Introduction
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is the most common monogenic disease, inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, which is caused by pathogenic variants in the LDLR, APOB, PCSK9, APOE, or LDLRAP1 genes [1]. FH leads to the accelerated development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) due to persistently elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) from birth [2]. Atherosclerosis in familial hypercholesterolemia progresses slowly and insidiously, reaching an advanced stage before any clinical symptoms appear [3, 4].
Despite increasing medical knowledge, diagnostic testing, and a growing number of therapeutic options, the effectiveness of detecting and treating FH remains insufficient. Globally, it is estimated that fewer than 10% of individuals with FH are diagnosed [2, 5].
The low detection rate is primarily because of the lack of screening programs and the asymptomatic course of the disease at a young age. According to data from the European Atherosclerosis Society FH Studies Collaboration (EAS FHSC) global registry, the average age of diagnosis is 44.4 years [6], while in Poland, it is around 41 years [7]. Diagnostics for FH are most often carried out after the first cardiovascular event. Thus, patients receive treatment as secondary prevention despite the availability of effective and well-tolerated primary prevention.
It is important to note that FH carries many social and economic consequences. The risk of death from cardiovascular incidents is significantly higher and is an independent factor regardless of age, gender, smoking, body mass index, hypertension, or diabetes [8, 9]. Only early detection and optimal treatment in pediatric patients will lead to a significant reduction in morbidity and mortality from ASCVD in later years [10]. An essential aspect of education involves emphasizing the significance of screening in children and cascade screening in families of FH patients.
The recommendations aim to present the current epidemiological situation, guidelines for diagnosing FH in children and adolescents in Poland, and options for effective treatment. This document complements the joint position of the Polish Lipid Association (PoLA), the Polish Cardiac Society, the Polish Diabetes Society, the Polish Society for Laboratory Diagnostics, and the College of Family Physicians in Poland from 2021 [11], updating the 2014 position of the Lipid Expert Forum [12].
Epidemiology and pathogenesis of familial hypercholesterolemia
FH is the most common monogenic disease. Because of its autosomal dominant inheritance, there are two forms of the condition: heterozygous (HeFH) and homozygous (HoFH) [13]. The homozygous form of the disease (HoFH) is classified as a rare disease, occurring from 1 in 160,000 to 1 in 300,000 cases, and results from inheriting pathogenic variants from both parents [14]. It results in highly elevated levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) > 500 mg/dl (> 13.0 mmol/l) in plasma and an accelerated rate of atherosclerosis, with symptoms that can manifest as early as childhood [15]. To date, 6 cases of HoFH have been reported in Poland [16–18].
The heterozygous form is much more common. Based on a meta-analysis of six extensive observational studies, the estimated prevalence of FH in Poland is approximately 1 in 250 individuals between 20 and 79 years of age, with only 4–5% of affected individuals diagnosed [19, 20]. According to the LIPIDOGRAM studies, the prevalence may be as high as 1 in less than 200 individuals [21]. FH is primarily caused by pathogenic variants in the LDLR gene (> 90% of detected cases), followed by variants in APOB (5%) and PCSK9 (< 1%). Autosomal dominant forms of FH include rare (<< 1%), in-frame three base-pair deletion at position 167 in exon 4 of APOE. Finally, rare homozygous LDLRAP1 variants lead to autosomal recessive hypercholesterolemia (ARH) [1, 22]. Interestingly, causal variants cannot be identified in more than one in five individuals, even when FH diagnostic criteria are met. In such instances, polygenic inheritance may be suspected. Talmud et al. demonstrated that the accumulation of common alleles that mildly elevate LDL-C can increase levels to those observed in monogenic FH, leading to polygenic hypercholesterolemia [23].
Elevated lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) levels may account for up to 25% of clinical cases of FH. Lp(a) levels should be measured in all children suspected of FH. If LDL-C is calculated using the Friedewald formula, this value should be adjusted for the Lp(a) result [1, 24]. It is advisable to use direct LDL cholesterol measurement for improved accuracy.
