Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors NEW
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
CLINICAL RESEARCH
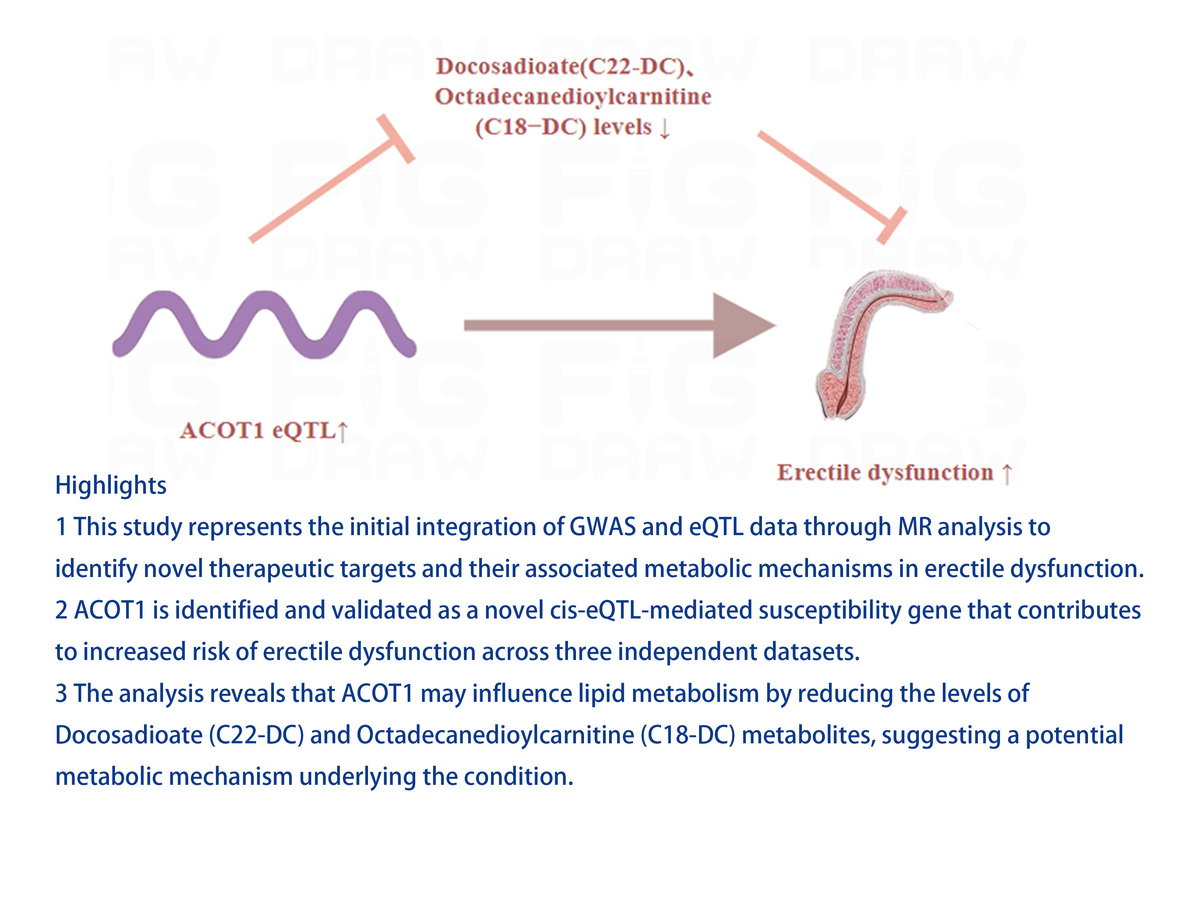
ACOT1 eQTL: a gene involved in lipid metabolism that modulates erectile dysfunction progression via metabolites
1
Department of Urology, Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
2
Department of Urology, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu Province, China
These authors had equal contribution to this work
Submission date: 2024-10-31
Final revision date: 2025-01-02
Acceptance date: 2025-01-22
Online publication date: 2025-03-04
Corresponding author
Yi Wang
Department of Urology Shanghai General Hospital Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine No. 85 Wujin Road Hongkou District Shanghai 200080, China Department of Urology Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University No. 20 West Temple Road Nantong, 226001 Jiangsu Province, China
Department of Urology Shanghai General Hospital Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine No. 85 Wujin Road Hongkou District Shanghai 200080, China Department of Urology Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University No. 20 West Temple Road Nantong, 226001 Jiangsu Province, China
Shujie Xia
Department of Urology Shanghai General Hospital Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine No. 85 Wujin Road Hongkou District Shanghai, 200080, China
Department of Urology Shanghai General Hospital Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine No. 85 Wujin Road Hongkou District Shanghai, 200080, China
KEYWORDS
Mendelian randomizationeQTLACOT1erectile dysfunctionmetabolitespathologygene expressioncastrated rats
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
The causal relationship between expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) and erectile dysfunction (ED) remains underexplored. This study applied Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis to investigate potential causal links between novel susceptibility genes for ED and their underlying mechanisms.
