Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH
An immune-related long non-coding RNA signature predicts prognosis in glioblastoma patients
1
Nanchang University, Nanchang 330031, Jiangxi, China
2
Department of Neurosurgery, Jiangxi provincial People’s Hospital,The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang Medical College, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi, China
3
Department of Neurosurgery, Department of Neurosurgery, People’s Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan271100, Shandong, China
4
Department of Neurosurgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong Provincial, China
Submission date: 2021-04-24
Final revision date: 2021-07-01
Acceptance date: 2021-07-21
Online publication date: 2021-07-27
Corresponding author
Peng Qiu
Department of Neurosurgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, No.324, Jingwu Road, Jinan 250000, Shandong Provincial, China., China
Department of Neurosurgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, No.324, Jingwu Road, Jinan 250000, Shandong Provincial, China., China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
This study aimed to explore the prognostic value of immune-related long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in glioblastoma (GBM).
Material and methods:
Expression and clinical data were acquired, including the GSE111260 dataset: 67 GBM and 3 normal brain samples; the GSE103227 dataset: 5 GBM and 5 normal brain samples; and TCGA data: 187 GBM samples. Immune-related genes were retrieved from the ImmPort database. Immune-related differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and lncRNAs were screened. Prognostic lncRNAs were then screened to establish a prognostic risk score model. Survival analysis and differential expression analysis were performed in high- vs. low-risk groups, followed by the protein-protein interaction network and the lncRNA-mRNA co-expression network.
Results:
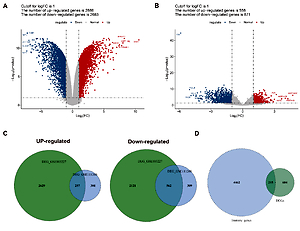
A total of 251 immune-related DEGs were screened. After correlation analysis, 387 immune-related lncRNAs that co-expressed with 140 immune-related DEGs were screened. Univariate analysis identified 18 lncRNAs that were significantly associated with prognosis. The prognostic risk score was able to stratify GBM patients into high- and low-risk groups, and patients with high risk scores displayed worse outcomes than those with low risk scores in both the training set and the validation set. A total of 272 genes had abnormal expression between high- and low-risk groups. Of these, 22 genes were immune-related, such as SNAP25, SNAP91, SNCB, and RAB3A. These genes were mainly enriched in synaptic vesicle cycle/exocytosis and insulin secretion. The co-expression network contained 22 genes and 11 lncRNAs, and lncRNA LINC01574 co-expressed with the great number of mRNAs.
Conclusions:
We identified 18 immune-related prognostic lncRNAs, and the established lncRNA-based prognostic risk model could stratify GBM patients into different risk levels.
This study aimed to explore the prognostic value of immune-related long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in glioblastoma (GBM).
Material and methods:
Expression and clinical data were acquired, including the GSE111260 dataset: 67 GBM and 3 normal brain samples; the GSE103227 dataset: 5 GBM and 5 normal brain samples; and TCGA data: 187 GBM samples. Immune-related genes were retrieved from the ImmPort database. Immune-related differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and lncRNAs were screened. Prognostic lncRNAs were then screened to establish a prognostic risk score model. Survival analysis and differential expression analysis were performed in high- vs. low-risk groups, followed by the protein-protein interaction network and the lncRNA-mRNA co-expression network.
Results:
A total of 251 immune-related DEGs were screened. After correlation analysis, 387 immune-related lncRNAs that co-expressed with 140 immune-related DEGs were screened. Univariate analysis identified 18 lncRNAs that were significantly associated with prognosis. The prognostic risk score was able to stratify GBM patients into high- and low-risk groups, and patients with high risk scores displayed worse outcomes than those with low risk scores in both the training set and the validation set. A total of 272 genes had abnormal expression between high- and low-risk groups. Of these, 22 genes were immune-related, such as SNAP25, SNAP91, SNCB, and RAB3A. These genes were mainly enriched in synaptic vesicle cycle/exocytosis and insulin secretion. The co-expression network contained 22 genes and 11 lncRNAs, and lncRNA LINC01574 co-expressed with the great number of mRNAs.
Conclusions:
We identified 18 immune-related prognostic lncRNAs, and the established lncRNA-based prognostic risk model could stratify GBM patients into different risk levels.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.