Clinical presentation of familial hypercholesterolemia in children and adolescents
Typically, FH is asymptomatic in children and adolescents. In HeFH individuals, initial symptoms generally appear in the third to fifth decades of life, whereas in HoFH patients, symptoms may emerge within the first two decades [25]. The median LDL-C level is 206.3 mg/dl (5.4 mmol/l) and 558.6 mg/dl (14.7 mmol/l) in HeFH and HoFH individuals, respectively [6, 26]. Genetic variants have a significant impact on the disease phenotype since LDL receptor activity has an impact on the severity of the symptoms [27]. In the null phenotype (LDLR activity < 2%), symptoms manifest very early, with possible in-utero fetal demise [25]. Physical findings may include tendon xanthomas on the extensor tendons of the hands and feet, the Achilles tendons, xanthelasma on the eyelids, and corneal arcus [28]. Coronary artery disease symptoms typically occur in the fourth decade of life. Studies have shown that FH patients have at least a threefold higher risk of developing ASCVD compared to individuals without the pathogenic variants. However, early detection, treatment, and a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce this risk [29].
Current guidelines emphasize the importance of initiating lipid-lowering therapy early in children with FH. Therefore, an early diagnosis at 5 years of age is recommended. Consequently, this expert panel supports implementing lipid profile screening during preventive healthcare visits at the age of 6.
Guidelines for conducting lipid profile assessment in children and adolescents
Cholesterol levels fluctuate with age and developmental stages, presenting a specific diagnostic challenge. Total cholesterol (TC) and LDL-C concentrations in serum are lower during the intrauterine period and shortly after birth. Subsequently, these levels rise rapidly within the first week of life, gradually stabilizing by age 2 [30, 31]. In the following years, lipid and lipoprotein levels remain relatively stable until puberty [30, 32]. During adolescence, LDL-C levels decrease by an average of 15% [30, 33].
Lipid profiling involves measuring total cholesterol, triglycerides (TG), and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) in venous plasma, as well as calculating LDL-C and non-HDL cholesterol fractions [33]. The latest guidelines from the Polish Cardiac Society and the Polish Lipid Association also recommend measuring lipoprotein(a) in individuals under 18 for risk assessment, cascade screening, monitoring, and lifestyle modification [34].
Current recommendations indicate that lipid profiling does not necessarily need to be performed in a fasting state. It is supported by studies showing that a slight increase in triglyceride levels after a meal does not significantly affect the results compared to fasting measurements. However, if triglyceride levels exceed 440 mg/dl (5 mmol/l) postprandially, it is advisable to consider repeating the measurement in a fasting state [35]. When making further diagnostic or therapeutic decisions, the lipid profile results obtained twice (within 2 weeks to 3 months) should guide the process [11]. Lipid profiling should not be conducted earlier than 3 months after experiencing an acute infectious illness. Significant alterations in the lipid profile have been observed in patients during the SARS-CoV-2 virus infection. Many reports have shown a transient decrease in HDL-C and LDL-C and an increase in TG and lipoprotein(a). Some sources suggest that higher levels of HDL-C correlate with a milder course of COVID-19 infection [36].
Criteria for diagnosing FH in children and adolescents
In Poland, as in many European countries, familial hypercholesterolemia is often diagnosed too late, frequently when clinical or subclinical atherosclerosis symptoms are already present. Based on available data, the average age of FH diagnosis in Poland is approximately 40 years for adults and around 9–10 years for children. However, it should be underlined that these data come from specialized lipid clinics, so the situation in other healthcare settings may be significantly worse [7].
According to the current guidelines from the American Academy of Pediatrics published in 2011 and updated in 2023, it is recommended to conduct lipid profile screening in:
– children over 2 years old whose parents have been diagnosed with familial hypercholesterolemia,
– children over 2 years old with an unclear family history who present other risk factors, such as overweight, obesity, systolic and/or diastolic blood pressure readings between the 90th and 95th percentiles on three separate measurements, hypertension, diabetes, and low physical activity (< 60 min daily) [37, 38].
In other cases, according to the position of PoLA/CFPiP/PCS, the optimal age for performing a lipid profile is between 9 and 11 years. If lipid levels are within the normal range, the test should be repeated around the age of 18 as these results have the most significant prognostic value for lipid levels over the next two decades [21]. However, the optimal age for screening is a matter of ongoing discussion. Given the ESC/EAS guidelines published in 2019, which emphasize the early adoption of healthy dietary habits and potential statin use for familial hypercholesterolemia in children aged 6 to 10, earlier screening seems reasonable [13]. Given the numerous studies and the access to drug programs with PCSK9 inhibitors (evolocumab) from 10 years of age in Poland, the Expert Panel of this document recommends evaluating the lipid profile starting from the age of 6. Therefore, the treatment may be implemented as soon as possible.