Material and methods:
Two-sample MR analysis was employed to examine causal connections between eQTLs, metabolites, and ED progression. Furthermore, summary-data-based MR (SMR) analysis was used to validate the causal association between cis-eQTLs and ED. A castrated rat model was also established to validate gene expression via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
Results:
The results provide novel evidence that ACOT1 eQTL promoted ED progression. SMR analysis confirmed a causal relationship between the ACOT1 cis-eQTL and ED progression (p < 0.05). Regarding ACOT1’s potential role in ED, the study suggested that the ACOT1 eQTL may negatively regulate docosadioate (C22-DC) and octadecanedioylcarnitine (C18−DC), both of which inhibited ED progression. In SD rats, castration led to a decrease in the ratio of intracavernous pressure (ICP) to mean arterial pressure (MAP) and a reduction in smooth muscle to collagen, accompanied by an increase in -SMA expression in the castration group. These findings confirm the successful establishment of a castrated ED model. Additionally, further analysis of ACOT1 expression revealed significant upregulation in the castrated group (p < 0.05).
Conclusions:
This study, for the first time, elucidates the mechanisms by which ACOT1, as a novel eQTL-mediated ED susceptibility gene, accelerates ED progression by negatively regulating levels of docosadioate (C22-DC) and octadecanedioylcarnitine (C18-DC) metabolites. These insights offer potential new therapeutic targets for ED.
The causal relationship between expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) and erectile dysfunction (ED) remains underexplored. This study applied Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis to investigate potential causal links between novel susceptibility genes for ED and their underlying mechanisms.
Material and methods:
Two-sample MR analysis was employed to examine causal connections between eQTLs, metabolites, and ED progression. Furthermore, summary-data-based MR (SMR) analysis was used to validate the causal association between cis-eQTLs and ED. A castrated rat model was also established to validate gene expression via quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
Results:
The results provide novel evidence that ACOT1 eQTL promoted ED progression. SMR analysis confirmed a causal relationship between the ACOT1 cis-eQTL and ED progression (p < 0.05). Regarding ACOT1’s potential role in ED, the study suggested that the ACOT1 eQTL may negatively regulate docosadioate (C22-DC) and octadecanedioylcarnitine (C18−DC), both of which inhibited ED progression. In SD rats, castration led to a decrease in the ratio of intracavernous pressure (ICP) to mean arterial pressure (MAP) and a reduction in smooth muscle to collagen, accompanied by an increase in -SMA expression in the castration group. These findings confirm the successful establishment of a castrated ED model. Additionally, further analysis of ACOT1 expression revealed significant upregulation in the castrated group (p < 0.05).
Conclusions:
This study, for the first time, elucidates the mechanisms by which ACOT1, as a novel eQTL-mediated ED susceptibility gene, accelerates ED progression by negatively regulating levels of docosadioate (C22-DC) and octadecanedioylcarnitine (C18-DC) metabolites. These insights offer potential new therapeutic targets for ED.
REFERENCES (39)
1.
Zhang F, Xiong Y, Zhang Y, Wu K, Zhang B. Genetically proxied intestinal microbiota and risk of erectile dysfunction. Andrology 2024; 12: 793-800.
