Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ONCOLOGY / RESEARCH PAPER
Allicin depresses biological activities of pancreatic cancer cells by regulating miRNA-339-5p/ZNF-689 axis
1
Zhongda Hospital, Southeast University, China
2
Jiangsu Province Hospital of Chinese Medicine, China
Submission date: 2021-04-20
Final revision date: 2021-05-19
Acceptance date: 2021-06-03
Online publication date: 2021-06-11
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The aim of this study was to discuss Allicin’s anti-tumor effects and relative in pancreatic cancer cell via vitro and vivo study.
Material and methods:
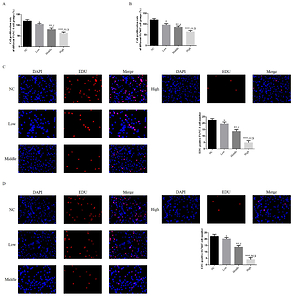
Using PANC-1 and Hs766T cell as research cell lines in our study. The PANC-1 abd GS799T cell were respectively treated with difference concentrations of Allicin. In next step, the PANC-1 abd GS799T cell were transfected with si-miRNA-339-5p which knockdown miRNA-339-5p. The cells were treated with difference concentration of Allicin. Measuring cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and migration by MTT, EDU, flow cytometry, TUNEL, transwell and wound healing assay. Relative gene (miRNA-339-5p, ZNF-689, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, E-cadherin and Vimentin) and protein (ZNF-689, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, E-cadherin and Vimentin) expression were evaluated by RT-qPCR and WB assay.
Results:
Allicin had effects to suppress PANC-1 and Hs766T cell biological activities including cell proliferation, invasion and migration with cell apoptosis significantly increasing, however, with si-miRNA-339-5p which inhibit miRNA-339-5p expression transfection, the cells biological activities enhancing with cell apoptosis depressing, Compared with NC group, miRNA-339-5p, Caspase-3, Caspase-8 and E-cadherin expression were significantly increased and ZNF-689 and Vimentin expression were significantly depressed in Allicin treated groups, however, with miRNA-339-5p inhibitor transfection, the Allicin’s effects significantly disappear.
Conclusions:
Allicin had anti-tumor effect to pancreatic cancer biological activities via regulation miRNA-339-5p/ZNF-689 axis in vitro study.
The aim of this study was to discuss Allicin’s anti-tumor effects and relative in pancreatic cancer cell via vitro and vivo study.
Material and methods:
Using PANC-1 and Hs766T cell as research cell lines in our study. The PANC-1 abd GS799T cell were respectively treated with difference concentrations of Allicin. In next step, the PANC-1 abd GS799T cell were transfected with si-miRNA-339-5p which knockdown miRNA-339-5p. The cells were treated with difference concentration of Allicin. Measuring cell proliferation, apoptosis, invasion and migration by MTT, EDU, flow cytometry, TUNEL, transwell and wound healing assay. Relative gene (miRNA-339-5p, ZNF-689, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, E-cadherin and Vimentin) and protein (ZNF-689, Caspase-3, Caspase-8, E-cadherin and Vimentin) expression were evaluated by RT-qPCR and WB assay.
Results:
Allicin had effects to suppress PANC-1 and Hs766T cell biological activities including cell proliferation, invasion and migration with cell apoptosis significantly increasing, however, with si-miRNA-339-5p which inhibit miRNA-339-5p expression transfection, the cells biological activities enhancing with cell apoptosis depressing, Compared with NC group, miRNA-339-5p, Caspase-3, Caspase-8 and E-cadherin expression were significantly increased and ZNF-689 and Vimentin expression were significantly depressed in Allicin treated groups, however, with miRNA-339-5p inhibitor transfection, the Allicin’s effects significantly disappear.
Conclusions:
Allicin had anti-tumor effect to pancreatic cancer biological activities via regulation miRNA-339-5p/ZNF-689 axis in vitro study.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.