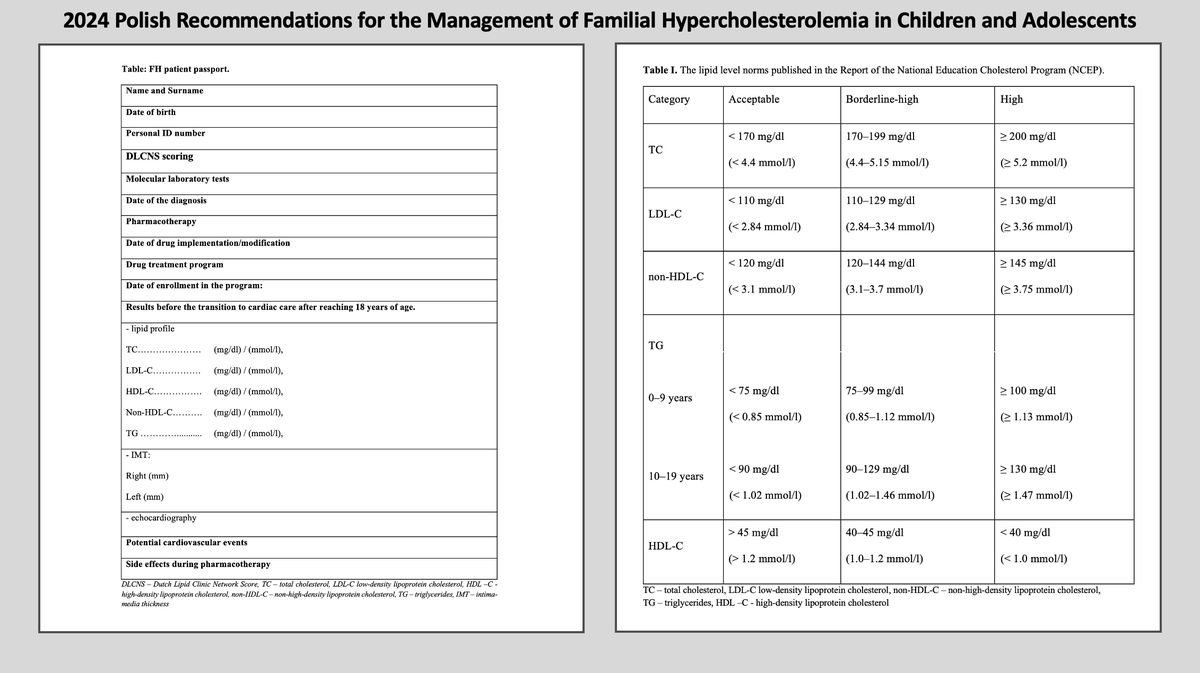
Table I presents the classification of total, LDL and HDL cholesterol published in the Report of the National Education Cholesterol Program (NCEP) – Expert Panel on Blood Cholesterol Levels in Children and Adolescents. The proposed norms are reliable and consistently valid.
Table I
The classification of total, LDL and HDL cholesterol published in the Report of the National Education Cholesterol Program (NCEP)
The diagnosis of FH in the Polish population is based on adapted criteria from the Dutch Lipid Clinic Network and Simon Broome Register. However, the most practical approach in the pediatric population is the framework developed by the Simon Broome Register Group (Table II). These criteria do not account for clinical symptoms in the patient, which rarely appear in children with the heterozygous form of the condition. FH is diagnosed in children based on phenotypic criteria, including elevated LDL-C levels and a family history of elevated LDL-C, premature coronary artery disease, and/or positive results of molecular testing. Children with TC levels ≥ 240 mg/dl (≥ 6.21 mmol/l) and LDL-C levels ≥ 160 mg/dl (≥ 4.14 mmol/l) have an elevated likelihood of being diagnosed with heterozygous FH [30, 37]. In families where a pathogenic variant has been identified, children should undergo testing even if their lipid profiles appear normal.
Table II
Simon Broome Register Group Criteria
Genetic testing is typically performed using DNA isolated from a peripheral blood sample collected in EDTA tubes. However, nucleic acids isolated from buccal swabs can also be used. Molecular testing of probands should allow the identification of genetic variants located within all exons and approximately ±25 intronic nucleotides of LDLR, APOB, and LDLRAP1, fragments of APOB (exon 26: ~c.10438–10757, exon 29: ~c.13009–13301) and APOE (~c.225–521) genes. Notably, the test should also enable LDLR copy number analysis to detect large rearrangements within the gene. The Human Genome Variation Society nomenclature should be applied to report detected alterations. All variants should be interpreted and classified according to the current guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG).