2.
Greenstein A, Abramov L, Matzkin H, Chen J. Sexual dysfunction in women partners of men with erectile dysfunction. Int J Impotence Res 2006; 18: 44-6.
3.
Palmer MR, Holt SK, Sarma AV, et al. Longitudinal patterns of occurrence and remission of erectile dysfunction in men with type 1 diabetes. J Sex Med 2017; 14: 1187-94.
4.
Mark KP, Arenella K, Girard A, Herbenick D, Fu J, Coleman E. Erectile dysfunction prevalence in the United States: report from the 2021 National Survey of Sexual Wellbeing. J Sex Med 2024; 21: 296-303.
5.
Wang W, Fan J, Huang G, et al. Meta-analysis of prevalence of erectile dysfunction in mainland China: evidence based on epidemiological surveys. Sex Med 2017; 5: e19-30.
6.
Salama AB, Abdrabo MS, Abouelnaga WA. Effect of physical exercise combined with shockwave therapy on erectile dysfunction in diabetic patients. Arch Med Sci 2023; 19: 1207-13.
7.
Xiong J, Zhang J, Cai Z, Ma C, Li H. Erectile dysfunction in testicular cancer survivors: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. Arch Med Sci 2024; 20: 822-30.
8.
Boutari C, Kokkorakis M, Stefanakis K, et al. Recent research advances in metabolism, clinical and experimental. Metab Clin Exp 2023; 149: 155722.
9.
Xu R, Liu S, Li LY, et al. Exploring the causal association between serum metabolites and erectile dysfunction: a bidirectional Mendelian randomisation study. Int J Impot Res 2024; doi: 10.1038/s41443-024-00926-2.
10.
Wang Y, Ji H, Chen G, Zhou J, Zhang D, Wang X. GNLY as a novel cis-eQTL and cis-pQTL mediated susceptibility gene in suppressing prostatitis. Mendelian randomization study. Arch Med Res 2024; 56: 103098.
11.
Elsworth B, Lyon M, Alexander T, et al. The MRC IEU OpenGWAS data infrastructure. bioRxiv 2020; 2020.2008.2010.244293.
12.
Chen Y, Lu T, Pettersson-Kymmer U, et al. Genomic atlas of the plasma metabolome prioritizes metabolites implicated in human diseases. Nat Genet 2023; 55: 44-53.
13.
Võsa U, Claringbould A, Westra HJ, et al. Unraveling the polygenic architecture of complex traits using blood eQTL metaanalysis. bioRxiv 2018; 447367.
14.
Zhang Y, Peng R, Chen Z, et al. Evidence for a causal effect of major depressive disorder, anxiety on prostatitis risk: a univariate and multivariate Mendelian randomization study. Prostate 2023; 83: 1387-92.
15.
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet 2018; 50: 693-8.
16.
Greco MF, Minelli C, Sheehan NA, Thompson JR. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat Med 2015; 34: 2926-40.
17.
Krishnamoorthy S, Li GH, Cheung CL. Transcriptome-wide summary data-based Mendelian randomization analysis reveals 38 novel genes associated with severe COVID-19. J Med Virol 2023; 95: e28162.
18.
Chen ZB, Li G, Lin H, Jiang J, Jiang R. Low androgen status inhibits erectile function by increasing pyroptosis in rat corpus cavernosum. Andrology 2021; 9: 1264-74.
19.
Li R, Meng X, Zhang Y, et al. Testosterone improves erectile function through inhibition of reactive oxygen species generation in castrated rats. PeerJ 2016; 4: e2000.
20.
Liu S, Jiang C, Hu J, Chen H, Han B, Xia S. Low-Intensity pulsed ultrasound enhanced adipose-derived stem cell-mediated angiogenesis in the treatment of diabetic erectile dysfunction through the piezo-ERK-VEGF axis. Stem Cells Inter 2022; 2022: 6202842.
21.
Wang Y, Zhang X, Chen Y, Zhu B, Xing Q. Identification of hub biomarkers and exploring the roles of immunity, M6A, ferroptosis, or cuproptosis in rats with diabetic erectile dysfunction. Andrology 2023; 11: 316-31.
