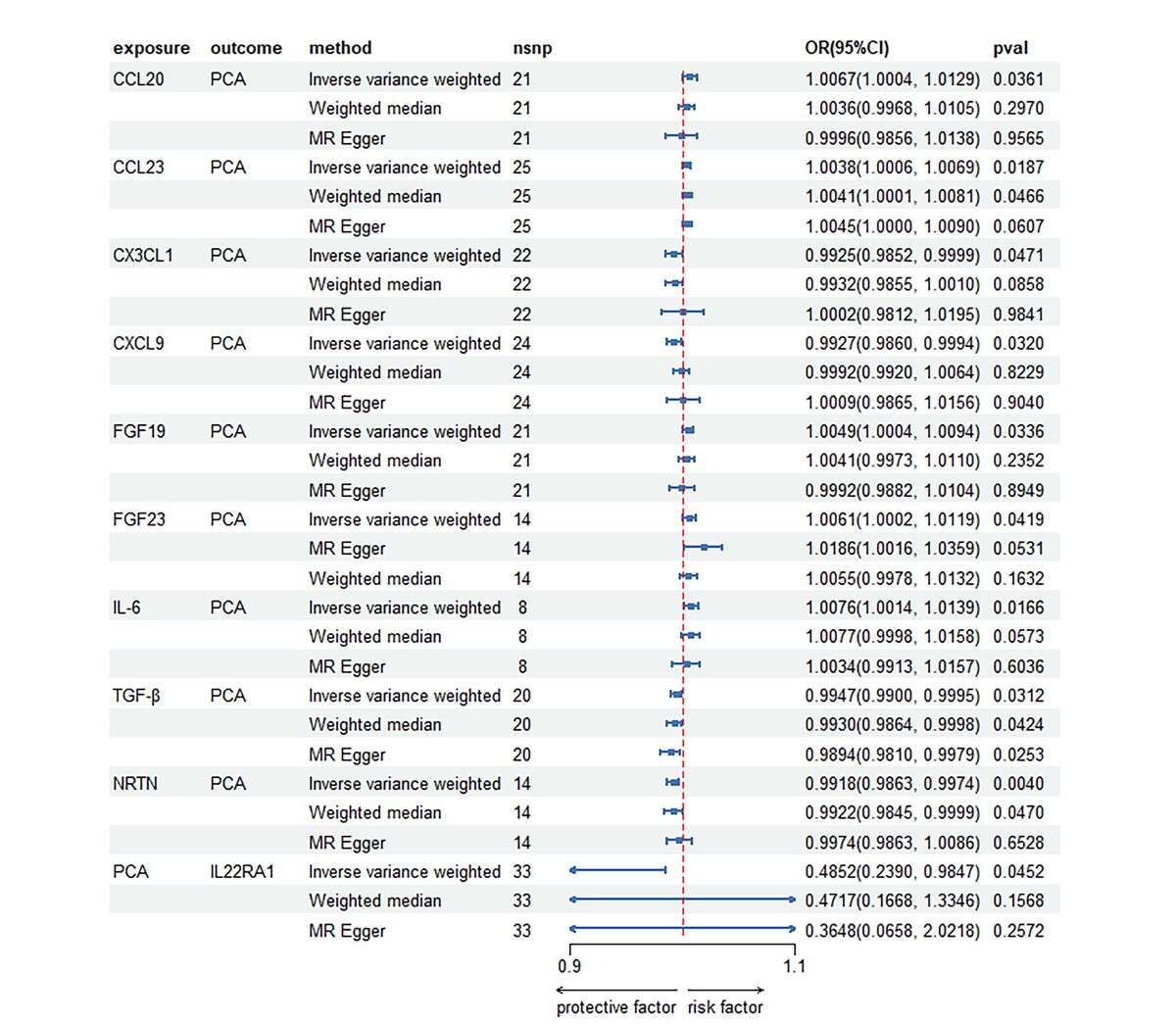
Following Bonferroni correction, the IVW analysis revealed positive correlations between PCa and the levels of C-C motif chemokine 20 (CCL20), C-C motif chemokine 23 (CCL23), fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19), fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Notably, IL-6 exhibited the strongest positive association effect (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.0076 [1.0014, 1.0139]), followed by CCL-20 (1.0067 [1.0004, 1.0129]) and FGF23 ([1.0002, 1.0119]). Reverse MR analysis indicated a negative causal relationship between PCa and interleukin-22 receptor subunit alpha-1 levels (IL22RA1) (0.4852 [0.2390, 0.9847]).
Conclusions:
This study proposes that there exists a positive correlation between the levels of CCL20, CCL23, FGF19, FGF23, and IL-6 and the occurrence of PCa. Furthermore, we found evidence to support the causal relationship between decreased levels of IL22RA1 and the development of PCa. These findings unveil novel biomarkers and pathways that could potentially be targeted for the prevention and clinical treatment of PCa.
We conducted bidirectional two-sample Mendelian Randomization (MR) analysis to investigate the causal relationship between 91 inflammatory cytokines and prostate cancer (PCa).
Material and methods:
The Inverse Variance Weighted (IVW) model served as the primary two-sample MR analysis method, utilized to estimate the causal effect of exposure on the outcome. The Weighted Median (WM) and MR Egger methods were additionally employed to complement the IVW model. Sensitivity analyses were performed using Cochran's Q test for both the IVW and MR Egger methods. To assess the presence of horizontal pleiotropy, the instrumental variables (IVs) were subjected to the MR-Egger intercept test.
Results:
Following Bonferroni correction, the IVW analysis revealed positive correlations between PCa and the levels of C-C motif chemokine 20 (CCL20), C-C motif chemokine 23 (CCL23), fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19), fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Notably, IL-6 exhibited the strongest positive association effect (odds ratio [95% confidence interval]: 1.0076 [1.0014, 1.0139]), followed by CCL-20 (1.0067 [1.0004, 1.0129]) and FGF23 ([1.0002, 1.0119]). Reverse MR analysis indicated a negative causal relationship between PCa and interleukin-22 receptor subunit alpha-1 levels (IL22RA1) (0.4852 [0.2390, 0.9847]).
Conclusions:
This study proposes that there exists a positive correlation between the levels of CCL20, CCL23, FGF19, FGF23, and IL-6 and the occurrence of PCa. Furthermore, we found evidence to support the causal relationship between decreased levels of IL22RA1 and the development of PCa. These findings unveil novel biomarkers and pathways that could potentially be targeted for the prevention and clinical treatment of PCa.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.