Differential diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia
During the diagnostic evaluation of lipid disorders, it is crucial to exclude secondary dyslipidemia. Several factors can elevate TC, LDL-C, and TG levels, occasionally leading to concentrations resembling those observed in FH. Causes of secondary hypercholesterolemia include conditions such as hypothyroidism, nephrotic syndrome, diabetes mellitus, Cushing’s syndrome, porphyria, anorexia, and celiac disease [39]. Additionally, prolonged use of certain medications, such as thiazide and loop diuretics, corticosteroids, cyclosporine, estrogens, progestins, retinoids, protease inhibitors, and some psychiatric drugs, including tricyclic antidepressants and selected antipsychotics, can also contribute to elevated lipid levels [11, 12, 40].
Differential diagnosis should incorporate familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCH), particularly in the case of mixed dyslipidemia. This condition is characterized by elevated TG levels and reduced HDL-C levels. The LDL-C levels may be normal, borderline elevated, or high. FCH predominantly occurs in individuals who are overweight or obese and is frequently associated with insulin resistance [33, 41].
Treatment of familial hypercholesterolemia in children and adolescents
Although placebo-controlled studies have not been conducted in children, observational research suggests that early initiation of the therapy can lower LDL-C levels, improve endothelial function, and significantly delay the progression of atherosclerosis. Treatment for children with FH includes a combination of a healthy lifestyle and pharmacological therapy. Patients and their families should be supported by multidisciplinary care teams comprising specialized healthcare professionals, including a specialist physician (pediatrician, diabetologist, and/or endocrinologist, metabolic disease specialist certified by the Polish Lipid Association) psychologist, dietitian, and nursing staff. Genetic consultation is also advisable.
Lifestyle changes should include the introduction and maintenance of a healthy diet, promotion of physical activity, maintenance of a healthy weight, prevention of passive tobacco smoking, and, in the case of adolescents, a strict prohibition on active smoking and alcohol consumption. These changes should be implemented in every child over the age of 2 who has an LDL-C level > 100 mg/dl (> 2.6 mmol/l) and/or has elevated triglyceride levels (children < 10 years with TG ≥ 100 mg/dl (≥ 1.1 mmol/l); children aged 10–19 years with TG ≥ 130 mg/dl (≥ 1.5 mmol/l)) [12, 42]. Statin therapy should be considered for children aged 6–10 years.
Patient education
Proper education of the patients and their families is crucial in fostering collaboration and adherence to medical recommendations. The patients and their caregivers should be thoroughly informed about the diagnosis, future cardiovascular risk, and available therapeutic options. This knowledge should be communicated by the entire therapeutic team, which includes both physicians and dietitians. Since FH is a chronic condition that often requires lifelong medication starting in childhood, ongoing collaboration with the patients and their families is essential. Therefore, there is a need to provide psychological support, particularly in cases where motivation for the treatment is lacking [11, 43].
Education of healthcare professionals
Diagnosing new patients should take place at various levels of the healthcare system. It is essential to increase the awareness of family physicians and pediatricians regarding FH through educational programs and training within specialty programs. This approach ensures that patients and their families receive appropriate guidance for diagnosis and treatment at every level of care. Since its launch in 2014, the lipidology certification program of the Polish Lipid Association has trained nearly 600 physicians, including many pediatricians. This initiative addresses the significant gaps in medical education concerning FH. Additionally, simple algorithms for recognizing and managing patients with FH should be readily available in medical journals, online platforms, and other media.
Dietary treatment
Dietary intervention should be implemented for every child with dyslipidemia starting from the age of 2. If earlier dietary modifications are considered safe, they should be carried out under the guidance of an experienced specialist in collaboration with a dietitian. Closely monitoring the child’s development is essential throughout this process [44]. A low-fat diet is recommended to reduce saturated fat intake to less than 7% of total caloric intake and limit daily cholesterol intake to under 200 mg. It is advisable to increase the consumption of marine fish, vegetables (including legumes), fruits, nuts, and seeds and incorporate plant sterols and stanols (up to 2 g/day) into the diet. Elevated triglyceride levels indicate a need to decrease simple sugar intake, increase dietary fiber and complex carbohydrates, and work towards achieving a healthy body weight [45].
Nutritional interventions are considered the first-line treatment for patients with increased cardiovascular risk, holding particular importance for children and adolescents. Many scientific studies confirm the significant role of dietary patterns; however, large, randomized trials evaluating the reduction of hard endpoints, such as decreased cardiovascular events, are lacking.