22.
Jiang J, Xu C, Han D, et al. Functional heterogeneity of cancer-associated fibroblasts with distinct neoadjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy response in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomarker Res 2024; 12: 113.
23.
Feng H, Liu Q, Deng Z, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate erectile dysfunction in rats with diabetes mellitus through the attenuation of ferroptosis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2022; 13: 450.
24.
Li S, Li Y, Cai Y, et al. Lacticaseibacillus paracasei NCU-04 relieves constipation and the depressive-like behaviors induced by loperamide in mice through the microbiome-gut-brain axis. Curr Res Food Sci 2024; 9: 100875.
25.
Zhang T, Mao C, Chang Y, Lyu J, Zhao D, Ding S. Hypoxia activates the hypoxia-inducible factor-1/vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in a prostatic stromal cell line: a mechanism for the pathogenesis of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Curr Urol 2024; 18: 185-93.
26.
Bai Y, Wen H, Lin J, et al. Tanshinone I improves renal fibrosis by promoting gluconeogenesis through upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1. Renal Failure 2024; 46: 2433710.
27.
Fisher WA, Rosen RC, Eardley I, Sand M, Goldstein I. Sexual experience of female partners of men with erectile dysfunction: the female experience of men’s attitudes to life events and sexuality (FEMALES) study. J Sex Med 2005; 2: 675-84.
28.
Xiao Y, Xie T, Peng J, et al. Factors associated with anxiety and depression in patients with erectile dysfunction: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychol 2023; 11: 36.
29.
De Leonardis F, Colalillo G, Finazzi Agrò E, Miano R, Fuschi A, Asimakopoulos AD. Endothelial dysfunction, erectile deficit and cardiovascular disease: an overview of the pathogenetic links. Biomedicines 2022; 10: 1848.
30.
Mei Y, Chen Y, Zhang B, Xia W, Shao N, Feng X. Association between a novel inflammation-lipid composite marker CRP/HDL and erectile dysfunction: evidence from a large national cross-sectional study. Front Endocrinol 2024; 15: 1492836.
31.
Tillander V, Alexson SEH, Cohen DE. Deactivating fatty acids: acyl-CoA thioesterase-mediated control of lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2017; 28: 473-84.
32.
Xia C, Dong R, Chen C, Wang H, Wang DW. Cardiomyocyte specific expression of Acyl-coA thioesterase 1 attenuates sepsis induced cardiac dysfunction and mortality. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2015; 468: 533-40.
33.
Yang S, Chen C, Wang H, et al. Protective effects of acyl-coA thioesterase 1 on diabetic heart via PPAR/PGC1 signaling. PLoS One 2012; 7: e50376.
34.
Heden TD, Franklin MP, Dailey C, Mashek MT, Chen C, Mashek DG. ACOT1 deficiency attenuates high-fat diet-induced fat mass gain by increasing energy expenditure. JCI Insight 2023; 8: e160987.
35.
Fernandes Silva L, Ravi R, Vangipurapu J, Oravilahti A, Laakso M. Effects of SLCO1B1 genetic variant on metabolite profile in participants on simvastatin treatment. Metabolites 2022; 12: 1159.
36.
Ding HZ, Wang H, Wu D, et al. Serum metabolomics analysis of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and ‘frequent exacerbator’ phenotype. Mol Med Rep 2024; 30: 137.
37.
Shi C, Ao Z, Liu B, et al. Increased acylcarnitine ratio indices in newborn screening for carnitine-acylcarnitine translocase deficiency shows increased sensitivity and reduced false-positivity. Transl Pediatr 2023; 12: 871-81.
38.
Deda O, Panteris E, Meikopoulos T, et al. Correlation of serum acylcarnitines with clinical presentation and severity of coronary artery disease. Biomolecules 2022; 12: 354.
39.
Wang C, Zhu D, Zhang D, et al. Causal role of immune cells in schizophrenia: Mendelian randomization (MR) study. BMC Psychiatry 2023; 23: 590.
Share
RELATED ARTICLE
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.