Osteoporosis (OP) is a widespread chronic condition characterized by a reduction in bone mineral density (BMD), compromised bone strength, and an elevated susceptibility to fractures [1]. In the USA, over 10.2 million individuals are affected by OP, and over 3 million cases of fractures associated with OP are expected annually, leading to a projected treatment cost of approximately $25.3 billion [2]. OP is strongly linked to aging, and it is worrisome that as the world’s population continues to age, the prevalence of osteoporosis will also increase [3].
According to the 2016 data provided by the WHO, around 91% of the global population resided in areas with low air quality [4]. Common air pollutants are usually divided into particulate matter (PM) and various gases, such as nitrogen dioxide, nitrogen oxides and more. PM is categorized according to its size, with particles smaller than 10 μm classified as PM10, those smaller than 2.5 μm as PM2.5, and particles with diameters between 2.5 μm and 10 μm as PM2.5-10 [5].
Observational studies have provided some indications of the connection between air pollution and BMD. A study found a negative association between BMD in the femoral neck and exposure to air pollutants like PM2.5 and PM10 [6]. Likewise, another study demonstrated a correlation between exposure to PM2.5 and PM10 and reduced BMD in a group of 590 men aged 75 years and older [7].
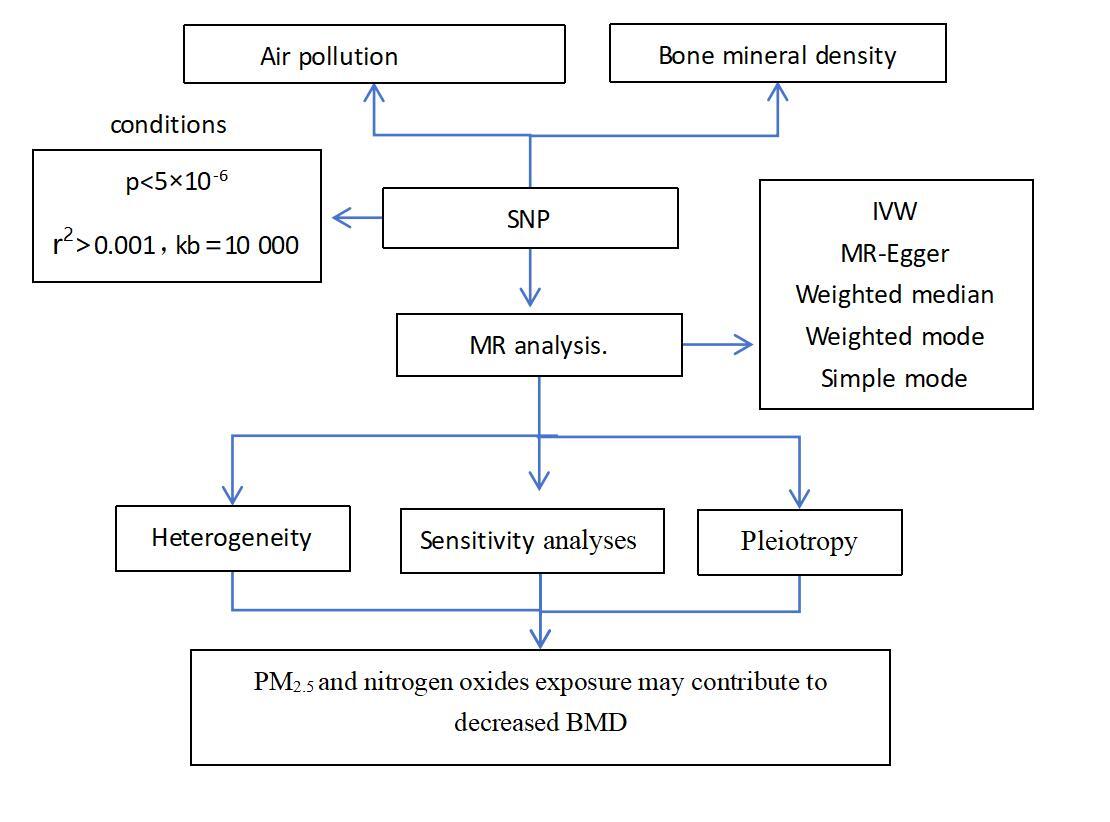
Although numerous studies have shown a connection between air pollution and BMD, the question of causality is still being actively researched. In this study, we conducted an MR study using publicly available GWAS data, employing PM2.5, PM2.5-10, PM10, nitrogen dioxide, and nitrogen oxides as exposures and BMD as the outcome. The study aimed to clarify the potential causal relationship between air pollution and BMD.
Methods
Study design
In our study, air pollution served as the exposure factor, and IVs consisting of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) displayed a strong correlation with air pollution (PM2.5, PM2.5–10, PM10, nitrogen dioxide, and nitrogen oxides). BMD served as the outcome variable in this study. Therefore, we employed an MR investigation to analyze the causal relationship between air pollution and BMD.
GWAS data sources
GWAS data related to SNPs were obtained from publicly available GWAS. Summary-level genetic data for PM2.5, PM2.5–10, PM10, nitrogen dioxide, and nitrogen oxides were obtained from the UK Biobank (http://www.nealelab.is/uk-biobank), including 423,796; 423,796; 455,314; 456,380; 456,380 individuals of European ancestry, respectively. Summary-level genetic data for BMD were obtained from a meta-GWAS study, including 365,403 individuals of European ancestry. Additional data details are listed in Table I.