The DASH, Nordic, and specific plant-based diets show the most promise for cardiovascular health in the developmental age, though further research and long-term observation are needed [46]. While the beneficial effects of the DASH and Mediterranean diets are well-documented in adult patients with lipid disorders, this area requires further investigation in the pediatric population. In children, cardiovascular risk factors are assessed, as well as growth, sexual maturation, and neurological development. Consequently, dietary patterns deemed heart-healthy for adults may not be equally beneficial for pediatric populations.
Unfortunately, the effectiveness of a low-fat diet in treating FH is limited. Replacing saturated fats with polyunsaturated fats can reduce LDL-C levels by only about 5–15% [47]. Therefore, pharmacotherapy is essential in managing FH.
Nutraceuticals and modified foods
Recent guidelines recommend considering nutraceuticals as part of lifestyle modification for adult patients with dyslipidemia before initiating pharmacological treatment [11, 48, 49]. Nutraceuticals may be an option for individuals not qualifying for statin therapy, those who decline statin treatment, patients with statin intolerance, or those who have not reached therapeutic targets [11]. Nutraceuticals lead to moderate lipid-lowering effects, can safely support endothelial function and modulate arterial stiffness in adults, provided that they have proven lipid-lowering efficacy, a favorable safety profile (nutrivigilance), and high production quality (free from contaminants) [11]. However, there are limited studies on the effects of nutraceuticals on dyslipidemia in children and adolescents, with most research focused on the role of fiber and plant sterols/stanols.
Plant sterols and stanols
Plant sterols and stanols are bioactive compounds derived from plants, structurally similar to cholesterol. They naturally occur in vegetable oils and smaller amounts in fresh fruits, nuts, grains, and legumes. Sterols can be found in free form or as esters (e.g., fatty acid esters), while stanols are hydrogenated plant sterols. Plant sterols and stanols reduce cholesterol absorption in the digestive tract by competing with cholesterol for attachment to free receptors within intestinal micelles. Consequently, it increases cholesterol elimination from the body [50].
Consuming 2 g of plant sterols daily can reduce TC and LDL-C by around 7–10%, with minimal or no effect on HDL-C or TG levels [51]. However, there are no studies on the long-term cardiovascular effects of plant sterol and stanol consumption. Given the LDL-C reduction and lack of adverse side effects, the consumption of functional foods with plant sterols/stanols (2 g/day with a main meal) is recommended, including adults and children (over 6 years old) with familial hypercholesterolemia [52].
Dietary fiber
The cholesterol-lowering effect of dietary fiber primarily results from its viscosity. Soluble fibers in water form a gel that binds to bile salts in the intestines, increasing their excretion in feces. Since cholesterol is one of the main components of bile, enhanced bile salt excretion implies greater cholesterol utilization for bile production in the liver. The higher the viscosity of the fiber, the stronger its cholesterol-lowering effect [53]. It is recommended to consume adequate amounts of dietary fiber – approximately 10 g at the age of 5, 15 g at the age of 10, and 20 g at the age of 15. Most studies on fiber use in children and adolescents have shown good adherence to the suggested therapy, with adverse effects reported only sporadically [54]. However, data on the safety of long-term fiber treatment in the younger population remains limited.
Red yeast rice extract
Red yeast rice is produced through the fermentation of specific yeast strains, during which monacolin K is generated – a compound structurally and functionally similar to lovastatin. This similarity accounts for its cholesterol-lowering effect, with many reports suggesting that doses below 3 mg/day can reduce LDL-C by approximately 15% to 25% [11]. However, most data on red yeast rice pertain to adult patients [55], and evidence on its safety and efficacy in children is limited [56]. Clinical studies in adults have shown LDL-C reductions without significant adverse effects [55, 56]. Due to its statin-like mechanism, regular clinical and biochemical monitoring is essential [57].
Bergamot
Bergamot, commonly known as Citrus bergamia, is a fruit rich in flavonoids. Some compounds exhibit lipid-lowering effects similar to statins by inhibiting [58].
There is also evidence that bergamot may increase cholesterol excretion in the stool, reduce its intestinal absorption, and stimulate bile acid turnover and elimination. Clinical studies on the lipid-lowering properties of bergamot suggest polyphenols derived from this plant (at doses of 500 to 1500 mg/day) can effectively reduce LDL-C levels (with reductions reported between 15% and 40% depending on the study), TG, non-HDL-C, as well as fasting insulin, leptin, and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). These effects are dose-dependent and influenced mainly by the degree of extract purification [59]. However, data on its use in children are significantly limited.
