Current issue
Archive
Manuscripts accepted
About the Journal
Editorial office
Editorial board
Section Editors
Abstracting and indexing
Subscription
Contact
Ethical standards and procedures
Most read articles
Instructions for authors
Article Processing Charge (APC)
Regulations of paying article processing charge (APC)
ONCOLOGY / CLINICAL RESEARCH
A pre-clinical trial study on afzelin: anti-human lung cancer, anti-cholinesterase, and anti-glucosidase properties
1
Department of Cerebral Surgery, The First Hospital Affiliated with Shandong First Medical University, Jinan, Shandong Province, China
2
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Hospital Affiliated with Shandong First Medical University, Lixia District, Jinan, Shandong Province, China
Submission date: 2021-04-16
Final revision date: 2021-04-27
Acceptance date: 2021-04-29
Online publication date: 2021-05-14
Corresponding author
Junling Wang
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Hospital Affiliated with Shandong First Medical University, No.16766, Lixia District,Jingshi Road,Jinan,Shandong Province,250014,China., China
Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Hospital Affiliated with Shandong First Medical University, No.16766, Lixia District,Jingshi Road,Jinan,Shandong Province,250014,China., China
KEYWORDS
TOPICS
ABSTRACT
Introduction:
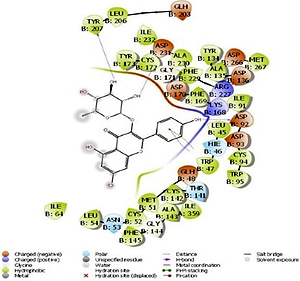
Afzelin is a glycosyloxyflavone that consists of kaempferol attached to an α-L-rhamnosyl residue at position 3 via a glycosidic linkage. It has a role as a plant metabolite, an antibacterial agent and an anti-inflammatory agent. It is a glycosyloxyflavone, a trihydroxyflavone and a monosaccharide derivative. In this study, we determined the anticholinergic, antiepileptic, antidiabetic, and anti-human lung cancer capacities of afzelin.
Material and methods:
IC50 values were calculated for both acetylcholinesterase and α-glycosidase as key enzymes affected by afzelin. The cytotoxicity and anticancer potential of afzelin in human lung was evaluated using the common cytotoxicity test, i.e. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay in in vitro conditions.
Results:
IC50 values of 365.11 nM for acetyl cholinesterase and 0.94 nM for α-glycosidase were calculated in this study. For these enzymes, Ki values were found to be 300.65 ±56.01 nM for acetyl cholinesterase and 1.65 ±0.11 nM for α-glucosidase. Cell viability of afzelin was very low against lung poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (PC-14), lung moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (LC-2/ad), and lung well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma (HLC-1) cell lines without any cytotoxicity towards the normal cell line.
Conclusions:
Afzelin shows significant antioxidant and anti-human lung cancer properties. It appears that the anti-human lung carcinoma effect of afzelin is due to its antioxidant effects.
Afzelin is a glycosyloxyflavone that consists of kaempferol attached to an α-L-rhamnosyl residue at position 3 via a glycosidic linkage. It has a role as a plant metabolite, an antibacterial agent and an anti-inflammatory agent. It is a glycosyloxyflavone, a trihydroxyflavone and a monosaccharide derivative. In this study, we determined the anticholinergic, antiepileptic, antidiabetic, and anti-human lung cancer capacities of afzelin.
Material and methods:
IC50 values were calculated for both acetylcholinesterase and α-glycosidase as key enzymes affected by afzelin. The cytotoxicity and anticancer potential of afzelin in human lung was evaluated using the common cytotoxicity test, i.e. 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay in in vitro conditions.
Results:
IC50 values of 365.11 nM for acetyl cholinesterase and 0.94 nM for α-glycosidase were calculated in this study. For these enzymes, Ki values were found to be 300.65 ±56.01 nM for acetyl cholinesterase and 1.65 ±0.11 nM for α-glucosidase. Cell viability of afzelin was very low against lung poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma (PC-14), lung moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (LC-2/ad), and lung well-differentiated bronchogenic adenocarcinoma (HLC-1) cell lines without any cytotoxicity towards the normal cell line.
Conclusions:
Afzelin shows significant antioxidant and anti-human lung cancer properties. It appears that the anti-human lung carcinoma effect of afzelin is due to its antioxidant effects.
We process personal data collected when visiting the website. The function of obtaining information about users and their behavior is carried out by voluntarily entered information in forms and saving cookies in end devices. Data, including cookies, are used to provide services, improve the user experience and to analyze the traffic in accordance with the Privacy policy. Data are also collected and processed by Google Analytics tool (more).
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.
You can change cookies settings in your browser. Restricted use of cookies in the browser configuration may affect some functionalities of the website.