Table I
Overview of the data sources of phenotypes used in the MR study
Selection of IVs
First, we established uniform filtering criteria (p < 5 × 10–8) for the IVs to ensure statistical significance [8]. However, insufficient SNPs were identified. Drawing upon the correlation analysis findings of relatively reliable thresholds in the existing literature, we relaxed the criteria to 5 × 10–6 for screening IVs [9]. For each corresponding SNP of each IV, we considered the linkage disequilibrium correlation coefficient (r2 < 0.001) and base pair distance between the two SNPs (kb > 10,000). Then, we excluded those with intermediate allele frequencies, palindrome SNPs, incompatible SNPs, and confounder-related SNPs. Finally, we set a stringent threshold for statistical strength, with F > 10 as the criterion for strong correlation, minimizing the potential for weak instrument bias.
MR analysis method
In our study, we employed the inverse variance weighted (IVW) approach as the main methodology to evaluate the potential causality between air pollution and BMD. Additionally, we incorporated additional validation through MR-Egger and weighted median analyses. Then, we utilized MR-Egger regression and Cochran’s Q test to ascertain the presence of pleiotropy and heterogeneity.
Results
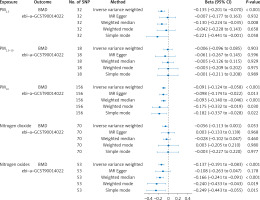
In our research, 32 SNPs robustly linked to PM2.5, 18 SNPs strongly related to PM2.5-10, 156 SNPs robustly associated with PM10, 70 SNPs robustly correlated with nitrogen dioxide, and 53 SNPs strongly related to nitrogen oxides. F-statistics of all IVs surpassed a threshold of 10. Detailed information about these IVs is provided in Supplementary Table SI.
The IVW method showed that the Beta and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) for various exposures are as follows: PM2.5: Beta = –0.135, 95% CI = [–0.201, –0.070], p = 8.23 × 10–5; PM2.5-10: Beta = –0.006, 95% CI = [–0.006, 0.085], p = 9.03 × 10–1; PM10: Beta = –0.091, 95% CI = [–0.124, –0.058], p = 3.3 × 10–7; nitrogen dioxide: Beta = –0.056, 95% CI = [–0.113, 0.001], p = 6.59 × 10–2; nitrogen oxides: Beta = –0.137, 95% CI = [–0.191, –0.083], p = 1.52 × 10–6 (Figure 1). All significance levels are FDR-adjusted. As indicated by the finding, we identified a causality linking air pollution (PM2.5, PM10, nitrogen oxides) with BMD. Other methods demonstrated that these relationships persisted (Figure 1). Furthermore, this study did not observe any evidence of causality between PM2.5-10, nitrogen dioxide, and BMD (Figure 1).
This study showed no evidence of pleiotropy (Table II), indicating IVs do not affect the outcome via the confounding factors. No heterogeneity was observed in our study for PM2.5, PM2.5-10, PM10, and nitrogen oxides, except for nitrogen dioxide (p = 0.034, Q = 91.968) (Table II). The “leave-one-out” analysis indicated that findings remained consistent even with the exclusion of any individual SNP.
Table II
Pleiotropy and heterogeneity test of air pollution genetic instrumental variables in GWAS for BMD
Discussion
The connection between air pollutants and bone mineral metabolism is not fully comprehended due to the complexity of the biological processes involved. However, an increasing amount of proof suggests that increased inflammatory reactions caused by air pollution exposure can be considered a contributing element [10]. Exposure to air pollutants can increase overall inflammation by triggering certain proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and IL-17. These cytokines, in turn, influence the differentiation and function of osteoblasts and osteoclasts [11]. Additionally, air pollution is likely to induce cellular oxidative stress, which is one of the pathogenic mechanisms. Studies suggest that bone loss in estrogen-deficient mice is caused by oxidative stress, which activates T cells through increased activation of bone marrow dendritic cells [12]. Besides, vitamin D (Vit D) deficiency serves as an additional factor connecting air pollution to OP. Low levels of Vit D can lead to decreased serum calcium levels, which can then increase osteoclast activity and the transfer of calcium from the bones to the outside of cells [13]. Air pollution might be associated with a decrease in outdoor activities, leading to reduced exposure to solar ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation. Insufficient absorption of UVB by the skin is a significant contributor to Vit D deficiency [14]. Additional studies are needed to elucidate the biological mechanisms linking air pollutant exposure and reduced BMD.
This study presents several advantages. Firstly, our study harnessed Mendel’s principle of independent assortment, opting for IVs as the exposure in MR analysis. This choice greatly boosts the reliability of our results as we investigate the cause-and-effect connection between air pollution and BMD. Secondly, reverse causality is precluded as genes precede the onset of the disease. Thirdly, our study leveraged data from publicly available GWAS pooled investigations, benefiting from a substantial sample size that enhances the robustness of our analysis. Additionally, our study offers a novel theoretical and practical groundwork to address the hazards posed by air pollution to bone health.
Nevertheless, our study comes with inherent limitations. Firstly, it is noteworthy that the population under investigation for air pollution and BMD predominantly comprises individuals of European descent. This potential ethnic homogeneity may limit the broader applicability of our findings to the entire population. Secondly, due to our reliance solely on summary statistics from the MR study, our conclusions are limited to finding that air pollution (PM2.5 and nitrogen oxides) is negatively correlated with BMD. Further research is imperative to elucidate the specific mechanisms.
In conclusion, this MR study has robust evidence affirming a causal relationship between air pollution-related indicators (PM2.5, PM10 and nitrogen oxides) and decreased BMD. The outcomes of this study offer the potential to guide clinical decision-making and shape public health strategies. Ultimately, these findings can contribute to the formulation of targeted interventions and alleviate the impact of air pollution on bone health, thereby enhancing the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.