Berberine
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid derived from various plants, with lipid-lowering effects resulting from multiple mechanisms. Studies suggest that berberine increases the expression and half-life of LDL receptors (LDL-R) on the surface of hepatocytes [60]. It also enhances the transcriptional activity of the LDL-R promoter and stabilizes its mRNA [61]. Additionally, berberine inhibits PCSK9 activity, reducing the lysosomal degradation of LDL-R and increasing its availability in the liver [62].
Supplementation with berberine is associated with reductions in LDL-C levels (15–20% depending on the study) and in TG, as well as increases in HDL-C. Recommended dosages range from 500 to 1500 mg [49].
Despite limited data on its use for lipid disorders in children, studies have found no serious adverse events when using it for diarrhea in this age group [63].
Pharmacological treatment
In the absence of a molecular diagnosis, pharmacotherapy should be considered for children with significant lipid disorders after 6 months of lifestyle modification if therapeutic goals have not been achieved. However, it should be noted that this approach’s long-term efficacy and safety have not yet been established. Before initiating the treatment, a thorough assessment should be conducted, considering the patient’s age, sex, pubertal maturity, detailed family history, and specific risk factors, such as myopathies as well as liver, kidney, and neurological disorders, severe infections, and metabolic, hormonal, and electrolyte disturbances.
Additionally, it is advisable to determine the initial carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT) and monitor this parameter throughout the treatment. Although the clinical manifestation of cardiovascular disease in children is rare, first atherosclerotic abnormalities develop already in childhood. Carotid IMT enables identifying the subclinical atherosclerosis. The examination takes approximately 5 min, is easy to perform, and is painless. Common artery IMT complex is measured around 1.5–2 cm below the carotid bifurcation in the end-diastolic phase. The examination should be repeated three times for each site, and the arithmetic mean is calculated. Doyon et al. established the norms in the pediatric population [64]. The results above the 95th percentile are alarming. The deterioration of IMT values may be a valuable argument in discussions with unconvinced parents about the implementation of statin therapy in childhood.
Statins
Statins, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are the recommended first-line therapy for hypercholesterolemia. Treatment should be initiated in children with persistent elevation of LDL-C > 190 mg/dl (4.9 mmol/l) at 6 years of age (according to the ‘earlier the better’ principle) [13], even in the absence of concomitant risk factors. In contrast, in the case of positive family history of premature cardiovascular disease (< 55 years of age) and one high-risk factor (hypertension requiring pharmacotherapy, renal failure, body mass index (BMI) > 97th percentile) or two intermediate risk factors (e.g. hypertension without pharmacotherapy, HDL < 40 mg/dl (1.0 mmol/l), BMI 95–97th percentile, chronic inflammatory disease, nephritic syndrome), statins should be introduced at LDL-C levels > 160 mg/dl (4.14 mmol/l). In children with molecular confirmation of FH, treatment should be commenced even earlier when LDL-C levels reach ≥ 130 mg/dl (3.4 mmol/l) [11]. Besides, it should be emphasized that patients with diabetes should receive pharmacotherapy as soon as their LDL-C exceeds 100 mg/dl (2.6 mmol/l), regardless of their metabolic compensation.
Statin treatment begins with the lowest dose available, typically 2–10 mg/day (depending on the type of statin), taken once daily, often in the evening [12]. The dose is gradually increased until the therapeutic goal is achieved. The total effect of statins on lipid metabolism is observed after approximately 6 weeks. LDL-C concentrations decrease by about 90% after 2 weeks on the appropriate statin dose [30, 65].
The aim of hypolipidemic therapy in the pediatric population is LDL-C < 130 mg/dl (< 3.4 mmol/l, below the 95th percentile) or a reduction of LDL-C levels by 30–50%. In children with diabetes and FH who have a positive family history of coronary heart disease before 40 years of age, it is recommended to achieve an LDL-C concentration < 100 mg/dl (< 2.6 mmol/l) or a reduction of at least 50% [12, 42]. Similar cut-off points for non-HDL-C and TG have not been established to date.
The most common issues regarding hypolipidemic therapy are the gradual increase and administration of too low doses of statins (subsequently sustained for a very long time), as well as insufficient monitoring of therapeutical effects. Ultimately, it leads to the very rare achievement of the therapeutic goal in the pediatric population [7].
Different statin preparations vary in metabolic profile and potency depending on the dose. Rosuvastatin is registered for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia from 6 years of age. Available doses range from 5 to 20 mg/day. In HeFH patients aged 6 to 9 years, the recommended dose is usually 5–10 mg daily. For those aged 10 to 17 years, it typically ranges from 5 to 20 mg. The safety and efficacy of higher doses in these age groups have not been studied [66, 67]. The recommended initial dose for atorvastatin treatment is 10 mg/d at the age of 10, which can be raised to 40 mg/day over time [68, 69]. The other therapeutical option is pitavastatin. It is registered for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia from 6 years of age. The maximum dose for children aged 6–9 years is 2 mg/day; for children aged ≥ 10 years, it is 4 mg/day. Although fewer studies are available than for rosuvastatin and atorvastatin, it is the third most potent statin, with the lowest risk of side effects and a favorable metabolic profile [70]. Given the good treatment tolerance, it appears reasonable to raise the statin dose until it reaches the therapeutic target.
It is important to assess baseline levels of creatine kinase (CK) activity, as well as liver parameters such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) prior to statin therapy. Aminotransferases should be checked 8–12 weeks after statin inclusion and tested every 6 months thereafter. If liver enzyme levels increase 3-fold or higher above the upper limit of normal, it is recommended to withdraw the hypolipidemic treatment or reduce its doses. The aminotransferases must be rechecked in 4–6 weeks [13]. The elevation of liver enzymes is usually transient and resolves within 2–3 months after the medication is discontinued [71, 72]. Besides, it is crucial to determine CK levels before the implementation of pharmacotherapy. If the initial CK value exceeds 4 times the upper limit of normal, therapy should not be introduced [13]. Routine CK check-ups are not recommended unless there are muscle complaints, such as myopathy (muscle pain and/or muscle weakness). However, in the pediatric population, it seems reasonable to check CK after each increase in the statin dose because of the specificity of the age group and caregivers’ concerns about the child’s development. It is advisable to avoid checking CK levels after intense exercise or in case of other potential causes of increased CK activity, such as an ongoing infection, which can lead to misinterpretation of the results.
It has been established that statins are safe in children. However, there are some contraindications. The most important ones are hypersensitivity to the drug, states of muscle damage, myopathy associated with statin administration, active liver parenchymal disease or persistently high aminotransferase activity, increase in aminotransferase levels 3 times above the upper limit of normal during statin therapy, renal failure, severe infections, major surgeries, major trauma, severe metabolic, endocrine, electrolyte disorders, and uncontrolled epileptic seizures [12].
Moreover, statins may cause a slight increase in serum glucose levels – most pronounced with high doses [73]. Therefore, patients with carbohydrate metabolism disorders, including those with diabetes, should use pitavastatin or a combination treatment with a lower dose of statin with ezetimibe as the first choice and/or intensify the treatment of carbohydrate metabolism disorders.
Pediatricians specializing in FH (typically endocrinologists and diabetologists) should monitor children taking statins regularly, every 3–6 months in the first year and every 6–12 months thereafter, as needed. At the appointments, it is crucial to not only assess cholesterol levels and monitor medication side effects but also evaluate the child’s development, stage of sexual maturity, and nutritional status [74].
Ezetimibe
Despite using the maximum dose of statins approved in children, achieving the recommended LDL-C levels may be challenging. In this case, it is advised to introduce ezetimibe, which inhibits cholesterol absorption in the intestines and complements the effects of statins [75]. Regrettably, the use of ezetimibe in children is rare, although it significantly increases the probability of reaching the LDL cholesterol target when added to statins [7]. The combined therapy reduces LDL-C levels by an additional 15–25%, usually achieving the maximum hypolipemic effect within 2 weeks [37].
The recommended dose of ezetimibe is 10 mg daily from the age of 10 years. Treatment with ezetimibe should be implemented under the supervision of a specialist. There are currently scarce data regarding the safety and efficacy of ezetimibe in patients below 17 years old. However, the treatment is very well tolerated. Caution should be exercised in patients with hepatic impairment and malabsorption syndromes. The most common adverse effect is diarrhea, which is usually rare and transient.
PCSK9 inhibitors
PCSK9 is a key protein involved in LDL-C metabolism that binds to LDL-C receptors on the surface of liver cells and in the blood. After binding to LDL receptors (LDLRs) on hepatocytes, PCSK9 and LDL-C are endocytosed and then degraded in lysosomes, leading to a reduction of LDLRs on the surface of liver cells and in the blood, which in turn raises LDL-C levels [76].
PCSK-9 inhibitors (evolocumab and alirocumab) effectively lower LDL-C levels. They lead to LDL-C reduction by 45% to 65% compared to placebo and by approximately 35 to 45% compared to ezetimibe treatment. Therefore, the vast majority of patients (up to 80–90%) attain therapeutic goals. Moreover, PCSK-9 inhibitors have beneficial effects on other lipid profile parameters, effectively lowering non-HDL-C, Apo B, TG, Lp(a) and increasing HDL-C and Apo A1 concentrations [76].
In Poland, the drug program with PCSK-9 inhibitors has been successfully used for several years in adults. Clinical trials showed that these drugs are also safe and highly effective in reducing LDL-C (44.5–46%) in children with HoFH and HeFH [77, 78]. In 2024, the drug program with evolocumab was extended to pediatric patients. The target group includes FH individuals > 10 years of age who do not achieve a therapeutic effect (LDL-C < 100 mg/dl (< 2.6 mmol/l)) despite the treatment with a maximum dose of statin, even without any other hypolipidemic drugs. Besides, it encompasses individuals who developed statin intolerance.
Inclisiran
Inclisiran is a double-stranded small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA). The drug interferes with the mRNA of the PCSK9 protein by increasing the number of receptors for LDL-C on the liver surface, effectively reducing its levels [79]. The ORION trial demonstrated a reduction in LDL-C by around 50% and displayed a high level of safety [80, 81]. Since November 2022, inclisiran has been available in Poland for adults in a drug program. A study on the pediatric population with FH is underway [82].
In conclusion, the new drugs may be effective in cases of complete statin intolerance or as a combined hypolipidemic treatment when therapeutic goals are not achieved.
Coordinated care for families with familial hypercholesterolemia
It is crucial to provide coordinated care for the entire family with FH and ensure the continuity of treatment beyond the age of 18. The National FH Center in Gdansk, Poland has been operating since 2020. A similar comprehensive Centre for Rare Diseases that ensures ongoing healthcare of children and whole families with FH has existed since 2017 in the Polish Mother’s Memorial Research Institute (PMMHRI) in Lodz. The National FH Center in Gdansk leads the only official registry operating under the Regulation of the Minister of Health of January 8, 2020 [83]. The registry guarantees data collection in accordance with good registry practice and Polish law in order to effectively identify family members for cascade screening. Since 2020, it has supported cascade diagnosis of families in Poland and cooperates with more than 40 centers in Poland. Moreover, it enables care coordination for patients from different parts of the country admitted to lipid clinics during other periods.
The transition from an FH pediatric outpatient clinic to a cardiac center specialized in FH should be completed as soon as the patient reaches the age of majority. The network of pediatric and adult sites treating FH is currently being established in Poland. It should be emphasized that apart from the physician’s care, FH centers should also provide dietary and psychological support.
To facilitate communication between a pediatrician and a cardiologist, a patient should receive a transition document upon reaching the age of majority. It should specify the medical facility where the treatment will be continued and include information on the molecular diagnosis and therapeutic interventions to date. This document should be standardized for all centers.
In FH therapy, cascade diagnostics hold utmost importance; thus, screening the proband’s family members is necessary. The patient should raise awareness among relatives about the possibility of inheriting the disease and recommend genetic testing. The doctor must ensure that the patient understands the nature of the disease and should emphasize the seriousness of the problem. Providing educational materials and distributing them to family members is advisable. However, encouraging relatives to undergo testing for FH may remain an enormous challenge.
Genetic diagnosis should be conducted in all first-degree family members (including parents, siblings, and children of the proband), regardless of lipid profile results, if a pathogenic variant has been detected. Subsequently, the diagnosis should be extended as far as possible if further individuals harboring genetic variants are detected.
It should be emphasized that some individuals with a confirmed mutation may not present high cholesterol levels. These patients and their families must be monitored regularly every 2–5 years. On the other hand, in a subset of patients with hypercholesterolemia, no pathogenic variants in the FH-associated genes are found, which excludes ADH or ARH. However, if the clinical presentation strongly suggests FH, these patients require the same care as individuals with genetically confirmed conditions [6].
Conclusions
FH is a common lipid disorder characterized by high LDL-C levels and early onset of atherosclerosis, even in children. Unfortunately, it is diagnosed rarely and often too late, leading to serious cardiovascular incidents already in young adults. In Poland, a limited number of patients receive successful treatment and reach therapeutic targets. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of FH in children can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and sudden death in adults. It is therefore necessary to introduce screening in the pediatric population to diagnose lipid disorders and then implement a cascade screening of family members to detect the disease. The presented approach can significantly reduce the cost of treating complications associated with untreated hypercholesterolemia.
Various sources, including the National Health Fund, government agencies, academic institutions, and the pharmaceutical industry, should fund FH-related diagnostic, treatment, education, and research activities (Table III).
Table III
FH patient passport